Abstract
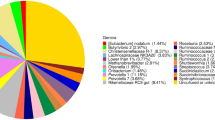
Vanadium (V) is a trace element which can induce dysfunction of gastro-intestine and egg quality deterioration of laying hens. This study was conducted to determine the effect of tea polyphenols (TP) on intestinal morphology, microflora, and short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) profile of laying hens fed vanadium containing diets. A total of 120 Lohman laying hens (67-week-old) were randomly divided into 4 groups with 6 replicates and 5 birds each for a 35-day feeding trial. The dietary treatments were as follows: (1) control (CON), fed a basal diet; (2) vanadium treatment (V10), CON +10 mg V/kg; (3) TP treatment 1 (TP1): V10 + 600 mg TP/kg; (4) TP treatment 2 (TP2): V10 + 1000 mg TP/kg. Fed 10 mg V/kg diets to laying hens did not affect the cecum flora diversity index (H), degree of homogeneity (EH), and richness (S), but hens fed TP2 diet decreased the H, EH, and S (P < 0.05). The cecum butyrate acid concentration was lower in V10 treatment and higher in TP2 treatment (P < 0.05). Addition of 10 mg/kg V resulted in an increased (P < 0.01) duodenal cell apoptosis rate, and 1000 mg/kg TP supplementation overcame (P < 0.01) this reduction effect induced by vanadium. The results indicated that supplementation of 10 mg/kg vanadium increased duodenal cell apoptosis and reduced cecum butyrate acid content. Addition of 1000 mg/kg TP increased the SCFA production to affect cecum flora ecology and protected the duodenal cell from excess apoptosis caused by vanadium.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cui W, Cui H, Peng X, Fang J, Zuo Z, Liu X, Wu B (2011) Dietary excess vanadium induces lesions and changes of cell cycle of spleen in broilers. Biol Trace Elem Res 143(2):949–956. doi:10.1007/s12011-010-8938-0
Nielsen FH (1990) New essential trace elements for the life sciences. Biol Trace Elem Res 26(1):599–611
Uthus E, Nielsen F (1990) Effect of vanadium, iodine and their interaction on growth, blood variables, liver trace elements and thyroid status indices in rats. Magnes Trace Elem 9(4):219–226
Huang X, Wang J, Ding X, Zhang K, Zeng Q, Bai S, Luo Y (2015) Effects of vanadium on health of chickens and its mechanism. Journal of animal nutrition 08:2335–2341
Domingo JL (2000) Vanadium and diabetes. What about vanadium toxicity? Mol Cell Biochem 203(1):185–187
Domingo J, Gomez M, Llobet J, Corbella J, Keen C (1991) Oral vanadium administration to streptozotocin-diabetic rats has marked negative side-effects which are independent of the form of vanadium used. Toxicology 66(3):279–287
Henry PR, Miles RD (2006) Heavy metals–vanadium in poultry. Ciência Animal Brasileira 2(1):11–26
Yuan Z, Huang X, Zhang K, Ding X, Zeng Q, Bai S, Luo Y, Wang J (2015) Research on the heavy metal content in the compound feed and eggs of laying hens of Sichuan Province. Journal of animal nutrition 11:3485–3494
Henry PR, Miles RD (2006) Heavy metals—vanadium in poultry. Ciência Animal Brasileira 2:11–26.
