Abstract
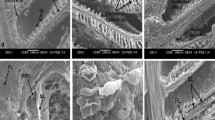
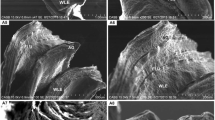
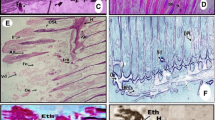
Surface ultrastructure of the gill and liver of 3-month-old Asian sea bass, Lates calcarifer, after copper exposure, was investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Fish samples were exposed to copper concentrations of 6.83 and 13.66 ppm (sublethal) for 28 days with parallel untreated control. These structures showed structural modifications in both low and high concentrations of copper exposure. Oedema, hyperplasia, desquamation, necrosis, epithelial lifting, lamellar fusion, collapsed secondary lamellae, curling of secondary lamellae and aneurism in the secondary lamellae were observed in gill tissues exposed to copper. Hepatic lesions related to cloudy swelling of hepatocytes, congestion, vacuolar degeneration, dilation of sinusoids and nuclear hypertrophy were evident in the exposed sea bass liver tissue.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batley GE, Apte S (1995) Trace metal speciation of labile chemical species in natural waters and sediments: non-electrochemical approaches. In: Tessier A, Turner D (eds) Metal speciation and bioavailability in aquatic systems. Wiley, New York
Straus DL, Tucker CS (1993) Acute toxicity of copper sulfate and chelated copper to channel cat fish Ictalurus punctatus. J World Aqu Soc 24:390–395
Heo GJ (1997) Antibacterial efficacy and safety of copper sulfate pentahydrate to cultured fish. Korean J Vet Res 37:203–212
Taylor LN, Mc Geer JC, Wood CM, Mc Donald DG (2000) Physiological effects of chronic copper exposure to rainbow trout (Oncorhychus mykiss) in hand and soft water, evaluation of chronic indicators. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2298–2308
Lodhi HS, Khan MA, Verma RS, Sharma UD (2006) Acute toxicity of copper sulphate to fresh water prawns. J Environ Biol 27:585–588
Van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57–149
Alazemi BM, Lewis JW, Andrews EB (1996) Gill damage in the fresh water fish Gnathonemus petersii (family, Mormyridae) exposed to selected pollutants: an ultrastructural study. Environ Technol 17:225–238
Braunbeck T (1998) Cytological alterations in fish hepatocytes following in vivo and in vitro sublethal exposure to xenobiotics structural biomarkers of environmental contamination. In: Braunbeck T, Streit B, Hinton DE (eds) Fish ecotoxicology. Birkhauser Verlag, Switzerland, pp 61–140
Bernet D, Schmidt H, Meier W, Brkhardt-Holm P, Wahli T (1999) Histopathology in fish: proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. J Fish Dis 22:25–34
Au DWT (2004) The application of histocytopathological biomarkers in marine pollution monitoring: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 48:817–834
Roberts JR (1978) The pathophysiology and systematic pathology of teleosts. In fish pathology. 1st ed. Bailliere Tindall, London 67–70
Evans DH (1987) The fish gill: site of action and model for toxic effects of environmental pollutant. Environ Heal Perspect 71:47–58
Lindesjoo E, Thulin J (1994) Histopathology of skin and gills of fish in pulp mill effluents. Dis Aqua Org 18:81–93
Karan V, Vitorovic S, Tutundzic V, Poleksic V (1998) Functional enzyme activity and gill histology of carp after copper sulfate exposure and recovery. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 40:49–55
Oliveira Ribeiro CA, Vollaire Y, Sanchez-Chardi A, Roche H (2005) Bioaccumulation and the effects of organochlorine pesticides, PAH and heavy metals in the eel (Anguilla anguilla) at the Camargue Nature Reserve, France. Aquat Toxicol 74:53–69
Maharajan A, Rajalakshmi S, Vijayakumaran M, Kumarasamy P (2012) Sublethal effect of copper toxicity against histopathological changes in the spiny lobster, Panulirus homarus (Linnaeus, 1758). Biol Tra Ele Rese 145:201–210
Arellano JM, Storch V, Sarasquete C (2004) Ultrastructural and histochemical study on gills and skin of the Senegal sole, Solea senegalensis. J Appl Ichthyol 20:452–460
Evans DH, Piermarini PM, Choe KP (2005) The multifunctional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid–base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol Rev 85:97–177
Vigliano FA, Aleman N, Quiroga MI, Nieto JM (2006) Ultrastructural characterization of gills in juveniles of the Argentinian Silverside, Odontesthes bonariensis (Valenciennes, 1835) (Teleostei: Atheriniformes). Anat Histol Embryol 35:76–83
