Abstract
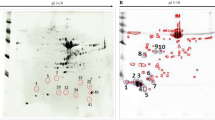
Predator fish can accumulate high levels of mercury, which qualifies them as potential indicators of this toxic metal. The predatory species Brachyplatystoma filamentosum, popularly known as filhote, is among the most consumed species in the Brazilian Amazon. Continuing the metalloproteomic studies of mercury in Amazonian fishes that have been developed in the last 5 years, the present paper provides the data of protein characterization associated with mercury in muscle and liver samples of filhote (Brachyplatystoma filamentosum) collected in the Madeira River, Brazilian Amazon. The mercury concentration in the muscle and liver samples was determined by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (GFAAS). The protein fraction was extracted in an aqueous medium, and later, a fractional precipitation procedure was performed to obtain the protein pellets. Then, the proteome of the tissue samples of this fish species was separated by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (2D-PAGE), and a mercury mapping of the protein spots was carried out by GFAAS after acid digestion. Protein spots that had mercury were characterized by mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization in sequence (ESI-MS/MS) after tryptic digestion. It was possible to characterize 11 mercury-associated protein spots that presented biomarker characteristics and could be used to monitor mercury in fish species of the Amazon region. Thus, the metalloproteomic strategies used in the present study allowed us to characterize 11 mercury-associated protein spots. It should be noted that the protein spots identified as GFRP, TMEM186, TMEM57B, and BHMT, which have coordination sites for elements with characteristics of soft acids, such as mercury, can be used as biomarkers of mercury contamination in monitoring studies of this toxic metal in fish species from the Amazon region.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moraes PM, Santos FA, Cavecci B, Padilha CCF, Vieira JCS, Roldan PS, Padilha PM (2013) GFAAS determination of mercury in muscle samples of fish from Amazon, Brazil. Food Chem 141:2614–2617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.05.008
Braga CP, Bittarello a C, Padilha CCF et al (2015) Mercury fractionation in dourada (Brachyplatystoma rousseauxii) of the Madeira River in Brazil using metalloproteomic strategies. Talanta 132:239–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.09.021
Vieira JCS, Braga CP, de Oliveira G, do Carmo Federici Padilha C, de Moraes PM, Zara LF, de Lima Leite A, Buzalaf MAR, de Magalhães Padilha P (2017) Correction to: mercury exposure: protein biomarkers of mercury exposure in Jaraqui fish from the Amazon region. Biol Trace Elem Res 183(1):172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1195-8
Vieira JCS, Cavecci B, Queiroz JV, Braga CP, Padilha CCF, Leite AL, Figueiredo WS, Buzalaf MAR, Zara LF, Padilha PM (2015) Determination of the mercury fraction linked to protein of muscle and liver tissue of Tucunaré (Cichla spp.) from the Amazon region of Brazil. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 69:422–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-015-0160-9
Silva FA, Cavecci B, Baldassini WA, Lima PM, Moraes PM, Roldan PS, Padilha CCF, Padilha PM (2013) Selenium fractionation from plasma, muscle and liver of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J Food Meas Charact 7:158–165
dos Santos FA, Lima PM, Neves RCF et al (2011) Metallomic study on plasma samples from Nile tilapia using SR-XRF and GFAAS after separation by 2D PAGE: initial results. Microchim Acta 173:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0522-y
Lima PM, Neves RDCF, dos Santos FA et al (2010) Analytical approach to the metallomic of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) liver tissue by SRXRF and FAAS after 2D-PAGE separation: preliminary results. Talanta 82:1052–1056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2010.06.023
Garcia JS, De Magalhães CS, Arruda MAZ (2006) Trends in metal-binding and metalloprotein analysis. Talanta 69:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2005.08.041
Cavalcante J, Vieira S, Braga CP et al (2017) Mercury exposure: protein biomarkers of mercury exposure in Jaraqui fish from the Amazon region. Biol Trace Elem Res 183:164–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1129-5
Shevchenko A, Tomas H, Havlis J et al (2006) In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat Protoc 1:2856–2860. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.468
