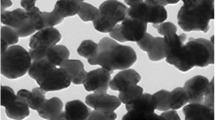
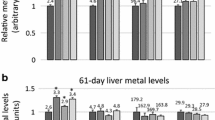
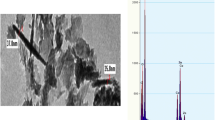
Abstract
The toxicological effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles (nano-ZnOs) are related to their dissolution and interference with zinc ion homeostasis. High-soluble zinc sources may produce more severe and acute toxicity; however, the evaluation of potential toxicity of long-term exposure to nano-ZnOs and high-soluble sources of zinc remains obscure. This study aimed at evaluating effects of nano-ZnOs and zinc sulfate on development, serum and hematological parameters, and mineral concentrations in selected tissues and intestinal microbiota in mice via gastrointestinal administration for 7 weeks. Results indicated that 250 mg/kg nano-ZnOs reduced the body weight from weeks 8 to 11, increased serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase activity, and increased the zinc concentrations of the serum, liver, and kidney while did not affect the relative organ weight, intestinal microbiota, and other mineral concentrations (Fe, Cu, and Mn) in the kidney, liver, and thigh muscle. Oral administration with 250 mg/kg zinc sulfate seemed to show more severe and acute toxicity since mice in zinc sulfate group exhibited reduced body weight from weeks 5 to 11, decreased relative pancreas weight, and increased serum glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase activity and intestinal enteric group.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yah CS, Simate GS, Iyuke SE (2012) Nanoparticles toxicity and their routes of exposures. Pak J Pharm Sci 25(2):477–491
Singh S, Nalwa HS (2007) Nanotechnology and health safety—toxicity and risk assessments of nanostructured materials on human health. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 7(9):3048–3070
Maynard AD, Aitken RJ, Butz T, Colvin V, Donaldson K, Oberdörster G, Philbert MA, Ryan J, Seaton A, Stone V (2006) Safe handling of nanotechnology. Nature 444(7117):267–269
Ma H, Williams PL, Diamond SA (2013) Ecotoxicity of manufactured ZnO nanoparticles—a review. Environ Pollut 172:76–85
Zhao CY, Tan SX, Xiao XY, Qiu XS, Pan JQ, Tang ZX (2014) Effects of dietary zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth performance and antioxidative status in broilers. Biol Trace Elem Res 160(3):361–367. doi:10.1007/s12011-014-0052-2
Sirelkhatim A, Mahmud S, Seeni A, Kaus NHM, Ann LC, Bakhori SKM, Hasan H, Mohamad D (2015) Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Letters 7(3):219–242
Wang B, Feng W, Wang M, Wang T, Gu Y, Zhu M, Ouyang H, Shi J, Zhang F, Zhao Y (2008) Acute toxicological impact of nano- and submicro-scaled zinc oxide powder on healthy adult mice. J Nanopart Res 10(2):263–276
Yan G, Huang Y, Bu Q, Lv L, Deng P, Zhou J, Wang Y, Yang Y, Liu Q, Cen X (2012) Zinc oxide nanoparticles cause nephrotoxicity and kidney metabolism alterations in rats. J Environ Sci Health A 47(4):577–588
Hong JS, Park MK, Kim MS, Lim JH, Park GJ, Maeng EH, Shin JH, Kim MK, Jeong J, Park JA, Kim JC, Shin HC (2014) Prenatal development toxicity study of zinc oxide nanoparticles in rats. Int J Nanomedicine 9(Suppl 2):159–171. doi:10.2147/IJN.S57932
Hong JS, Park MK, Kim MS, Lim JH, Park GJ, Maeng EH, Shin JH, Kim YR, Kim MK, Lee JK, Park JA, Kim JC, Shin HC (2014) Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on dams and embryo-fetal development in rats. Int J Nanomedicine 9(Suppl 2):145–157. doi:10.2147/IJN.S57931
Wang L, Wang L, Ding W, Zhang F (2010) Acute toxicity of ferric oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles in rats. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 10(12):8617–8624
Beckett WS, Chalupa DF, Pauly-Brown A, Speers DM, Stewart JC, Frampton MW, Utell MJ, Huang LS, Cox C, Zareba W (2005) Comparing inhaled ultrafine versus fine zinc oxide particles in healthy adults: a human inhalation study. American Journal of Respiratory & Critical Care Medicine 171(10):1129–1135