Zeeman MG, Brindley WA (1981) Effects of toxic agents upon fish immune systems: a review. In: Sharma RP (ed) Immunologic considerations in toxicology. CRC Press/Lewis Publisher, Boca Raton, pp 1–60
Schwaiger J, Wanke R, Adam S, Pawert M, Honnen W, Triebskorn R (1997) The use of histopathological indicators to evaluated contaminant-related stress in fish. J Aqua Ecosyst Str Recov 6:75–86
Teh SJ, Adams SM, Hinton DE (1997) Histopathological biomarkers in feral fresh water fish populations exposed to different types of contaminant stress. Aquat Toxicol 37:51–70
Chambers JE, Yarbrough JD (1976) Xenobiotic transformation systems in fishes. Comp Biochem Physiol 55C:77–84
Statham CN, Croft WA, Lech JJ (1978) Uptake, distribution, and effects of carbon tetrachloride in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 45:131–140
Racicot CG, Gaudet M, Leray C (1975) Blood and liver enzymes in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) with emphasis on their diagnostic use study of CCl4 toxicity and a case of Aeromonas infection. J Fish Biol 7:825–835
Gingerich WH, Weber LJ, Larson RE (1978) Carbontetrachloride-induced retention of sulfobromophthalein in the plasma of rainbow trout. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 43:147–158
Gingerich WH (1982) Hepatic toxicology of fishes. In: Weber LJ (ed) Aquatic toxicology. Raven, New York, pp 55–105
Buck WB (1978) Copper/molybdenum toxicity in animals. In: Oehme FW (ed) Toxicity of heavy metals in the environment. Marcel Dekker, Inc, New York, pp 491–515, Part I
Buckley LA, Jiang XZ, James RA, Morgan KT, Barrow CS (1982) Respiratory tract lesions induced by sensory irritants at the RD50 concentration. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 74:417–429
Shearer KD (1984) Changes in elemental composition of hatchery reared rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri, associated with growth and reproduction. Can J Fish Aqua Sci 41:1592–1600
Li J, Quabius SE, Wendelaar Bong SE, Flick G, Lock RAC (1998) Effects of waterborne copper on branchial chloride cells and Na+/K+-ATPase activities in Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Aquat Toxicol 43:1–11
Dang Z, Lock R, Flik G, Wendelaar Bonga SE (2000) Na+/ K+- ATPase immuno reactivity in branchial chloride cells of Oreochromis mossambicus exposed to copper. J Exp Bio 203:379–387
Monteiro SM, Rocha E, Fontaínhas-Fernandes AA, Sousa M (2008) Quantitative histopathology of Oreochromis niloticus gills after copper exposure. J Fish Biol 73:1376–1392
Monteiro SM, Rocha E, Mancera JM, Fontaínhas- Fernandes AA, Sousa M (2009) A stereological study of copper toxicity in gills of Oreochromis niloticus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:213–223
Monteiro SM, Rocha E, Mancera JM, Fontaínhas- Fernandes AA, Sousa M (2009) Copper toxicity in gills of the teleost fish, Oreochromis niloticus: effects in apoptosis induction and cell proliferation. Aquat Toxicol 94:219–228
Muthuwan V (1998) Green water recirculation system for intensive marine shrimp culture. PhD thesis, School of environmental, resource and development, Asian Institute of Technology 91–120
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Pollution Control Federation, Washington, D.C
Pawert M, Mu¨ller E, Triebskorn R (1998) Ultrastructural changes in fish gills as biomarker to assess small stream pollution. Tissue Cell 30(6):617–626
Thophon S, Kruatrache M, Upatham ES, Pokethitiyook S, Sahaphong P, Jaritkhuan S (2003) Histopathological alterations of white sea bass Lates calcarifer, in acute and subchronic cadmium exposure. Environ Pollut 121:307–320
Mallatt J (1985) Fish gill structural changes induced by toxicants and other irritants, a statistical review. Can J Fish Aqua Sci 42:630–648
Global Tox A (1997) Technical evaluation of histopathology as an environmental monitoring tool for the mining industry in Canada. Report prepared for Aquatic Effects Technology Evaluation (AETE) Program, Ottawa. 1997, Natural Resources Canada by Global Tox International Consultants Inc. 153
Jiraung Koorskul W, Upatham ES, Kruatrachue M, Vichasrigrams S, Pokelhitiyook P (2003) Biochemical and histopathological effects of glyphosate herbicide on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Environ Toxicol 18(4):260–267
Dezfuli BS, Simoni E, Giari L, Manera M (2006) Effects of experimental terbuthylazine exposure on the cells of Dicentrarchus labrax (L.). Chemistry 64:1684–1694
