Abstract
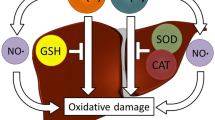
Free iron leads to the formation of pro-oxidant reactive oxygen species (ROS). Humic acids (HAs) enhance permeability of cellular wall and act as a chelator through electron transferring. This study was designed to test chelator effect of HA on iron as well as its anti-oxidant effect against the iron-induced hepatotoxicity and cardiotoxicity. The rats used were randomly divided into four groups (n = 8/group): group I (the control group); group II (the HA group), humic acid (562 mg/kg) was given over 10 days by oral gavage; group III (the iron group), iron III hydroxide polymaltose (250 mg/kg) was given over 10 days by intraperitoneal route; and group IV (the HA plus iron group), received the iron (similar to group II) plus humic acid (similar to those in groups II and III) group. Blood and two tissue samples both from liver and heart were obtained for biochemical and histopathological evaluations. Iron deposition, the iron-induced hepatotoxicity, and cardiotoxicity were demonstrated by histopathological and biochemical manner. However, no significant differences were observed in the serum biochemical values and the histopathological results among the iron and the HA plus iron groups in the liver tissue but not in the heart tissue. The protective effects of humic acid against iron-induced cardiotoxicity were shown but not against hepatotoxicity in our study.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reddy ACP, Lokesh B (1996) Effect of curcumin and eugenol on iron-induced hepatic toxicity in rats. Toxicology 107(1):39–45
Tandara L, Salamunić I (2012) Iron metabolism: current facts and future directions. Biochemia Medica 22(3):311–328
Singh N, Haldar S, Tripathi AK, Horback K, Wong J, Sharma D, Beserra A, Suda S, Anbalagan C, Dev S (2014) Brain iron homeostasis: from molecular mechanisms to clinical significance and therapeutic opportunities. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 20(8):1324–1363
Garrick MD, Garrick LM (2009) Cellular iron transport. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects 1790(5):309–325
Siah CW, Ombiga J, Adams LA, Trinder D, Olynyk JK (2006) Normal iron metabolism and the pathophysiology of iron overload disorders. Clin Biochem Rev 27(1):5
Donovan A, Lima CA, Pinkus JL, Pinkus GS, Zon LI, Robine S, Andrews NC (2005) The iron exporter ferroportin/Slc40a1 is essential for iron homeostasis. Cell Metab 1(3):191–200
Bresgen N, Eckl PM (2015) Oxidative stress and the homeodynamics of iron metabolism. Biomolecules 5(2):808–847
Chyka PA, Butler AY (1993) Assessment of acute iron poisoning by laboratory and clinical observations. The American Journal of Emergency Medicine 11(2):99–103
Liebelt EL, Kronfol R, Ewald MB, Traub SJ, Wiley JF (2008) Acute iron poisoning. UpToDate. Last updated Sep 9
Das A, Chaudhuri D, Ghate NB, Panja S, Chatterjee A, Mandal N (2015) Protective effect of clerodendrum colebrookianum leaves against iron-induced oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity in Swiss albino mice. Indian J Exp Biol 53:281–291
SA EL-M, Rizk SM, MM E-S (2009) Hepatoprotective potential of crocin and curcumin against iron overload-induced biochemical alterations in rat. Afr J Biochem Res 3(5):215–221
Pari L, Karthikeyan A, Karthika P, Rathinam A (2015) Protective effects of hesperidin on oxidative stress, dyslipidaemia and histological changes in iron-induced hepatic and renal toxicity in rats. Toxicology Reports 2:46–55
Tapia G, Troncoso P, Galleano M, Fernandez V, Puntarulo S, Videla LA (1998) Time course study of the influence of acute iron overload on kupffer cell functioning and hepatotoxicity assessed in the isolated perfused rat liver. Hepatology 27(5):1311–1316
Ramm GA, Ruddell RG (2005) Seminars in liver disease, 2005. vol 04. In: Hepatotoxicity of iron overload: mechanisms of iron-induced hepatic fibrogenesis. Copyright© 2005 by Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc., 333 Seventh Avenue, New York, NY 10001, USA, pp. 433–449
Marx J, Walls R, Hockberger R (2013) Rosen’s emergency medicine-concepts and clinical practice. Elsevier Health Sciences, London
Madiwale T, Liebelt E (2006) Iron: not a benign therapeutic drug. Curr Opin Pediatr 18(2):174–179
Ackerman Z, Pappo O, Link G, Glazer M, Grozovski M (2014) Liver toxicity of thioacetamide is increased by hepatocellular iron overload. Biological Trace Element Research 1:8
Fibach E, Rachmilewitz EA (2010) The role of antioxidants and iron chelators in the treatment of oxidative stress in thalassemia. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1202(1):10–16
Wang Q-M, Du J-L, Duan Z-J, Guo S-B, Sun X-Y, Liu Z (2013) Inhibiting heme oxygenase-1 attenuates rat liver fibrosis by removing iron accumulation. World Journal of Gastroenterology: WJG 19(19):2921
Najafzadeh H, Jalali MR, Morovvati H, Taravati F (2010) Comparison of the prophylactic effect of silymarin and deferoxamine on iron overload-induced hepatotoxicity in rat. Journal of Medical Toxicology 6(1):22–26
Breitbart R, Abu-Kishk I, Kozer E, Ben-Assa E, Goldstein LH, Youngster I, Berkovitch M (2011) Intraperitoneal N-acetylcysteine for acute iron intoxication in rats. Drug Chem Toxicol 34(4):429–432
Cetin E, Guclu BK, Cetin N (2011) Effect of dietary humate and organic acid supplementation on social stress induced by high stocking density in laying hens. J Anim Vet Adv 10(18):2402–2407
