Abstract
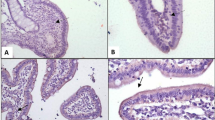
The effects of oral supplementation of chromium picolinate (CrPic) on various blood parameters and their possible toxicity on the liver, kidneys, lungs, heart, and testis were investigated. Twenty-four Santa Inês (SI) lambs were treated with four different concentrations of CrPic (six animals/treatment): placebo, 0.250, 0.375, and 0.500 mg CrPic/animal/day for 84 days. The basal diet consisted of hay Panicum maximum cv Massai and concentrate. Blood and serum were collected fortnightly for analysis. On day 84, the animals were euthanized, and histopathological analysis in the liver, kidney, heart, lung, and testis was made. The liver and kidney were also submitted to electronic microscopy analysis. Differences between treatments (P < 0.05) were observed for packed cell volume (day 84), hemoglobin (day 84), total plasm protein (day 56 and day 84), and triglycerides (day 70). There was no statistically significant relationship between Cr supplementation and histopathology findings, although some animals treated with supplementary Cr showed morphological changes in the liver, kidney, and testis. Thus, the effectiveness of supplementation with Cr remains in doubt as to its physiological action and toxicity in sheep.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grant RS, Coggan SE, Smythe GA (2009) The physiological action of picolinic acid in the human brain. Int J Tryptophan Res IJTR 2:71–79
Di Bona KR, Love S, Rhodes NR, McAdory D, Sinha SH, Kern N, Kent J, Strickland J, Wilson A, Beaird J, Ramage J, Rasco JF, Vincent JB (2011) Chromium is not an essential trace element for mammals: effects of a “low-chromium” diet. J Biol Inorg Chem 16(3):381–390. doi:10.1007/s00775-010-0734-y
Anderson RA (1987) Chromium. In: Mertz E (ed) Trace elements in human and animal nutrition, 1st edn. Academic, New York, pp 225–244
Merrill JC, Morton JJP, Soileau SD (2001) Metals. In: Hayes AW (ed) Principles and methods of toxicology, 4th edn. Taylor & Francis, Boston, pp 649–698
Hodgson E, Cope WG, Leidy RB (2004) Classes of toxicants: use classes. In: Hodgson E (ed) A textbook of modern toxicology, 3rd edn. Wiley-Interscience, New Jersey, pp 49–74
Klaassen CD (2006) Metais pesados e antagonistas dos metais pesados. In: Brunton LL, Lazo JS, Parker KL (eds) Goodman & Gilman: As Bases Farmacológicas da Terapêutica, 11ªth edn. McGraw-Hill, Rio de Janeiro, pp 1585–1605
Stoecker BJ (2006) Chromium. In: Shils ME, Shike M, Ross AC, Caballero B, Cousins RL (eds) Modern nutrition in health and disease, 10th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 332–337
Speetjens JK, Collins RA, Vincent JB, Woski SA (1999) The nutritional supplement chromium(III) tris(picolinate) cleaves DNA. Chem Res Toxicol 12(6):483–487. doi:10.1021/tx9900167
Subramanian S, Rajendiran G, Sekhar P, Gowri C, Govindarajulu P, Aruldhas MM (2006) Reproductive toxicity of chromium in adult bonnet monkeys (Macaca radiata Geoffrey). Reversible oxidative stress in the semen. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 215(3):237–249. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2006.03.004
Stearns DM, Silveira SM, Wolf KK, Luke AM (2002) Chromium(III) tris(picolinate) is mutagenic at the hypoxanthine (guanine) phosphoribosyltransferase locus in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mutat Res 513(1–2):135–142
Dallago BS, McManus CM, Caldeira DF, Lopes AC, Paim TP, Franco E, Borges BO, Teles PH, Correa PS, Louvandini H (2011) Performance and ruminal protozoa in lambs with chromium supplementation. Res Vet Sci 90(2):253–256. doi:10.1016/j.rvsc.2010.06.015
Dallago B, McManus C, Caldeira DF, Campeche A, Burtet RT, Paim T, Gomes EF, Branquinho R, Braz S, Louvandini H (2013) Humoral and cellular immunity in chromium picolinate-supplemented lambs. Biol Trace Elem Res 154(2):196–201. doi:10.1007/s12011-013-9731-7
Souza CE, Araujo AA, Oliveira JT, Lima Souza AC, Neiva JN, Moura AA (2010) Reproductive development of Santa Ines rams during the first year of life: body and testis growth, testosterone concentrations, sperm parameters, age at puberty and seminal plasma proteins. Reprod Domest Anim Zuchthygiene 45(4):644–653. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0531.2008.01322.x
Aguiar GV, Araújo AA, Moura AAA (2006) Desenvolvimento testicular, espermatogênese e concentrações hormonais em touros Angus. Rev Bras Zootec 35:1629–1638