Giari L, Manera M, Simoni E, Dezfuli BS (2007) Cellular alterations in different organs of European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax (L.) exposed to cadmium. Chemistry 67(6):1171–1181
Mauceri A, Fossi MC, Leonzio C, Ancora S, Minniti F, Malsano M, Lo Cascio P, Ferrando S, Fasulo S (2005) Stress factors in the gills of (Mugilidae, Teleosts) living in polluted environments. Ital J Zool 72:285–293
Jagoe CH, Faivre A, Newman MC (1996) Morphological and morphometric changes in the gills of mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) after exposure to mercury. Aquat Toxicol 34:163–183
Oransaye JAO, Brafield AE (1984) The effect of dissolved cadmium on the chloride cells of the gills of the stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus L. J Fish Biol 25:253–258
Gill TS, Pant JC, Pant J (1988) Gill, liver and kidney lesions associated with experimental exposures to carbaryl and dimethoate in the fish (Puntius conchonius Ham). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 41:71–78
Fu H, Steinbach OM, Van den Hamer CJA, Balm PHM, Lock RAC (1990) Involvement of cortisol and metallothionein like proteins in the physiological responses to tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) to sublethal cadmium stress. Aquat Toxicol 16:257–270
Bradbury L (1987) British Columbia: metropolis and hinterland in microcosm. In: McCann LD (ed) Heartland and hinterland: a geography of Canada. Prentice-Hall Canada Inc, Scarborough, pp 400–441
Wise ML, Stiebel CL, Grizzp JM (1987) Acute toxicity of nitrofurazone to channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus and gold fish Carassius auratus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 38:42–46
Dutta HM (1997) A composite approach for evaluation of the effect of pesticides on fish. In: Munshi JSD, Dutta HM (eds) Fish morphology: horizon of new research. Sci Pub Inc, USA, pp 249–277
Hemalatha S, Banerjee TK (1997) Histopathological analysis of sublethal toxicity of zinc chloride to the respiratory organs of the air-breathing cat fish Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch). Biol Res 30:11–21
Handy RD, Eddy FB (1991) The absence of mucus on the secondary lamellae of unstressed rainbow trout. Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Biol 38(1):153–155
Mazon AF, Cerqueira CCC, Monteiro EAS, Fernandes MN (1999) Acute copper exposure in freshwater fish: morphological and physiological effects. In: Val AL, Almeida-Val VMF (eds) Biology of tropical fishes. INPA, Manaus, pp 263–275
Powell MD, Speare DJ, Burka JF (1992) Fixation of mucous on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) gills for light and electron microscopy. J Fish Biol 41:813–824
Braunbeck T, Volkl A (1991) Induction of biotransformation in the liver of eel (Anguilla anguilla L.) by sublethal exposure to dinitro-o-cresol: ultrastructural and biochemical study. Ecotoxi Environ Saf 21:109–127
Al-Bairuty GA, Shaw BJ, Handy RD, Henry TB (2013) Histopathological effects of waterborne copper nanoparticles and copper sulphate on the organs of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aqua Toxicol 126:104–115
Hinton DE, Lauren DJ (1990) Liver structural alterations accompanying chronic toxicity in fishes potential biomarkers of exposure. In: McCarthy JF, Shugart LR (eds) Biomarkers of environmental contamination. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 17–57
Franchini A, Barbanti E, Bolognani Fantin AM (1991) Effects of lead on hepatocyte ultrastructure in Carassius carassius (L.) var.auratus. Tiss Cell 23(6):893–901
Thophon S, Pokethitiyook P, Chalermwat K, Upatham ES, Sahaphong S (2004) Ultrastructural alterations in the liver and kidney of white sea bass, Lates calcarifer, in acute and subchronic cadmium exposure. Environ Toxicol 19(1):11–19
Ezhilmathy R, Rajalakshmi K, Chezhian A (2014) Histological alterations in sea bass. Lates calcarifer exposed to combined stressors of pesticide and metal (Profenofos and lead nitrate). Inter J Rese Mar Sci 3(2):44–47
Cheville NF (1994) Ultrastructural pathology: an introduction to interpretation, 1st edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames, pp 67–68
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paruruckumani, P.S., Maharajan, A., Ganapiriya, V. et al. Surface Ultrastructural Changes in the Gill and Liver Tissue of Asian Sea Bass Lates calcarifer (Bloch) Exposed to Copper. Biol Trace Elem Res 168, 500–507 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0370-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0370-z