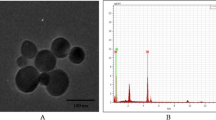
Abstract
Despite an increasing surge in application of nanoparticles in industries, there is a serious lack of information concerning their impact on human health and the environment. The present study investigated effects of molybdenum nanoparticles (Mo NPs) injected intraperitoneally into Sprague-Dawley rats at different doses of Mo NPs (5, 10, and 15 mg/kg BW per day) during a period of 28 days. Hematological and biochemical parameters as well as sexual hormones and histopathological examinations of the liver and testis were assessed and compared with control group. The results showed that the serum levels of testosterone decreased significantly in both groups of 10 and 15 mg (Mo NPs)/kg BW in comparison with the control group (p < 0.05). However, there were insignificant differences observed in luteinizing hormone (LH) levels and hematological parameters when compared with the control group (p > 0.05). The results of liver enzymes showed that serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) decreased significantly in both dosage groups of 5 and 10 mg/kg BW (Mo NPs) when compared with the control group (p < 0.05), and significant decrease obtained in lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels at dose of 5 mg/kg BW in comparison with the control group (p < 0.05). The histopathological examination of testis showed a decrease in number of Leydig cells. Also, the number of chronic inflammatory cells increased in portal triad and parenchyma in liver tissue of rats exposed to Mo NPs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burguera JL, Burguera M (2007) Molybdenum in human whole blood of adult residents of the Merida state (Venezuela). J Trace Elem Med Biol 21:178–183
Shrivas K, Agrawal K, Harmukh N (2009) Trace level determination of molybdenum in environmental and biological samples using surfactant-mediated liquid–liquid extraction. J Hazard Mater 161:325–329
Kikuchi K, Hamano S, Mochizuki H, et al. (2012) Molybdenum cofactor deficiency mimics cerebral palsy: differentiating factors for diagnosis. Pediatr Neurol 47(2):147–149
Levina A, McLeod A, Seuring J, et al. (2007) Reactivity of potential anti-diabetic molybdenum (VI) complexes in biological media: a XANES spectroscopic study. J Inorg Biochem 101(11–12):1586–1593
Burrell RJW, Roach WA, Shadwell A (1966) Esophageal cancer in the bantu of the ranskei associated with mineral deficiency in garden plants. J Natl Cancer Inst 36:201–209
Seaborn CD, Yang SP (1993) Effect of molybdenum supplementation on N-nitroso-N-methylurea-induced mammary carcinogenesis and molybdenum excretion in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 39:245–256
Wei HJ, Luo XM, Yang SP (1985) Effects of Molybdenumm and tungsten on mammary carcinoqenesis in SD rats. J Natl Cancer Inst 74:469–473
Yang F, Cui H, Xiao J, et al. (2011) Increased apoptotic lymphocyte population in the spleen of young chickens fed on diets high in molybdenum. Biol Trace Elem Res 140:308–316
Langard S, Norseth T (1986) Handbook on the toxicology of metals. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Colvin VL (2003) The potential environmental impacts of engineered nanomaterials. Nat Biotechnol 21:1166–1170
Thakur M, Gupta H, Singh D, et al. (2014) Histopathological and ultra structural effects of nanoparticles on rat testis following 90 days (chronic study) of repeated oral administration. J Nanobiotechnol 12:42–54
Mills CF, Davis GK (1987) Trace elements in human and animal nutrition. Academic Press, San Diego
Capasso L, Camatini M, Gualtieri M (2014) Nickel oxide nanoparticles induce inflammation and genotoxic effect in lung epithelial cells. Toxicol Lett 226:28–34
Fahmy B, Cormier SA (2009) Copper oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in airway epithelial cells. Toxicol in Vitro 23:1365–1371
Paz-Elizur T, Sevilya Z, Leitner-Dagan Y, et al. (2008) DNA repair of oxidative DNA damage in human carcinogenesis: potential application for cancer risk assessment and prevention. Cancer Lett 266:60–72
