Abstract
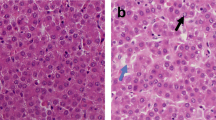
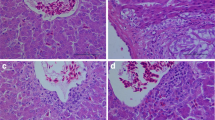
The objective of this study was to determine the effects of mercury chloride (HgCl2) on laying performance, egg quality, hepatic and renal histopathology, and serum biochemical profiles in laying hens. A total of 768 Hy-line brown laying hens aged 40 weeks were randomly allocated to four groups (8 pens per group and 24 hens per pen). The concentrations of mercury (Hg) in four groups were 0.280, 3.325, 9.415, and 27.240 mg/kg. Results revealed that dietary Hg could significantly reduce laying performance (P < 0.05) and egg quality (P < 0.05) and was dose-dependently deposited in albumen, yolk, eggshell, and whole egg. Meanwhile, the thicknesses of palisade layer, mammillary layer, and total layer, and the percent of palisade layer were significantly decreased (P < 0.05), while the percent of mammillary layer was sharply increased (P < 0.05) in eggshell. In addition, with increasing dietary dosage of Hg, accumulation of Hg in viscera was significantly increased (P < 0.05), and histopathological damages in liver and kidney were more and more severe. Serum alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and globulin were significantly increased (P < 0.05), while serum albumin and albumin to globulin ratio were significantly decreased (P < 0.05) in 27.240 mg/kg Hg group. Blood urea nitrogen, uric acid, and creatinine were significantly increased (P < 0.05) in 3.325, 9.415, and 27.240 mg/kg Hg groups. These results suggested that dietary HgCl2 could reduce laying performance and egg quality with hepatic and renal function disorders in laying hens.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caban G, Rasmussen JB (1994) Modelling food chain structure and contaminant bioaccumulation using stable nitrogen isotopes. Nature 372(6503):255–257. https://doi.org/10.1038/372255a0
Gochfeld M (2003) Cases of mercury exposure, bioavailability, and absorption. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 56(1):174–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0147-6513(03)00060-5
Sanfeliu C, Sebastià J, Cristòfol R, Rodríguez-Farré E (2003) Neurotoxicity of organomercurial compounds. Neurotox Res 5(4):283–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033386
Azevedo BF, Furieri LB, Peçanha FM, Wiggers GA, Vassallo PF, Simões MR, Fiorim J, de Batista PR, Fioresi M, Rossoni L, Stefanon I, Alonso MJ, Salaices M, Vassallo AV (2012) Toxic effects of mercury on the cardiovascular and central nervous system. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/949048
Mela M, Randi MAF, Ventura DF, Carvalho CEV, Pelletier E, Oliveira Ribeiro CA (2007) Effects of dietary methylmercury on liver and kidney histology in the neotropical fish Hoplias malabaricus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 68(3):426–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.11.013
Davis BJ, Price HC, O’Connor RW, Fernando R, Rowland AS, Morgan DI (2001) Mercury vapor and female reproduction toxicity. Toxicol Sci 59(2):291–296. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/59.2.291
Clarkson TW, Magos L, Myers GJ (2003) The toxicology of mercury-current exposures and clinical manifestations. N Engl J Med 349(18):1731–1737. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra022471
Wolfe MF, Schwarzbach S, Sulaiman RA (1998) Effects of mercury on wildlife: a comprehensive review. Environ Toxicol Chem 17(2):146–160. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620170203
Henny CJ, Hill EF, Hoffman DJ, Spalding MG, Grove RA (2002) Nineteenth century mercury: hazard to wading birds and cormorants of the Carson River, Nevada. Ecotoxicology 11(8):213–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(00)00258-1
Hoffman DJ, Heinz GH (1998) Effects of mercury (Hg) and selenium (Se) on glutathione metabolism and oxidative stress in Mallard ducks. Environ Toxicol Chem 17(2):161–166. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620170204
