Abstract
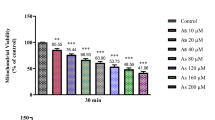
To further characterize the mechanisms underlying liver toxicity induced by arsenic, we examined in this study the effect of arsenic on thioredoxin (Trx) and the apoptotic signaling pathways in human liver HHL-5 cells. The cells were treated with 0, 2, 5, and 10 μM of sodium arsenite for 24 h, and the changes of Trx1 and thioredoxin reductase (TrxR1) as well as intracellular ROS and apoptosis were examined. A concentration-dependent increase in mRNA and protein levels of Trx1 and TrxR1 was observed in arsenic-treated cells. Intracellular ROS levels and apoptosis were also significantly increased in a concentration-dependent manner. In line with this, protein levels of Bax and cytochrome C were increased and Bcl-2 was decreased by arsenic treatments. Increases in caspase 3 activity were observed. These results indicate that Trx is involved in arsenic-induced liver cell injury, probably through the apoptotic signaling pathway. However, further studies are needed to elucidate on these findings.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Islam K, Haque A, Karim R et al (2011) Dose-response relationship between arsenic exposure and the serum enzymes for liver function tests in the individuals exposed to arsenic: a cross sectional study in Bangladesh. Environ Health 10:64
Das N, Paul S, Chatterjee D et al (2012) Arsenic exposure through drinking water increases the risk of liver and cardiovascular diseases in the population of West Bengal, India. BMC Public Health 12:639
Naujokas MF, Anderson B, Ahsan H et al (2013) The broad scope of health effects from chronic arsenic exposure: update on a worldwide public health problem. Environ Health Perspect 121:295–302
Mazumder DN (2005) Effect of chronic intake of arsenic-contaminated water on liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 206:169–175
Hong YS, Song KH, Chung JY (2014) Health effects of chronic arsenic exposure. J Prev Med Public Health 47:245–252
Abu El-Saad AM, Al-Kahtani MA, Abdel-Moneim AM (2016) N-Acetylcysteine and meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid alleviate oxidative stress and hepatic dysfunction induced by sodium arsenite in male rats. Drug Des Devel Ther 10:3425–3434
Shen H, Niu Q, Xu M et al (2016) Factors affecting arsenic methylation in arsenic-exposed humans: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13:205
Chen CJ, Hsu LI, Wang CH et al (2005) Biomarkers of exposure, effect, and susceptibility of arsenic-induced health hazards in Taiwan. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 206:198–206
Han J, Wu S (2014) A review of liver injury induced by endemic arsenicosis. Chin J Public Health 30:38–42
Choudhury S, Ghosh S, Mukherjee S et al (2016) Pomegranate protects against arsenic-induced p53-dependent ROS-mediated inflammation and apoptosis in liver cells. J Nutr Biochem 38:25–40
Seyed IH (2011) The human thioredoxin system: modifications and clinical applications. Iran J Basic Med Sci 14:191–204
Bardullas U, Limón-Pacheco JH, Giordano M et al (2009) Chronic low-level arsenic exposure causes gender-specific alterations in locomotor activity, dopaminergic systems, and thioredoxin expression in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 239:169–177
Li Y, Gao Y, Zhao L et al (2012) Changes in serum thioredoxin among individuals chronically exposed to arsenic in drinking water. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 259:124–132
Li Y, Gao Y, Zhao L et al (2011) The effects of sodium arsenite on mRNA expression of TRX1 in the liver of rat. Chinese Journal of Endemiology 30:67–68
Wang C, Feng R, Li Y et al (2014) The metabolomic profiling of serum in rats exposed to arsenic using UPLC/Q-TOF MS. Toxicol Lett 229:474–481
Tan M, Schmidt RH, Beier JI et al (2011) Chronic subhepatotoxic exposure to arsenic enhances hepatic injury caused by high fat diet in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 257:356–364
Duan X, Fan J (2009) Thioredoxin and liver disease. Int J Dig Dis 29:83–84
Maulik N, Das DK (2008) Emerging potential of thioredoxin and thioredoxin interacting proteins in various disease conditions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1780:1368–1382
Tonissen KF, Di Trapani G (2009) Thioredoxin system inhibitors as mediators of apoptosis for cancer therapy. Mol Nutr Food Res 53:87–103
Shi Y, Wei Y, Qu S et al (2010) Arsenic induces apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells through mitochondrial pathways. Cardiovasc Toxicol 10:153–160
Liu X, Gao Y, Yao H et al (2013) Neuroglobin involvement in the course of arsenic toxicity in rat cerebellar granule neurons. Biol Trace Elem Res 155:439–446
Lu TH, Tseng TJ, Su CC et al (2014) Arsenic induces reactive oxygen species-caused neuronal cell apoptosis through JNK/ERK-mediated mitochondria-dependent and GRP 78/CHOP-regulated pathways. Toxicol Lett 224:130–140
Pan X, Jiang L, Zhong L et al (2016) Arsenic induces apoptosis by the lysosomal-mitochondrial pathway in INS-1 cells. Environ Toxicol 31:133–141
Chen H, Gu S, Dai H et al (2017) Dihydroartemisinin sensitizes human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells to arsenic trioxide via apoptosis. Biol Trace Elem Res. doi:10.1007/s12011-017-0975-5
Singh S, Greene RM, Pisano MM (2010) Arsenate-induced apoptosis in murine embryonic maxillary mesenchymal cells via mitochondrial-mediated oxidative injury. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 88:25–34
Hsu SY, Hsueh AJ (2000) Tissue-specific Bcl-2 protein partners in apoptosis: an ovarian paradigm. Physiol Rev 80:593–614
Yao XF, Zheng BL, Bai J et al (2015) Low-level sodium arsenite induces apoptosis through inhibiting TrxR activity in pancreatic β-cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40:486–491
Bustamante J, Nutt L, Orrenius S et al (2005) Arsenic stimulates release of cytochrome c from isolated mitochondria via induction of mitochondrial permeability transition. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 207:110–116
Scholz C, Wieder T, Stärck L et al (2005) Arsenic trioxide triggers a regulated form of caspase-independent necrotic cell death via the mitochondrial death pathway. Oncogene 24:1904–1913
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Arvind Patel (MRC Virology Unit, Glasgow, UK) for providing the immortalized human hepatocytes. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81502763), China Postdoctoral Research Fund (2013 M541414), and Postdoctoral Fund of Heilongjiang Province (2013LBH-Z13152). We would like to thank Drs. Yanmei Yang, Xiaona Liu, and Xiaoyan Fu in the Central Laboratory of the Center for Endemic Disease Control, Harbin Medical University, for their guidance on the test methods and data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Gao, Y. et al. Arsenic Induces Thioredoxin 1 and Apoptosis in Human Liver HHL-5 Cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 181, 234–241 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1052-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1052-9