Siddiqui MA, Saquib Q, Ahamed M, et al. (2015) Molybdenum nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity, oxidative stress,G2/M arrest, and DNA damage in mouse skin fibroblast cells (L929). Colloid Surface B 125:73–81
Akhtar MJ, Ahamed M, Alhadlaq HA (2015) Antioxidative and cytoprotective response elicited by molybdenum nanoparticles in human cells. J Colloid Interface Sci 457:370–377
Donaldson K, Tran L, Jimenez LA (2005) Combustion-derived nanoparticles: a review of their toxicology following inhalation exposure. Part Fibre Toxicol 2:10
Powers KW, Brown SC, Krishna VB, et al. (2006) Characterization of nanoscale particles for toxicological evaluation. Toxicol Sci 90:296–303
Braydich -Stolle L, Hussain S, Schlager JJ, et al. (2005) In vitro cytotoxicity of nanoparticles in mammalian germline stem cells. Toxicol Sci 88:412–419
Wu H, Yang R, Song B, et al. (2011) Biocompatible inorganic fullerene like molybdenum disulfide nanoparticles produced by pulsed laser ablation in water. ACS Nano 5:1276–1281
Tran TA, Krishnamoorthy K, Song YW, et al. (2014) Toxicity of nano molybdenum trioxide toward invasive breast cancer cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(4):2980–2986
Fakhri A, Afshar Nejad P (2016) Antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxic effect of molybdenum trioxide nanoparticles and application of this for degradation of ketamine under different light illumination. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 159:211–217
Hamrahi-michak M, Sadeghi SA, Haghighi H, et al. (2012) The toxicity effect of cerium oxide NP on blood cells of male rat. Ann Biol Res 3(6):2859–2866
Warnock LG, Stone WJ, Wagner C (1974) Decreased amino aspartate transferaz activity in serum of uremic patients. Clin Chem 20(9):1213–1216
Seldėn AI, Berg NP, Söderbergh A, et al. (2005) Occupational molybdenum exposure and a gouty electrician. Occup Med 55:145–148
Rana SVS, Kumar A (1981) Effect of molybdenum and cupper on key enzymes of rat kidney with special reference to physiological antagonism. Toxicol Lett 7:393–397
Carlson C, Hussain SM, Schrand AM, et al. (2008) Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles: size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. J Phys Chem B 112:13608–13619
Shin SW, Song IH, Um SH (2015) Role of physicochemical properties in nanoparticle toxicity. Nanomaterials 5:1351–1365
Iavicoli I, Fontana L, Leso V, et al. (2013) The effects of nanomaterials as endocrine disruptors. Int J Mol Sci 14:16732–16801
Zhang XF, Choi YJ, Han JW, et al. (2015) Differntial nanoreprotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in male somatic cells and spermatogonial stem cells. Int J Nanomedicine 10:1335–1357
Andric SA, Janjic MM, Stojkov NJ, et al. (2010) Testosterone induced modulation of nitric oxide-cGMP signaling pathway and andrgenesis in the rat leydig cells. Biol Reprod 83:434–442
Andric SA, Janjic MM, Stojkov NJ, et al. (2007) Protein kinase G-mediated stimulation of basal leydig cell steroidogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293:E1399–E1408
Ema M, Kobayashi N, Naya M, et al. (2010) Reproductive and developmental toxicity studies of manufactured nanomaterials. Reprod Toxicol 30:343–352
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Metabolic Diseases Research Center at Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, Zanjan, Iran, for financial and other supports. Special thanks to Dr. Mehrdad Pedram (Department of Medical Genetics and Molecular Medicine, ZUMS) for his help with editing of the manuscript and highly valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal experiments were performed in compliance with the ZUMS Ethics Committee.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asadi, F., Mohseni, M., Dadashi Noshahr, K. et al. Effect of Molybdenum Nanoparticles on Blood Cells, Liver Enzymes, and Sexual Hormones in Male Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 175, 50–56 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0765-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0765-5