Hoffman DJ, Ohlendore HM, Marn CM, Pendleton GW (1998) Association of mercury and selenium with altered glutathione metabolism and oxidative stress in diving ducks from the San Francisco Bay region, USA. Environ Toxicol Chem 17(2):167–172. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620170205
Parson AH (1982) Structure of the eggshell. Poult Sci 61(10):2013–2021. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.0612013
Oliveira VA, Favero G, Stacchiotti A, Giugno L, Buffoli B, de Oliveira CS, Lavazza A, Albanese M, Rodella LF, Pereira ME, Rezzani R (2016) Acute mercury exposition of virgin, pregnant, and lactating rats: histopathological kidney and liver evaluations. Environ Toxicol 32(5):1500–1512. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22370
Wadaan MAM (2009) Effects of mercury exposure on blood chemistry and liver histopathology of male rats. J Pharmacol Toxicol 4(3):126–131. https://doi.org/10.3923/jpt.2009.126.131
Stacchiotti A, Borsani E, Rodella L, Rezzani R, Bianchi R, Lavazza A (2003) Dose-dependent mercuric chloride tubular injury in rat kidney. Ultrastruct Pathol 27(4):253–259. https://doi.org/10.1080/01913120309921
Ghaedi M, Fathi MR, Shokrollahi A, Shajarat F (2006) Highly selective and sensitive preconcentration of mercury ion and determination by cold vapor atomic absorption spectroscopy. Anal Lett 39(6):1171–1185. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032710600622167
Solomon SE (1997) Egg and eggshell quality. Wolf Press, London
Akearok JA, Hebert CE, Braune BM, Mallory ML (2010) Inter- and intraclutch variation in egg mercury levels in marine bird species from the Canadian Arctic. Sci Total Environ 408(4):836–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.11.039
Sanpera C, Morera M, Ruiz X, Jover L (2000) Variability of mercury and selenium levels in clutches of Audouin’s gulls (Larus audouinii) breeding at the Chafarinas Islands, Southwest Mediterranean. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39(1):119–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010087
Ruiz X, Jover L, Pedrocchi V (1998) Audouin’s gull intraspecific variability in yolk and albumen egg contents: why is yolk size so contant? Biol Cons Fauna 102:327–334
Pribilincová J, Marettová E, Kosucký J, Maretta M (1996) The effect of phenyl mercury on reproductive performance in laying hens. Acta Vet Hung 44(3):377–387
Košutzka E, Pribilincova J, Ledeč M, Maretta MY (2002) The effect of selenium on mercury retention in the offspring of treated hens. Acta Vet Brno 52(5-6):5–6. https://doi.org/10.2298/AVB0206355K
Ruiz J, Lunam CA (2000) Ultrastructural analysis of the eggshell: contribution of the individual calcified layers and the cuticle to hatchability and egg viability in broiler breeders. Br Poult Sci 41(5):584–592. https://doi.org/10.1080/713654975
Clarkson TW, Vyas JB, Ballatori N (2007) Mechanisms of mercury disposition in the body. Am J Ind Med 50(10):757–764. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajim.20476
Şener G, Sehirli Ö, Tozan A, Velioğlu-Övunç A, Gedik N, Omurtag GZ (2007) Gingko biloba extract protects against mercury (II)-induced oxidative tissue damage in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 45(4):543–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2006.07.024
Raldúa D, Díez S, Bayona JM, Barceló D (2007) Mercury levels and liver pathology in feral fish liver in the vicinity of a mercury cell chlor-alkali factory. Chemosphere 66(7):1217–1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.07.053
Oliveira-Ribeiro CA, Belger L, Pelletier E, Rouleau C (2002) Histopathological evidence of inorganic mercury and methyl mercury toxicity in the arctic charr (Salvelinus alpines). Environ Res 90(3):217–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-9351(02)00025-7
Border WA, Noble NA (1994) Transforming growth factor beta in tissue fibrosis. N Engl J Med 331(19):1286–1292. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199411103311907
