Abstract
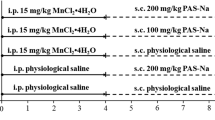
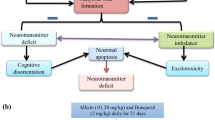
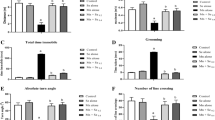
Excessive intake of manganese (Mn) may cause neurotoxicity. Sodium para-aminosalicylic acid (PAS-Na) has been used successfully in the treatment of Mn-induced neurotoxicity. The γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is related with learning and memory abilities. However, the mechanism of PAS-Na on improving Mn-induced behavioral deficits is unclear. The current study was aimed to investigate the effects of PAS-Na on Mn-induced behavioral deficits and the involvement of ultrastructural alterations and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) metabolism in the basal ganglia of rats. Sprague-Dawley rats received daily intraperitoneally injections of 15 mg/kg MnCl2.4H2O, 5d/week for 4 weeks, followed by a daily back subcutaneously (sc.) dose of PAS-Na (100 and 200 mg/kg), 5 days/week for another 3 or 6 weeks. Mn exposure for 4 weeks and then ceased Mn exposure for 3 or 6 weeks impaired spatial learning and memory abilities, and these effects were long-lasting. Moreover, Mn exposure caused ultrastructural alterations in the basal ganglia expressed as swollen neuronal with increasing the electron density in the protrusions structure and fuzzed the interval of neuropil, together with swollen, focal hyperplasia, and hypertrophy of astrocytes. Additionally, the results also indicated that Mn exposure increased Glu/GABA values as by feedback loops controlling GAT-1, GABAA mRNA and GABAA protein expression through decreasing GABA transporter 1(GAT-1) and GABA A receptor (GABAA) mRNA expression, and increasing GABAA protein expression in the basal ganglia. But Mn exposure had no effects on GAT-1 protein expression. PAS-Na treatment for 3 or 6 weeks effectively restored the above-mentioned adverse effects induced by Mn. In conclusion, these findings suggest the involvement of GABA metabolism and ultrastructural alterations of basal ganglia in PAS-Na’s protective effects on the spatial learning and memory abilities.







Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Anderson JG, Cooney PT, Erikson KM (2007) Brain manganese accumulation is inversely related to gamma-amino butyric acid uptake in male and female rats. Toxicol Sci 95(1):188–195
Anderson JG, Fordahl SC, Cooney PT, Weaver TL, Colyer CL, Erikson KM (2008) Manganese exposure alters extracellular GABA, GABA receptor and transporter protein and mRNA levels in the developing rat brain. Neurotoxicology 29(6):1044–1053
Bhang SY, Cho SC, Kim JW, Hong YC, Shin MS, Yoo HJ, Cho IH, Kim Y, Kim BN (2013) Relationship between blood manganese levels and children’s attention, cognition, behavior, and academic performance—a nationwide cross-sectional study. Environ Res 126:9–16
Bikashvili TZ, Shukakidze AA, Kiknadze GI (2001) Changes in the ultrastructure of the rat cerebral cortex after oral doses of manganese chloride. Neurosci Behav Physiol 31(4):385–389
Burton NC, Schneider JS, Syversen T, Guilarte TR (2009) Effects of chronic manganese exposure on glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmitter markers in the nonhuman primate brain. Toxicol Sci 111(1):131–139
Crawford S, Davis K, Saddler C, Joseph J, Catapane EJ, Carroll MA (2011) The ability of PAS, acetylsalicylic acid and calcium disodium EDTA to protect against the toxic effects of manganese on mitochondrial respiration in gill of Crassostrea virginica. In Vivo (Brooklyn) 33(1):7–14
Defazio G, Soleo L, Zefferino R, Livrea P (1996) Manganese toxicity in serumless dissociated mesencephalic and striatal primary culture. Brain Res Bull 40(4):257–262
Dong, X., D. Zhang and X. Meng 2006. The effects of Glu/GABA horizontal correlation on learning and memory ability. J Chin Gerontol (02):283–285
Erikson KM, Aschner M (2003) Manganese neurotoxicity and glutamate-GABA interaction. Neurochem Int 43(4–5):475–480
Fitsanakis VA, Au C, Erikson KM, Aschner M (2006) The effects of manganese on glutamate, dopamine and gamma-aminobutyric acid regulation. Neurochem Int 48(6–7):426–433
Guilarte TR (2013) Manganese neurotoxicity: new perspectives from behavioral, neuroimaging, and neuropathological studies in humans and non-human primates. Front Aging Neurosci 5:23
