Abstract
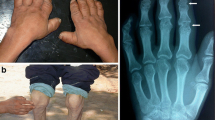
Kaschin-Beck disease (KBD) is an endemic, chronic, and degenerative osteoarthropathy, which seriously impairs the quality of patients’ life. We detected the expression of TrxR by ELISA and found that TrxR was lower in KBD than in normal control group significantly (P < 0.001); this result indicated that TrxR must be related to KBD. We retrieved cSNPs in NCBI SNP database and used three bioinformatics programmers, including SIFT, PolyPhen, and SNP3d, to help select the researched nsSNP. Then, we used PCR-RFLP to analyze the relationship between the SNP site rs5746841 in TrxR2 gene and susceptibility of KBD and detected the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 by western blot. The results showed that the genotype of rs5746841 in 93 normal controls and 103 KBD subjects were C/C totally, but A/A and A/C were not found, which indicated preliminarily that there was no correlation between rs5746841 in TrxR2 gene and susceptibility of KBD. The expression of TrxR was lower in KBD than in normal control group significantly, while the expressions of Nrf2 and HO-1 were higher in KBD than in normal control group. These results indicated that the low expression of selenoprotein TrxR may be a candidate factor of KBD, which related to Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guo X, Ma W, Zhang F, Ren F, Qu C, Lammi M (2014) Recent advances in the research of an endemic osteochondropathy in China: Kashin-Beck disease. Osteoarthr Cartil 22:1774–1783
Li S, Xiao T, Zheng B (2012) Medical geology of arsenic, selenium and thallium in China. Sci Total Environ 421-422:31–40
Sun LY, Li Q, Meng FG, Fu Y, Zhao ZJ, Wang LH (2012) T-2 toxin contamination in grains and selenium concentration in drinking water and grains in Kaschin-Beck disease endemic areas of Qinghai Province. Biol Trace Elem Res 150:371–375
Ying G, Jia Y, Luan R (2007) Research advance on relation between humic acid and chondrocyte injuries. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 36:238–241
Brown KM, Arthur JR (2001) Selenium, selenoproteins and human health: a review. Public Health Nutr 4:593–599
Yang L, Zhao GH, Yu FF, Zhang RQ, Guo X (2016) Selenium and iodine levels in subjects with Kashin-Beck disease: a meta-analysis. Biol Trace Elem Res 170:43–54
Yu FF, Han J, Wang X, Fang H, Liu H, Guo X (2016) Salt-rich selenium for prevention and control children with Kashin-Beck disease: a meta-analysis of community-based trial. Biol Trace Elem Res 170:25–32
Zhang B, Yang L, Wang W, Li Y, Li H (2011) Environmental selenium in the Kaschin-Beck disease area, Tibetan Plateau, China. Environ Geochem Health 33:495–501
Shi XW, Guo X, Ren FL, Lu AL, Zhang YZ (2008) Familial aggregation and sibling heritability in Kashin-Beck disease. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 28:1187–1189
Kryukov GV, Castellano S, Novoselov SV, Lobanov AV, Zehtab O, Guigo R et al (2003) Characterization of mammalian selenoproteomes. Science 300:1439–1443
Fradejas-Villar N (2018) Consequences of mutations and inborn errors of selenoprotein biosynthesis and functions. Free Radic Biol Med 127:206–214
Wu R, Zhang R, Xiong Y, Sun W, Li Y, Yang X, Liu JF, Jiang Y, Guo H, Mo XY, Cao JL (2018) The study on polymorphisms of Sep15 and TrxR2 and the expression of AP-1 signaling pathway in Kashin-Beck disease. Bone 120:239–245
Lu W, Mo XY, Xiong YM (2010) TrxR2 gene polymorphisms may not be associated with the susceptibility to Kashin-Beck disease. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 30:2246–2248
Lu J, Zhong L, Lonn ME, Burk RF, Hill KE, Holmgren A (2009) Penultimate selenocysteine residue replaced by cysteine in thioredoxin reductase from selenium-deficient rat liver. FASEB J 23:2394–2402
Zhao N, Guo FF, Xie KQ, Zeng T (2018) Targeting Nrf-2 is a promising intervention approach for the prevention of ethanol-induced liver disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 75(17):3143–3157
Liu R, Yan X (2018) Sulforaphane protects rabbit corneas against oxidative stress injury in keratoconus through activation of the Nrf-2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway. Int J Mol Med 42(5):2315–2328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Human Ethics Committee of Xi’an Jiaotong University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Mo, X. & Xiong, Y. The Study on Polymorphism of TrxR and Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in Kaschin-Beck Disease. Biol Trace Elem Res 190, 303–308 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1566-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1566-9