Yang H, Liu C, Yang D, Zhang H, Xi Z (2009) Comparative study of cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and genotoxicity induced by four typical nanomaterials: the role of particle size, shape and composition. J Appl Toxicol 29(1):69–78
Lin W, Xu Y, Huang CC, Ma Y, Shannon KB, Chen DR, Huang YW (2009) Toxicity of nano- and micro-sized ZnO particles in human lung epithelial cells. J Nanopart Res 11(1):25–39
Geiser M, Rothenrutishauser B, Kapp N, Schürch S, Kreyling W, Schulz H, Semmler M, Im HV, Heyder J, Gehr P (2005) Ultrafine particles cross cellular membranes by nonphagocytic mechanisms in lungs and in cultured cells. Environ Health Perspect 113(11):1555–1560
George S, Pokhrel S, Xia T, Gilbert B, Ji Z, Schowalter M, Rosenauer A, Damoiseaux R, Bradley KA, Mädler L (2010) Use of a rapid cytotoxicity screening approach to engineer a safer zinc oxide nanoparticle through iron doping. ACS Nano 4(1):15–29
Kao YY, Chen YC, Cheng TJ, Chiung YM, Liu PS (2012) Zinc oxide nanoparticles interfere with zinc ion homeostasis to cause cytotoxicity. Toxicological Sciences An Official Journal of the Society of Toxicology 125(2):462–472
Wang C, Lu JJ, Zhou L, Li J, Xu JM, Li WJ, Zhang LL, Zhong X, Wang T (2016) Effects of long-term exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles on development, zinc metabolism and biodistribution of minerals (Zn, Fe, Cu, Mn) in mice. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.06164434
Demirbaş A (1999) Proximate and heavy metal composition in chicken meat and tissues. Food Chem 67(1):27–31
Xie P, Wang Y, Wang C, Yuan C, Zou X (2013) Effect of different fat sources in parental diets on growth performance, villus morphology, digestive enzymes and colorectal microbiota in pigeon squabs. Arch Anim Nutr 67(2):147–160
Vaahtovuo J, Korkeamaki M, Munukka E, Mk TP (2005) Quantification of bacteria in human feces using 16S rRNA-hybridization, DNA-staining and flow cytometry. J Microbiol Methods 63(3):276–286
Abdelghani Sghir GG, Suau A, Rochet V, Pochart P, Dore J (2000) Quantification of bacterial groups within human fecal flora by oligonucleotide probe hybridization. Applied & Environmental Microbiology 66(5):2263–2266
Langendijk PS, Schut F, Jansen GJ, Raangs GC, Kamphuis GR, Wilkinson MH, Welling GW (1995) Quantitative fluorescence in situ hybridization of Bifidobacterium spp. with genus-specific 16S rRNA-targeted probe and its application in fecal samples. Applied & Environmental Microbiology 61(8):3069–3075
Smith J, Tokach M, Goodband R, Nelssen J, Richert B (1997) Effects of the interrelationship between zinc oxide and copper sulfate on growth performance of early-weaned pigs. J Anim Sci 75(7):1861–1866
Case C, Carlson M (2002) Effect of feeding organic and inorganic sources of additional zinc on growth performance and zinc balance in nursery pigs. J Anim Sci 80(7):1917–1924
Hu CH, Song ZH, Xiao K, Song J, Jiao le F, Ke YL (2014) Zinc oxide influences intestinal integrity, the expressions of genes associated with inflammation and TLR4-myeloid differentiation factor 88 signaling pathways in weanling pigs. Innate immunity 20(5):478–486. doi:10.1177/1753425913499947
Wang Y, Tang JW, Ma WQ, Feng J, Feng J (2009) Dietary zinc glycine chelate on growth performance, tissue mineral concentrations, and serum enzyme activity in weanling piglets. Biol Trace Elem Res 133(3):325–334
Wahab R, Dwivedi S, Umar A, Singh S, Hwang IH, Shin HS, Musarrat J, Al-Khedhairy AA, Kim YS (2013) ZnO nanoparticles induce oxidative stress in Cloudman S91 melanoma cancer cells. J Biomed Nanotechnol 9(3):441–449
Dwivedi S, Wahab R, Khan F, Mishra YK, Musarrat J, Alkhedhairy AA (2014) Reactive oxygen species mediated bacterial biofilm inhibition via zinc oxide nanoparticles and their statistical determination. PLoS One 9(11):e111289–e111289