Klaassen CD (2001) Casarett and Doull’s toxicology: the basic science of poisons, 6th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Program NT (2008) Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of chromium picolinate monohydrate in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice. NIH, Research Triangle Park
Anderson RA, Bryden NA, Polansky MM (1997) Lack of toxicity of chromium chloride and chromium picolinate in rats. J Am Coll Nutr 16(3):273–279
Derelanko MJ, Rinehart WE, Hilaski RJ, Thompson RB, Loser E (1999) Thirteen-week subchronic rat inhalation toxicity study with a recovery phase of trivalent chromium compounds, chromic oxide, and basic chromium sulfate. Toxicol Sci Off J Soc Toxicol 52(2):278–288
Hepburn DD, Vincent JB (2002) In vivo distribution of chromium from chromium picolinate in rats and implications for the safety of the dietary supplement. Chem Res Toxicol 15(2):93–100
Kaneko JJ, Harvey JW, Bruss ML (2008) Clinical biochemistry of domestic animals, 6th edn. Academic, San Diego
Jain NC (1993) Essentials of veterinary hematology. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia
Wood JD, Enser M, Fisher AV, Nute GR, Richardson RI, Sheard PR (1999) Manipulating meat quality and composition. Proc Nutr Soc 58(02):363–370. doi:10.1017/S0029665199000488
Thrall MA (2007) Hematologia e Bioquímica Clínica Veterinária, 1ªth edn. Roca, São Paulo
Zanetti MA, Salles MSV, Brisola ML, César MC (2003) Desempenho e resposta metabólica de bezerros recebendo dietas suplementadas com cromo. Rev Bras Zootec 32:1532–1535
Pechova A, Pavlata L (2007) Chromium as an essential nutrient: a review. Vet Med 52:1–18
Uyanik F (2001) The effects of dietary chromium supplementation on some blood parameters in sheep. Biol Trace Elem Res 84(1–3):93–101. doi:10.1385/BTER:84:1-3:093
Zhou BR, Wang HW, Luo GY, Niu RY, Wang JD (2013) Effect of dietary yeast chromium and L-carnitine on lipid metabolism of sheep. Biol Trace Elem Res 155(2):221–227. doi:10.1007/s12011-013-9790-9
Kitchalong L, Fernandez JM, Bunting LD, Southern LL, Bidner TD (1995) Influence of chromium tripicolinate on glucose metabolism and nutrient partitioning in growing lambs. J Anim Sci 73(9):2694–2705
Swanson KC, Harmon DL, Jacques KA, Larson BT, Richards CJ, Bohnert DW, Paton SJ (2000) Efficacy of chromium-yeast supplementation for growing beef steers. Anim Feed Sci Tech 86(1–2):95–105. doi:10.1016/S0377-8401(00)00142-5
Lefavi RG, Wilson GD, Keith RE, Anderson RA, Blessing DL, Hames CG, Mcmillan JL (1993) Lipid-lowering effect of a dietary chromium. 3. Nicotinic-acid complex in male-athletes. Nutr Res 13(3):239–249. doi:10.1016/S0271-5317(05)80421-X
Anderson RA (1995) Chromium, glucose tolerance, diabetes and lipid metabolism. J Adv Med 8:37–49
Sano H, Kato Y, Takebayashi A, Shiga A (1999) Effects of supplemental chromium and isolation stress on tissue responsiveness and sensitivity to insulin in sheep. Small Rumin Res 33(3):239–246. doi:10.1016/S0921-4488(99)00026-7
Vincent JB (2000) The biochemistry of chromium. J Nutr 130(4):715–718
Levina A, Lay PA (2008) Chemical properties and toxicity of chromium(III) nutritional supplements. Chem Res Toxicol 21(3):563–571. doi:10.1021/tx700385t
Russell KE, Roussel AJ (2007) Evaluation of the ruminant serum chemistry profile. Vet Clin N Am Food Anim Pract 23(3):403–426. doi:10.1016/j.cvfa.2007.07.003
Forbes CD, Fernandez JM, Bunting LD, Southern LL, Thompson DL, Gentry LR, Chapa AM (1998) Growth and metabolic characteristics of Suffolk and Gulf coast native yearling ewes supplemented with chromium tripicolinate. Small Rumin Res 28(2):149–160. doi:10.1016/S0921-4488(97)00078-3
Kegley EB, Spears JW (1999) Chromium and cattle nutrition. J Trace Elem Exp Med 12(2):141–147. doi:10.1002/(Sici)1520-670x(1999)12:2<141::Aid-Jtra11>3.0.Co;2-H
Mostafa-Tehrani A, Ghorbani G, Zare-Shahneh A, Mirhadi SA (2006) Non-carcass components and wholesale cuts of Iranian fat-tailed lambs fed chromium nicotinate or chromium chloride. Small Rumin Res 63(1–2):12–19. doi:10.1016/j.smallrumres.2005.01.013
Acknowledgments
This work received financial support from CNPq (INCT-Pecuária and Universal), FAP-DF, FINATEC, and CAPES/PROCAD New Frontiers 2007. Special thanks to Laboratory of Electronic Microscopy/UnB, to Professor Sonia Nair Bao, Embrapa-CPAC, Veterinary School/UFMG, and to Professor Roberto Mauricio Carvalho Guedes for their scientific support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dallago, B.S.L., Braz, S., Marçola, T.G. et al. Blood Parameters and Toxicity of Chromium Picolinate Oral Supplementation in Lambs. Biol Trace Elem Res 168, 91–102 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0347-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0347-y