Gwiazda RH, Lee D, Sheridan J, Smith DR (2002) Low cumulative manganese exposure affects striatal GABA but not dopamine. Neurotoxicology 23(1):69–76
Horning KJ, Caito SW, Tipps KG, Bowman AB, Aschner M (2015) Manganese is essential for neuronal health. Annu Rev Nutr 35:71–108
Jiang Y, Zheng W, Long L, Zhao W, Li X, Mo X, Lu J, Fu X, Li W, Liu S, Long Q, Huang J, Pira E (2007) Brain magnetic resonance imaging and manganese concentrations in red blood cells of smelting workers: search for biomarkers of manganese exposure. Neurotoxicology 28(1):126–135
Jiang YM, Mo XA, Du FQ, Fu X, Zhu XY, Gao HY, Xie JL, Liao FL, Pira E, Zheng W (2006) Effective treatment of manganese-induced occupational Parkinsonism with p-aminosalicylic acid: a case of 17-year follow-up study. J Occup Environ Med 48(6):644–649
Kim Y, Jeong KS, Song HJ, Lee JJ, Seo JH, Kim GC, Lee HJ, Kim HJ, Ahn JH, Park SJ, Kim SH, Kwon YJ, Chang Y (2011) Altered white matter microstructural integrity revealed by voxel-wise analysis of diffusion tensor imaging in welders with manganese exposure. Neurotoxicology 32(1):100–109
King C, Myrthil M, Carroll MA, Catapane EJ (2008) Effects of p-aminosalicylic acid on the neurotoxicity of manganese and levels of dopamine and serotonin in the nervous system and innervated organs of Crassostrea virginica. In Vivo (Brooklyn) 29(3):26–34
Ky SQ, Deng HS, Xie PY, Hu W (1992) A report of two cases of chronic serious manganese poisoning treated with sodium para-aminosalicylic acid. Br J Ind Med 49(1):66–69
Li, S. J., Y. Li, J. W. Chen, Z. X. Yuan, Y. H. Mo, G. D. Lu, Y. M. Jiang, C. Y. Ou, F. Wang, X. W. Huang, Y. N. Luo, S. Y. Ou and Y. N. Huang 2015a. Sodium para-aminosalicylic acid protected primary cultured basal ganglia neurons of rat from manganese-induced oxidative impairment and changes of amino acid neurotransmitters. Biol Trace Elem Res
Li SJ, Meng HY, Deng XF, Fu X, Chen JW, Huang S, Huang YS, Luo HL, Ou SY, Jiang YM (2015b) Protective effects of sodium p-aminosalicylic acid on learning and memory via increasing the number of basal forebrain choline acetyltransferase neurons in manganese-exposed rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 34(3):240–248
Lipe GW, Duhart H, Newport GD, Slikker W Jr, Ali SF (1999) Effect of manganese on the concentration of amino acids in different regions of the rat brain. J Environ Sci Health B 34(1):119–132
Long Z, Jiang YM, Li XR, Fadel W, Xu J, Yeh CL, Long LL, Luo HL, Harezlak J, Murdoch JB, Zheng W, Dydak U (2014) Vulnerability of welders to manganese exposure--a neuroimaging study. Neurotoxicology 45:285–292
Lu CS, Huang CC, Chu NS, Calne DB (1994) Levodopa failure in chronic manganism. Neurology 44(9):1600–1602
Lucchini RG, Albini E, Benedetti L, Borghesi S, Coccaglio R, Malara EC, Parrinello G, Garattini S, Resola S, Alessio L (2007) High prevalence of Parkinsonian disorders associated to manganese exposure in the vicinities of ferroalloy industries. Am J Ind Med 50(11):788–800
Lucchini RG, Guazzetti S, Zoni S, Benedetti C, Fedrighi C, Peli M, Donna F, Bontempi E, Borgese L, Micheletti S, Ferri R, Marchetti S, Smith DR (2014) Neurofunctional dopaminergic impairment in elderly after lifetime exposure to manganese. Neurotoxicology 45:309–317
McKinney AM, Filice RW, Teksam M, Casey S, Truwit C, Clark HB, Woon C, Liu HY (2004) Diffusion abnormalities of the globi pallidi in manganese neurotoxicity. Neuroradiology 46(4):291–295
Meyer-Baron M, Schaper M, Knapp G, Lucchini R, Zoni S, Bast-Pettersen R, Ellingsen DG, Thomassen Y, He S, Yuan H, Niu Q, Wang XL, Yang YJ, Iregren A, Sjogren B, Blond M, Laursen P, Netterstrom B, Mergler D, Bowler R, van Thriel C (2013) The neurobehavioral impact of manganese: results and challenges obtained by a meta-analysis of individual participant data. Neurotoxicology 36:1–9
Nachtman JP, Delor S, Brennan CE (1987) Manganese neurotoxicity: effects of varying oxygen tension and EDTA on dopamine auto-oxidation. Neurotoxicology 8(2):249–253
Noristani HN, Meadows RS, Olabarria M, Verkhratsky A, Rodriguez JJ (2011) Increased hippocampal CA1 density of serotonergic terminals in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: an ultrastructural study. Cell Death Dis 2:e210