Bailey SA, Zidell RH, Perry RW (2004) Relationships between organ weight and body/brain weight in the rat: what is the best analytical endpoint? Toxicol Pathol 32(4):448–466
Andersen H, Larsen S, Spliid H, Christensen ND (1999) Multivariate statistical analysis of organ weights in toxicity studies. Toxicology 136(2–3):67–77
Hadley JA, Fowler DR (2003) Organ weight effects of drowning and asphyxiation on the lungs, liver, brain, heart, kidneys, and spleen. Forensic Sci Int 133(3):190–196
Jo E, Seo G, Kwon JT, Lee M, Lee B, Eom I, Kim P, Choi K (2013) Exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles affects reproductive development and biodistribution in offspring rats. J Toxicol Sci 38(4):525–530
Ko JW, Hong ET, Lee IC, Park SH, Park JI, Seong NW, Hong JS, Yun HI, Kim JC (2015) Evaluation of 2-week repeated oral dose toxicity of 100 nm zinc oxide nanoparticles in rats. Laboratory Animal Research 31(3):139–147
Wang B, Feng WY, Wang TC, Jia G, Wang M, Shi JW, Zhang F, Zhao YL, Chai ZF (2006) Acute toxicity of nano- and micro-scale zinc powder in healthy adult mice. Toxicol Lett 161(2):115–123
Piao F, Yokoyama K, Ma N, Yamauchi T (2003) Subacute toxic effects of zinc on various tissues and organs of rats. Toxicol Lett 145(1):28–35
Sharma V, Singh P, Pandey AK, Dhawan A (2012) Induction of oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis in mouse liver after sub-acute oral exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis 745(1):84–91
Llobet JM, Domingo JL, Colomina MT, Mayayo E, Corbella J (1988) Subchronic oral toxicity of zinc in rats. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 41(1):36–43
Latimer KS, Jain AV, Inglesby HB, Clarkson WD, Johnson GB (1989) Zinc-induced anemia caused by ingestion of pennies by a pup. J Am Vet Med Assoc 195(1):77–80
Van Campen DR, Scaife PU (1967) Zinc interference with copper absorption in rats. J Nutr 91(4):473–476
Kruijsenjaarsma M, Révész D, Bierings MB, Buffart LM, Takken T (2013) Effects of exercise on immune function in patients with cancer: a systematic review. Exerc Immunol Rev 19(1):120–143
Schell T, Kornegay E (1996) Zinc concentration in tissues and performance of weanling pigs fed pharmacological levels of zinc from ZnO, Zn-methionine, Zn-lysine, or ZnSO4. J Anim Sci 74(7):1584–1593
Wang C, Xie P, Liu LL, Lu JJ, Zou XT (2013) Effects of dietary capsulated zinc oxide on growth performance, blood metabolism and mineral concentrations in weaning piglets. Asian Journal of Animal & Veterinary Advances 8(3):502–510
Bäckhed F, Gordon JI (2007) Mechanisms underlying the resistance to diet-induced obesity in germ-free mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(3):979–984
Round JL, Mazmanian SK (2009) The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 9(5):313–323
Vaahtovuo J, Korkeamäki M, Munukka E, Hämeenoja P, Vuorenmaa J (2007) Microbial balance index—a view on the intestinal microbiota. Livest Sci 109(1–3):174–178
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Hangzhou King Techina Technology Co., Ltd and by the Open Fund Project in Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Gastrointestinal Nutrition and Animal Health (Grant No. 2015js02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Experiments were approved and conducted under the supervision of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Nanjing Agriculture University, China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Cheng, K., Zhou, L. et al. Evaluation of Long-Term Toxicity of Oral Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Zinc Sulfate in Mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 178, 276–282 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-0934-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-0934-1