Abstract
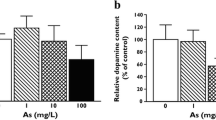
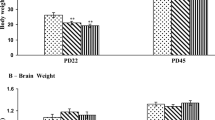
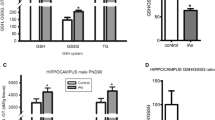
Although exposure to arsenic (As) induces developmental neurotoxicity, there is a lack of data regarding its specific effects on glutamatergic neurotransmission in offspring from dams exposed to As during gestation and lactation. In this study, the body weight, glutamate content, and expression of vesicular glutamate transporter 2 (VGLUT2) and metabotropic glutamate receptors mGluR2 and mGluR3 was examined in the striatum of offspring following treatment of the dams with As (10 or 100 mg/L NaAsO2 in drinking water). At postnatal day 21, body weight was decreased significantly, whereas the glutamate content in the striatum of offspring in the 100-mg/L As group were not significantly different from those in the control group. Although mGluR3 expression was not significantly different, VGLUT2 and mGluR2 expression was significantly lower in the striatum of offspring of As-exposed dams. These data indicate that altered glutamatergic neurotransmission may contribute to As-induced developmental neurotoxic effects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Del Razo LM, Corona JC, García-Vargas G, Albores A, Cebrián ME (1993) Fluoride levels in well-water from a chronic arsenicism area of Northern Mexico. Environ Pollut 80:91–94
Kinniburgh DG, Kosmus W (2002) Arsenic contamination in groundwater: some analytical considerations. Talanta 58:165–180
Farzan SF, Karagas MR, Chen Y (2013) In utero and early life arsenic exposure in relation to long-term health and disease. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 272:384–390
Argos M, Kalra T, Rathouz PJ, Chen Y, Pierce B, Parvez F, Islam T, Ahmed A, Rakibuz-Zaman M, Hasan R, Sarwar G, Slavkovich V, van Geen A, Graziano J, Ahsan H (2010) Arsenic exposure from drinking water, and all-cause and chronic-disease mortalities in Bangladesh (HEALS): a prospective cohort study. Lancet 376:252–258
Moon KA, Oberoi S, Barchowsky A, Chen Y, Guallar E, Nachman KE, Rahman M, Sohel N, D'Ippoliti D, Wade TJ, James KA, Farzan SF, Karagas MR, Ahsan H, Navas-Acien A (2017) A dose-response meta-analysis of chronic arsenic exposure and incident cardiovascular disease. Int J Epidemiol 46:1924–1939
Prakash C, Soni M, Kumar V (2016) Mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunction in arsenic neurotoxicity: A review. J Appl Toxicol 36:179–188
Tyler CR, Allan AM (2014) The effects of arsenic exposure on neurological and cognitive dysfunction in human and rodent studies: A review. Curr Environ Health Rep 21:132–147
Burdge GC, Hanson MA, Slater-Jefferies JL, Lillycrop KA (2007) Epigenetic regulation of transcription: a mechanism for inducing variations in phenotype (fetal programming) by differences in nutrition during early life? Br J Nutr 97:1036–1046
Wasserman GA, Liu X, Parvez F, Factor-Litvak P, Ahsan H, Levy D, Kline J, van Geen A, Mey J, Slavkovich V, Siddique AB, Islam T, Graziano JH (2011) Arsenic and manganese exposure and children’s intellectual function. Neurotoxicology 32:450–457
Wright RO, Amarasiriwardena C, Woolf AD, Jim R, Bellinger DC (2006) Neuropsychological correlates of hair arsenic, manganese, and cadmium levels in school-age children residing near a hazardous waste site. Neurotoxicology 27:210–216
Ehrenstein O, Poddar S, Yuan Y, Mazumder DG, Eskenazi B, Basu A, Hira-Smith M, Ghosh N, Lahiri S, Haque R, Ghosh A, Kalman D, Das S, Smith AH (2007) Children’s intellectual function in relation to arsenic exposure. Epidemiology 18:44–51
Rodríguez VM, Carrizales L, Mendoza MS, Fajardo OR, Giordano M (2002) Effects of sodium arsenite exposure on development and behavior in the rat. Neurotoxicol Teratol 24:743–750
Martinez-Finley EJ, Ali AMS, Allan AM (2009) Learning deficits in C57BL/6J mice following perinatal arsenic exposure: consequence of lower corticosterone receptor levels? Pharmacol Biochem Behav 94:271–277
Nagaraja TN, Desiraju T (1994) Effects on operant learning and brain acetylcholine esterase activity in rats following chronic inorganic arsenic intake. Hum Exp Toxicol 13:353–356
Rodríguez VM, Limón-Pacheco JH, Carrizales L, Mendoza-Trejo MS, Giordano M (2010) Chronic exposure to low levels of inorganic arsenic causes alterations in locomotor activity and in the expression of dopaminergic and antioxidant systems in the albino rat. Neurotoxicol Teratol 32:640–647
Escudero-Lourdes C (2016) Toxicity mechanisms of arsenic that are shared with neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive impairment: Role of oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. Neurotoxicology 53:223–235
Jiang S, Su J, Yao S, Zhang Y, Cao F, Wang F, Wang H, Li J, Xi S (2014) Fluoride and arsenic exposure impairs learning and memory and decreases mGluR5 expression in the hippocampus and cortex in rats. PLoS One 9:e96041
Castro-Coronel Y, Del Razo LM, Huerta M, Hernandez-Lopez A, Ortega A, Lopez-Bayghen E (2011) Arsenite exposure downregulates EAAT1/GLAST transporter expression in glial cells. Toxicol Sci 122:539–550
Luo JH, Qiu ZQ, Shu WQ, Zhang YY, Zhang L, Chen JA (2009) Effects of arsenic exposure from drinking water on spatial memory, ultra-structures and NMDAR gene expression of hippocampus in rats. Toxicol Lett 184:121–125