Kao YH, Chen CL, Jawan B, Chung YH, Sun CK, Kuo SM, Hu TH, Lin YC, Chan HH, Cheng KH, Wu DC, Goto S, Cheng YF, Chao D, Tai MH (2010) Upregulation of hepatoma-derived growth factor is involved in murine hepatic fibrogenesis. J Hepatol 52(1):96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2009.10.002
Woshner VM, O’Hara TM, Eurell JA, Walling MA, Bratton GR, Suydam RS, Beasley VR (2002) Distribution of inorganic mercury in liver and kidney of beluga and bowhead whales through autometallographic development of light microscopic tissue sections. Toxicol Pathol 30(2):209–215. https://doi.org/10.1080/019262302753559542
de Freitas AS, Funck VR, Rotta Mdos S, Bohrer D, Mörschbächer V, Puntel RL, Nogueira CW, Farina M, Aschner M, Rocha JB (2009) Diphenyl diselenide, a simple organoselenium compound, decreases methylmercury-induced cerebral, hepatic and renal oxidative stress and mercury deposition in adult mice. Brain Res Bull 79(1):77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2008.11.001
Pal M, Ghosh M (2012) Studies on comparative efficacy of α-linolenic acid and α-eleostearic acid on prevention of organic mercury-induced oxidative stress in kidney and liver of rat. Food Chem Toxicol 50(3-4):1066–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2011.12.042
Othman MS, Safwat G, Aboulkhair M, Abdel Moneim AE (2014) The potential effects of berberine in mercury-induced hepatornal toxicity in albino rats. Food Chem Toxicol 69:175–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.04.012
Khattab H, Fouad A, Hamza M, Mohey MA, El-Akel W, Ghoneim H, Abul-Fotouh A, Esmat G (2015) Relation of ALT and AST levels to the histopathological changes in liver biopsies of patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 4. Arab J Gastroenterol 16(2):50–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajg.2015.06.004
Wang CC, Lim LY, Deubner H, Tapia K, Lau AW, Manansala J, Krows M, Shuhart MC, Kowdley KV (2008) Factors predictive of significant hepatic fibrosis in adults with chronic hepatitis B and normal serum ALT. J Clin Gastroenterol 42(7):820–826. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0b013e318156feef
Kumar M, Sharma MK, Kumar A (2005) Spirulina fusiformis: a food supplement against mercury induced hepatic toxicity. J Health Sci 51(4):424–430. https://doi.org/10.1248/jhs.51.424
Azab BN, Bhatt VR, Vonfrolio S, Bachir R, Rubinshteyn V, Alkaied H, Habeshy A, Patel J, Picon AI, Bloom SW (2013) Value of the pretreatment albumin to globulin ratio in predicting long-term mortality in breast cancer patients. Am J Surg 206(5):764–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2013.03.007
Zhang J, Liu X, Yang Z, Chen Y, Luo R (2016) The pretreatment albumin to globulin ratio, a validated biomarker, predicts prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J BUON 21(4):925–934
Ita SO, Umana KT (2017) Evaluation of serum uric acid, creatinine and blood urea nitrogen as biomarkers of renal function of rats administered Nigerian bonny light crude oil (NBLCO) and 50% bee honey. Int J Curr Res 9:52547–52550
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Modern Argo-Industry Technology Research System of China (CARS-40-K10) and the National Key Technology R&D Program (204BAD13B04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The experiment was carried out according to the Guiding Principles in the Use of Animals in Toxicology, adopted by the Chinese Society of Toxicology. The animal procedures were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Zhejiang University (Hangzhou, China).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Shi, Y., Li, L. et al. Toxicological Effects of Mercury Chloride on Laying Performance, Egg Quality, Serum Biochemistry, and Histopathology of Liver and Kidney in Laying Hens. Biol Trace Elem Res 185, 465–474 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1263-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1263-8