Moura MN, Martín MJ, Burguillo FJ (2007) A comparative study of the adsorption of humic acid, fulvic acid and phenol onto Bacillus subtilis and activated sludge. J Hazard Mater 149(1):42–48
Sagbas S, Kantar C, Sahiner N (2014) Preparation of poly (humic acid) particles and their use in toxic organo-phenolic compound removal from aqueous environments. Water Air Soil Pollut 225(1):1–10
Madronová L, Kozler J, Čežíková J, Novák J, Janoš P (2001) Humic acids from coal of the north-bohemia coal field: III☆☆. Metal-binding properties of humic acids—measurements in a column arrangement. React Funct Polym 47(2):119–123
Zralý Z, Písaříková B, Navrátilová M (2008) The effect of humic acid on mercury accumulation in chicken organs and muscle tissues. Czech J Anim Sci 53:472–478
Zralý Z, Písaříková B, Trčková M, Navrátilová M (2008) Effect of humic acids on lead accumulation in chicken organs and muscles. Acta Veterinaria Brno 77(3):439–445
Vašková J, Veliká B, Pilátová M, Kron I, Vaško L (2011) Effects of humic acids in vitro. Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology-Animal 47(5–6):376–382
Vucskits A, Hullár I, Bersényi A, Andrásofszky E, Kulcsár M, Szabó J (2010) Effect of fulvic and humic acids on performance, immune response and thyroid function in rats. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 94(6):721–728
Ma B, Yu W, Jefferson WA, Liu H, Qu J (2015) Modification of ultrafiltration membrane with nanoscale zerovalent iron layers for humic acid fouling reduction. Water Res 71:140–149
Seymen O, Seven A, Candan G, Yigit G, Hatemi S, Hatemi H (1997) The effect of iron supplementation on GSH levels, GSH-Px, and SOD activities of erythrocytes in l-thyroxine administration. Acta Med Okayama 51(3):129–133
Altintas R, Parlakpinar H, Beytur A, Vardi N, Polat A, Sagir M, Odabas GP (2012) Protective effect of dexpanthenol on ischemia-reperfusion-induced renal injury in rats. Kidney Blood Press Res 36(1):220–230
Uchiyama M, Mihara M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 86(1):271–278
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34(3):497–500
Aebi H, Suter H (1969) Catalase. Methods of Enzymatic analysis 77:325
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. The Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine 70(1):158–169
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77
Erel O (2004) A novel automated method to measure total antioxidant response against potent free radical reactions. Clin Biochem 37(2):112–119
LeSage G, Baldus W, Fairbanks V, Baggenstoss A, McCall J, Moore SB, Taswell H, Gordon H (1983) Hemochromatosis: genetic or alcohol-induced? Gastroenterology 84(6):1471–1477
Dixon SJ, Stockwell BR (2014) The role of iron and reactive oxygen species in cell death. Nat Chem Biol 10(1):9–17
Zhang Y, Huang Y, Deng X, Xu Y, Gao Z, Li H (2012) Iron overload-induced rat liver injury: involvement of protein tyrosine nitration and the effect of baicalin. Eur J Pharmacol 680(1):95–101
Whittaker P, Chanderbhan R, Calvert R, Dunkel V (1994) Cellular and molecular responses in the Sprague-Dawley rat to chronic iron overload. The Journal of Trace elements in Experimental Medicine 7(1):19–31
Koskenkorva-Frank TS, Weiss G, Koppenol WH, Burckhardt S (2013) The complex interplay of iron metabolism, reactive oxygen species, and reactive nitrogen species: insights into the potential of various iron therapies to induce oxidative and nitrosative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 65:1174–1194
El-Baky AA, Abdullah A, Abd-El Hay E (2009) Amelioration of iron-overload adverse effect by iron chelator in rats. J Appl Sci Res 5(9):1155–1162
Hershko C (1989) Mechanism of iron toxicity and its possible role in red cell membrane damage. In: Seminars in hematology, vol 4. Elsevier, pp 277–285
Lubos E, Loscalzo J, Handy DE (2011) Glutathione peroxidase-1 in health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 15(7):1957–1997
Naik SR, Thakare VN, Patil SR (2011) Protective effect of curcumin on experimentally induced inflammation, hepatotoxicity and cardiotoxicity in rats: evidence of its antioxidant property. Exp Toxicol Pathol 63(5):419–431
Ozkan A, Sen HM, Sehitoglu I, Alacam H, Guven M, Aras AB, Akman T, Silan C, Cosar M, Karaman HIO (2015) Neuroprotective effect of humic acid on focal cerebral ischemia injury: an experimental study in rats. Inflammation 38(1):32–39
Li J-M, Gall NP, Grieve DJ, Chen M, Shah AM (2002) Activation of NADPH oxidase during progression of cardiac hypertrophy to failure. Hypertension 40(4):477–484
Jensen PD, Jensen FT, Christensen T, Nielsen JL, Ellegaard J (2003) Relationship between hepatocellular injury and transfusional iron overload prior to and during iron chelation with desferrioxamine: a study in adult patients with acquired anemias. Blood 101(1):91–96
Gao Y, Wang N, Zhang Y, Ma Z, Guan P, Ma J, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Wang J, Zhang J (2013) Mechanism of protective effects of Danshen against iron overload-induced injury in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 145(1):254–260
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cagin, Y.F., Sahin, N., Polat, A. et al. The Acute Effect of Humic Acid on Iron Accumulation in Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 171, 145–155 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0507-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0507-0