Ramos-Chavez LA, Rendon-Lopez CR, Zepeda A, Silva-Adaya D, Del Razo LM, Gonsebatt ME (2015) Neurological effects of inorganic arsenic exposure: altered cysteine/glutamate transport, NMDA expression and spatial memory impairment. Front Cell Neurosci 9:21
Wang JQ, Mao L, Parelkar NK, Tang Q, Choe ES, Yang L, Choe ES (2003) Glutamate-regulated behavior, transmitter release, gene expression and addictive plasticity in the striatum: roles of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Curr Neuropharmacol 1:1–20
Lewerenz J, Maher P (2015) Chronic Glutamate Toxicity in Neurodegenerative Diseases-What is the Evidence? Front Neurosci 9:469
Moechars D, Weston MC, Leo S, Callaerts-Vegh Z, Goris I, Daneels G, Buist A, Cik M, van der Spek P, Kass S, Meert T, D'Hooge R, Rosenmund C, Hampson RM (2006) Vesicular glutamate transporter VGLUT2 expression levels control quantal size and neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 26:12055–12066
Kaneko T, Fujiyama F, Hioki H (2002) Immunohistochemical localization of candidates for vesicular glutamate transporters in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 444:39–62
Ohishi H, Neki A, Mizuno N (1998) Distribution of a metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGluR2, in the central nervous system of the rat and mouse: An immunohistochemical study with a monoclonal antibody. Neurosci Res 30:65–82
Tamaru Y, Nomura S, Mizuno N, Shigemoto R (2001) Distribution of metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR3 in the mouse CNS: Differential location relative to pre- and postsynaptic sites. Neuroscience 106:481–503
Ritter-Makinson SL, Paquet M, Bogenpohl JW, Rodin RE, Chris Yun C, Weinman EJ, Smith Y, Hall RA (2017) Group II metabotropic glutamate receptor interactions with NHERF scaffold proteins: Implications for receptor localization in brain. Neuroscience 353:58–75
Chandravanshi LP, Gupta R, Shukla RK (2018) Developmental Neurotoxicity of Arsenic: Involvement of Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Functions. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1286-1
Jin Y, Xi S, Li X, Lu C, Li G, Xu Y, Qu C, Niu Y, Sun G (2006) Arsenic speciation transported through the placenta from mother mice to their newborn pups. Environ Res 101:349–355
Hall M, Gamble M, Slavkovich V, Liu X, Levy D, Cheng Z, van Geen A, Yunus M, Rahman M, Pilsner JR, Graziano J (2007) Determinants of arsenic metabolism: blood arsenic metabolites, plasma folate, cobalamin, and homocysteine concentrations in maternal-newborn pairs. Environ Health Perspect 115:1503–1509
Kile ML, Cardenas A, Rodrigues E, Mazumdar M, Dobson C, Golam M, Quamruzzaman Q, Rahman M, Christiani DC (2016) Estimating effects of arsenic exposure during pregnancy on perinatal outcomes in a Bangladeshi cohort. Epidemiology 27:173–181
Ahmad M, Wadaa MA, Farooq M, Daghestani MH, Sami AS (2013) Effectiveness of zinc in modulating perinatal effects of arsenic on the teratological effects in mice offspring. Biol Res 46:131–138
Rahman ML, Valeri L, Kile ML, Mazumdar M, Mostofa G, Qamruzzaman Q, Rahman M, Baccarelli A, Liang L, Hauser R, Christiani DC (2017) Investigating causal relation between prenatal arsenic exposure and birthweight: Are smaller infants more susceptible? Environ Int 108:32–40
Fremeau RT Jr, Voglmaier S, Seal RP, Edwards RH (2004) VGLUTs define subsets of excitatory neurons and suggest novel roles for glutamate. Trends Neurosci 27:98–103
Mendez JA, Bourque MJ, Dal Bo G, Bourdeau ML, Danik M, Williams S, Lacaille JC, Trudeau LE (2008) Developmental and target-dependent regulation of vesicular glutamate transporter expression by dopamine neurons. J Neurosci 28:6309–6318
Steinkellner T, Zell V, Farino ZJ, Sonders MS, Villeneuve M, Freyberg RJ, Przedborski S, Lu W, Freyberg Z, Hnasko TS (2018) Role for VGLUT2 in selective vulnerability of midbrain dopamine neurons. J Clin Invest 128:774–788
Amalric M (2015) Targeting metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol 20:29–34
Golubeva AV, Moloney RD, O'Connor RM, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2016) Metabotropic glutamate receptors in central nervous system diseases. Curr Drug Targets 17:538–616
Nelson-Mora J, Escobar ML, Rodríguez-Durán L, Massieu L, Montiel T, Rodríguez VM, Hernández-Mercado K, Gonsebatt ME (2018) Gestational exposure to inorganic arsenic (iAs3+) alters glutamate disposition in the mouse hippocampus and ionotropic glutamate receptor expression leading to memory impairment. Arch Toxicol 92:1037–1048
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No. NRF-2016R1A2B4011596).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experimental protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Keimyung University (approval no. KM-2014-78R2). Experiments were conducted according to NIH guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sung, K., Kim, M., Kim, H. et al. Perinatal Exposure to Arsenic in Drinking Water Alters Glutamatergic Neurotransmission in the Striatum of C57BL/6 Mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 187, 224–229 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1374-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1374-2