Wang J, He K, Ding X, Luo Y, Bai S, Zeng Q, Su Z, Xuan Y, Zhang K (2015) Effect of dietary vanadium and vitamin C on egg quality and antioxidant status in laying hens. Journal of animal physiology and animal nutrition. doi:10.1111/jpn.12377
Hirano S, Suzuki KT (1996) Exposure, metabolism, and toxicity of rare earths and related compounds. Environ Health Perspect 104(Suppl 1):85
Kangping W, Hengmin C, Xi P, Zhicai Z, Jing F, Junliang D, Yuanxin D, Wei C, Bangyuan W (2012) Effect of dietary vanadium on small intestinal morphology in broilers. Health 2012
Chiou P, Chen C, Chen K, Wu C (1999) Effect of high dietary copper on the morphology of gastro-intestinal tract in broiler chickens. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences 12(4):548–553
Ray RS, Rana B, Swami B, Venu V, Chatterjee M (2006) Vanadium mediated apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in MCF7 cell line. Chem Biol Interact 163(3):239–247
Wang K, Cui H, Deng Y, Peng X, Zuo Z, Fang J, Deng J, Cui W, Wu B (2012) Effect of dietary vanadium on intestinal microbiota in broiler. Biol Trace Elem Res 149(2):212–218. doi:10.1007/s12011-012-9409-6
O'Keefe SJ (2008) Nutrition and colonic health: the critical role of the microbiota. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 24(1):51–58
Frei B, Higdon JV (2003) Antioxidant activity of tea polyphenols in vivo: evidence from animal studies. J Nutr 133(10):3275S–3284S
Gultemirian ML, Corti HR, Chaia AP, Apella MC (2014) Fermentation in vitro of a mixture of dietary fibers and cane molasses by the cecal microbiota: application on mineral absorption through the laying hen's colonic epithelium. Anim Feed Sci Technol 191:76–82. doi:10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2014.01.019
Duda-Chodak A (2012) The inhibitory effect of polyphenols on human gut microbiota. J Physiol Pharmacol 63:497–503
Wang J, Tang C, Wang Q, Li R, Chen Z, Han X, Wang J, Xu X (2015) Apoptosis induction and release of inflammatory cytokines in the oviduct of egg-laying hens experimentally infected with H9N2 avian influenza virus. Vet Microbiol 177(3–4):302–314. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.04.005
Yuan Z, Wang J, Zhang K, Ding X, Zeng Q, Bai S, Luo Y, (2015) Effect of tea polyphenols on production performance, egg quality and hepatic antioxidant status of laying hens in vanadium containing diets. poultry science Publish online, 00:1–9. http://dx.doi.org/10.3382/ps/pew097
NRC (1994) Nutrient requirements of poultry. 9th, Rev. edn. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Onderci M, Sahin N, Sahin K, Cikim G, Aydin A, Ozercan I, Aydin S (2006) Efficacy of supplementation of α-amylase-producing bacterial culture on the performance, nutrient use, and gut morphology of broiler chickens fed a corn-based diet. Poult Sci 85(3):505–510
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA (1992) Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 119(3):493–501
Nübel U, Engelen B, Felske A, Snaidr J, Wieshuber A, Amann RI, Ludwig W, Backhaus H (1996) Sequence heterogeneities of genes encoding 16S rRNAs in Paenibacillus polymyxa detected by temperature gradient gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol 178(19):5636–5643
Sanguinetti CJ, Dias NE, Simpson A (1994) Rapid silver staining and recovery of PCR products separated on polyacrylamide gels. Biotechniques 17(5):914–921
Qi H, Xiang Z, Han G, Yu B, Huang Z, Chen D (2013) Effects of different dietary protein sources on cecal microflora in rats. Afr J Biotechnol 10(19):3704–3708
Fierer N, Jackson JA, Vilgalys R, Jackson RB (2005) Assessment of soil microbial community structure by use of taxon-specific quantitative PCR assays. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(7):4117–4120
Qi HW, Xiang ZT, Han GQ, Yu B, Huang ZQ, Chen DW (2011) Effects of different dietary protein sources on cecal microflora in rats. Afr J Biotechnol 10:3704–3708
AOAC (2005) Official methods of analysis. 18th ed. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Gaithersburg, MD