Moraes PM, Santos FA, Padilha CCF, Vieira JCS, Zara LF, de M. Padilha P (2012) A preliminary and qualitative metallomics study of mercury in the muscle of fish from Amazonas, Brazil. Biol Trace Elem Res 150:195–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-012-9502-x
Neves RCF, Lima PM, De Medicina F et al (2012) Artigo 35:493–498
Conesa A, Götz S (2008) Blast2GO: a comprehensive suite for functional analysis in plant genomics. Int J Plant Genomics 2008:619832–619812. https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/619832
Sharp MF, Lopata AL (2014) Fish allergy: in review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 46:258–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-013-8363-1
Kobayashi A, Tanaka H, Hamada Y, Ishizaki S, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K (2006) Comparison of allergenicity and allergens between fish white and dark muscles. Allergy: European. J Allergy Clin Immunol 61:357–363. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2006.00966.x
Arif SH (2009) A Ca2+-binding protein with numerous roles and uses: parvalbumin in molecular biology and physiology. BioEssays 31:410–421. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.200800170
Schwaller B (2009) The continuing disappearance of “pure” Ca2+ buffers. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:275–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-8564-6
Li L, Rezvan A, Salerno JC, Husain A, Kwon K, Jo H, Harrison DG, Chen W (2010) GTP cyclohydrolase i phosphorylation and interaction with GTP cyclohydrolase feedback regulatory protein provide novel regulation of endothelial tetrahydrobiopterin and nitric oxide. Circ Res 106:328–336. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.210658
Ichinose H, Ohye T, Matsuda Y, Hori TA, Blau N, Burlina A, Rouse B, Matalon R, Fujita K, Nagatsu T (1995) Characterization of mouse and human GTP cyclohydrolase I genes: mutations in patients with GTP cyclohydrolase I deficiency. J Biol Chem 270:10062–10071
Maita N, Okada K, Hatakeyama K, Hakoshima T (2002) Crystal structure of the stimulatory complex of GTP cyclohydrolase I and its feedback regulatory protein GFRP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:1212–1217. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.022646999
de Brevern AG (2010) 3D structural models of transmembrane proteins. Methods Mol Biol 654:387–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-762-4_20
von Heijne G (1994) Membrane proteins: from sequence to structure. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 23:167–192. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.001123
Mattjus P (2009) Glycolipid transfer proteins and membrane interaction. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:267–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.10.003
Abe A, Sasaki T (1989) Formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond of glycolipid transfer protein. BBA-Biomembranes 985:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2736(89)90101-6
Abe A, Sasaki T (1989) Sulfhydryl groups in glycolipid transfer protein: formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond and oligomers by Cu2+-catalyzed oxidation. BBA-Biomembranes 985:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2736(89)90100-4
Ratnam S, Wijekoon EP, Hall B, Garrow TA, Brosnan ME, Brosnan JT (2006) Effects of diabetes and insulin on betaine-homocysteine S-methyltransferase expression in rat liver. Am J Phys Endocrinol Metab 290:E933–E939. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00498.2005
Vlieghe P, Lisowski V, Martinez J, Khrestchatisky M (2010) Synthetic therapeutic peptides: science and market. Drug Discov Today 15:40–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2009.10.009
Funding
The authors thank the Brazilian research funding agency ANEEL/ESBR-P&D: 6631-0001/2012/Contract Jirau 004/2013, São Paulo State Research Foundation-FAPESP (Processes:2010/51332-5, 2013/21297-1 and 2016/19404-2), National Council for Scientific and Technological Development–CNPq (Process: 303719/2014-1), and Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel-CAPES for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Queiroz, J.V., Vieira, J.C.S., de Oliveira, G. et al. Identification of Biomarkers of Mercury Contamination in Brachyplatystoma filamentosum of the Madeira River, Brazil, Using Metalloproteomic Strategies. Biol Trace Elem Res 187, 291–300 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1363-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1363-5