Ou CY, Huang ML, Jiang YM, Luo HL, Deng XF, Wang C, Wang F, Huang XW (2011) [Effect of sodium para-aminosalicylic on concentrations of amino acid neurotransmitters in basal ganglia of manganese-exposed rats]. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 45(5):422–425
Racette BA, Aschner M, Guilarte TR, Dydak U, Criswell SR, Zheng W (2012) Pathophysiology of manganese-associated neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 33(4):881–886
Rodriguez-Barranco M, Lacasana M, Aguilar-Garduno C, Alguacil J, Gil F, Gonzalez-Alzaga B, Rojas-Garcia A (2013) Association of arsenic, cadmium and manganese exposure with neurodevelopment and behavioural disorders in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 454-455:562–577
Roels HA, Bowler RM, Kim Y, Claus Henn B, Mergler D, Hoet P, Gocheva VV, Bellinger DC, Wright RO, Harris MG, Chang Y, Bouchard MF, Riojas-Rodriguez H, Menezes-Filho JA, Tellez-Rojo MM (2012) Manganese exposure and cognitive deficits: a growing concern for manganese neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 33(4):872–880
Rosenstock HA, Simons DG, Meyer JS (1971) Chronic manganism. Neurologic and laboratory studies during treatment with levodopa. JAMA 217(10):1354–1358
Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz M, Aschner M (2013) Role of astrocytes in manganese mediated neurotoxicity. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol 14:23
Stanwood GD, Leitch DB, Savchenko V, Wu J, Fitsanakis VA, Anderson DJ, Stankowski JN, Aschner M, McLaughlin B (2009) Manganese exposure is cytotoxic and alters dopaminergic and GABAergic neurons within the basal ganglia. J Neurochem 110(1):378–389
Struve MF, McManus BE, Wong BA, Dorman DC (2007) Basal ganglia neurotransmitter concentrations in rhesus monkeys following subchronic manganese sulfate inhalation. Am J Ind Med 50(10):772–778
Tandon SK (1978) Chelation in metal intoxication. VI. Influence of PAS and CDTA on the excretion of manganese in rabbits given MnO2. Toxicology 9(4):379–385
Wade A, Jacobs P, Morton AJ (2008) Atrophy and degeneration in sciatic nerve of presymptomatic mice carrying the Huntington’s disease mutation. Brain Res 1188:61–68
Wang F, Wang C, Jiang Y, Deng X, Lu J, Ou S (2014) Protective role of sodium para-amino salicylic acid against manganese-induced hippocampal neurons damage. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37(3):1071–1078
Yamada M, Ohno S, Okayasu I, Okeda R, Hatakeyama S, Watanabe H, Ushio K, Tsukagoshi H (1986) Chronic manganese poisoning: a neuropathological study with determination of manganese distribution in the brain. Acta Neuropathol 70(3–4):273–278
Yoon H, Kim DS, Lee GH, Kim JY, Kim DH, Kim KW, Chae SW, You WH, Lee YC, Park SJ, Kim HR, Chae HJ (2009) Protective effects of sodium para-amino salicylate on manganese-induced neuronal death: the involvement of reactive oxygen species. J Pharm Pharmacol 61(11):1563–1569
Zheng W, Jiang YM, Zhang Y, Jiang W, Wang X, Cowan DM (2009) Chelation therapy of manganese intoxication with para-aminosalicylic acid (PAS) in Sprague-Dawley rats. Neurotoxicology 30(2):240–248
Zwingmann C, Leibfritz D, Hazell AS (2007) Nmr spectroscopic analysis of regional brain energy metabolism in manganese neurotoxicity. Glia 55(15):1610–1617
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Grant Support
ᅟ
ᅟ
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 81072320, 81460505, 30760210), Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (GXNSFAA 118232, 2015GXNSFAA139181) and the Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education.
Additional information
Drs. Chao-Yan Ou, Yi-Ni Luo, Sheng-Nan He and Xiang-Fa Deng contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ou, CY., Luo, YN., He, SN. et al. Sodium P-Aminosalicylic Acid Improved Manganese-Induced Learning and Memory Dysfunction via Restoring the Ultrastructural Alterations and γ-Aminobutyric Acid Metabolism Imbalance in the Basal Ganglia. Biol Trace Elem Res 176, 143–153 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0802-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0802-4