AOAC International (2000) Official methods of analysis. 17th ed. AOAC Int., Gaithersburg, MD
SAS Institute (1998) SAS user’s guide: statistics. Version 7.0 ed. SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC
Deng Y, Cui H, Peng X, Fang J, Zuo Z, Wang K, Cui W, Wu B (2012) Changes of IgA+ cells and cytokines in the cecal tonsil of broilers fed on diets supplemented with vanadium. Biol Trace Elem Res 147(1–3):149–155
Liu J, Cui H, Liu X, Peng X, Deng J, Zuo Z, Cui W, Deng Y, Wang K (2012) Dietary high vanadium causes oxidative damage-induced renal and hepatic toxicity in broilers. Biol Trace Elem Res 145(2):189–200
Hafez YS, Kratzer F (1976) The effect of diet on the toxicity of vanadium. Poult Sci 55(3):918–922
Wang K, Cui H, Peng X, Zuo Z, Fang J, Deng J, Deng Y, Cui W, Wu B (2012) Effect of dietary vanadium on small intestinal morphology in broilers. Health 04(09):667–674. doi:10.4236/health.2012.49105
Yang CS, Landau JM (2000) Effects of tea consumption on nutrition and health. J Nutr 130(10):2409–2412
Hassanpour H, Zamani Moghaddam AK, Yazdani A, Cheraghchi Bashi M (2009) Evaluation of intestinal morphology and nitric oxide metabolites in broiler chickens supplemented by green tea. Comp Clin Pathol 19(1):43–47. doi:10.1007/s00580-009-0831-x
Guo S, Bezard E, Zhao B (2005) Protective effect of green tea polyphenols on the SH-SY5Y cells against 6-OHDA induced apoptosis through ROS–NO pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 39(5):682–695
Lagerkvist JS, Oskarsson A (2007) Tellurium - handbook on the toxicology of metals (third edition) - chapter 40. Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals 11:815–825
Kuhnle G, Spencer JP, Schroeter H, Shenoy B, Debnam ES, Srai SKS, Rice-Evans C, Hahn U (2000) Epicatechin and catechin are O-methylated and glucuronidated in the small intestine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 277(2):507–512
Hervert-Hernández D, Goni I (2011) Dietary polyphenols and human gut microbiota: a review. Food Reviews International 27(2):154–169
Selma MV, Espin JC, Tomas-Barberan FA (2009) Interaction between phenolics and gut microbiota: role in human health. J Agric Food Chem 57(15):6485–6501
Corrier DE, Hinton A Jr, Ziprin RL, DeLoach JR (1990) Effect of dietary lactose on salmonella colonization of market-age broiler chickens. Avian Dis:668–676
Wong JM, de Souza R, Kendall CW, Emam A, Jenkins DJ (2006) Colonic health: fermentation and short chain fatty acids. J Clin Gastroenterol 40(3):235–243
Hamer HM, Jonkers D, Venema K, Vanhoutvin S, Troost F, BRUMMER RJ (2008) Review article: the role of butyrate on colonic function. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 27(2):104–119
Hu Z, Guo Y (2007) Effects of dietary sodium butyrate supplementation on the intestinal morphological structure, absorptive function and gut flora in chickens. Anim Feed Sci Technol 132(3–4):240–249. doi:10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2006.03.017
Iraporda C, Errea A, Romanin DE, Cayet D, Pereyra E, Pignataro O, Sirard JC, Garrote GL, Abraham AG, Rumbo M (2015) Lactate and short chain fatty acids produced by microbial fermentation downregulate proinflammatory responses in intestinal epithelial cells and myeloid cells. Immunobiology 220(10):1161–1169
Hijova E, Chmelarova A (2007) Short chain fatty acids and colonic health. Bratisl Lek Listy 108(8):354
Acknowledgments
This project was fanatically supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31402031) and Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Projects (13ZB0290, 2014BAD13B04, 2014NZ0043, 2014NZ0002, 2013NZ0054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Z.H., Wang, J.P., Zhang, K.Y. et al. Effect of Vanadium and Tea Polyphenols on Intestinal Morphology, Microflora and Short-Chain Fatty Acid Profile of Laying Hens. Biol Trace Elem Res 174, 419–427 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0721-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0721-4