Abstract
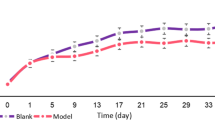
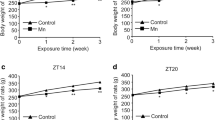
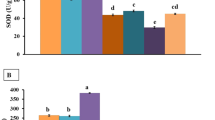
The present study was to evaluate the hepatotoxicity effects in mice exposed to copper (Cu) used as dietary supplements for 95 days. Cu-treated mice showed increased body weight, and no toxic symptoms were observed at the beginning, but the tendency gradually changed with progress of experiment. In the liver, beneficial metals [Cu, iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), and molybdenum (Mo)] were analyzed by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. The content of Cu maintained at the same level during the experiments, but not resulting in the imbalance of Fe, Zn, Mn, and Mo being distributed. The activities of alkaline phosphatase (AKP) and super oxidation dismutase (SOD) showed significantly improvement during the first 30 days in Cu-supplemented group (P < 0.01) but declined rapidly from 30th to 60th days, and later, they stabilized and were not statistically significant compared with control (P > 0.05). No statistically significant correlation of ceruloplasmin (CPL) activity was appreciated during the experiment. The histopathological and ultrastructural abnormalities changes were observed in the liver of mice including vacuolar degeneration, necrosis, karyorrhexis, and endolysis. Many hepatocytes showed increased collagenic fibers, appearance of triglyceride droplets, and swollen mitochondria due to oral route of copper, which may lead to lipid peroxidation and free radicals. In conclusion, our study showed that exposure to copper influenced behavioral pattern and body weight, affected several enzymatic activities, and led to the physiological and considerable structural changes in the liver of mice. The public should pay more attention to avoid being exposed to copper.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pan K, Wang WX (2012) Trace metal contamination in estuarine and coastal environments in China. Sci Total Environ 421–422:3–16
NBSC (National Bureau of Statistics of China) (2012) China statistical yearbook 2012. China Statistic Press, Beijing
Chen Y, Ebenstein A, Greenstone M, Li H (2013) Evidence on the impact of sustained exposure to air pollution on life expectancy from China’s Huai River policy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:12936–12941
Yang G, Wang Y, Zeng Y, Gao GF, Liang X, Zhou M, Wan X, Yu S, Jiang Y, Naghavi M, Vos T, Wang H, Lopez AD, Murray CJ (2013) Rapid health transition in China, 1990–2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 381:1987–2015
Chen Z, Wang JN, Ma GX, Zhang YS (2013) China tackles the health effects of air pollution. Lancet 382:1959–1960
Yuan CG, Shi JB, He B, Liu JF, Liang LN, Jiang GB (2004) Speciation of heavy metals in marine sediments from the East China Sea by ICP–MS with sequential extraction. Environ Int 30:769–783
Wang CY, Wang XL (2007) Spatial distribution of dissolved Pb, Hg, Cd, Cu and As in the Bohai Sea. J Environ Sci (China) 19:1061–1066
Zhang L, Ye X, Feng H, Jing Y, Ouyang T, Yu X, Liang R, Gao C, Chen W (2007) Heavy metal contamination in western Xiamen Bay sediments and its vicinity, China. Mar Pollut Bull 54:974–982
Pytharopoulou S, Grintzalis K, Sazakli E, Leotsinidis M, Georgiou CD, Kalpaxis DL (2011) Translational responses and oxidative stress of mussels experimentally exposed to Hg, Cu and Cd: one pattern does not fit at all. Aquat Toxicol 105:157–165
Stef DS, Gergen I (2012) Effect of mineral-enriched diet and medicinal herbs on Fe, Mn, Zn, and Cu uptake in chicken. Chem Cent J 6:19
Castillo-Durán C, Cassorla F (1999) Trace minerals in human growth and development. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 12:589–601
Franco R, Sánchez-Olea R, Reyes-Reyes EM, Panayiotidis MI (2009) Environmental toxicity, oxidative stress and apoptosis: ménage à trois. Mutat Res 674:3–22
Gaetke LM, Chow CK (2003) Copper toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidant nutrients. Toxicology 189:147–163
Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ (2002) Cellular response to oxidative stress: signaling for suicide and survival. J Cell Physiol 192:1–15
Huster D, Lutsenko S (2007) Wilson disease: nor just a copper disorder. Analysis of a Wilson disease model demonstrates the link between copper and lipid metabolism. Mol Biosyst 3:816–824
Wang H, Liu Y, Qi Z, Wang S, Liu S, Li X, Wang H, Wang X, Xia X, Zhu X (2014) The estimation of soil trace elements distribution and soil–plant–animal continuum in relation to trace elements status of sheep in Huangcheng area of Qilian mountain grassland, China. J Integ Agri 13:140–147
Araya M, Núñez H, Pavez L, Arredondo M, Méndez M, Cisternas F, Pizarro F, Sierralta W, Uauy R, González M (2012) Administration of high doses of copper to capuchin monkeys does not cause liver damage but induces transcriptional activation of hepatic proliferative responses. J Nutr 142:233–237
Liu X, Zuo N, Guan H, Han C, Xu SW (2013) Manganese-induced effects on cerebral trace element and nitric oxide of Hyline cocks. Biol Trace Elem Res 54:202–209
Sierralta WD (2001) Immunoelectron microscopy in embryos. Methods 24:61–69
Fry RS, Spears JW, Lloyd KE, O’Nan AT, Ashwell MS (2013) Effect of dietary copper and breed on gene products involved in copper acquisition, distribution, and use in Angus and Simmental cows and fetuses. J Anim Sci 91:861–871
Eybl V, Kotyzová D (2010) Protective effect of manganese in cadmium-induced hepatic oxidative damage, changes in cadmium distribution and trace elements level in mice. Interdiscip Toxicol 3:68–72
Villalobos V, Castro F, Bonilla E, Estévez J, Dávila JO (1994) Manganese toxicity: muscarinic receptor binding in the mouse brain. J Toxicol Environ Health 42:185–191
Zhou C, Liu B, Ge X, Xie J, Xu P (2013) Effect of dietary carbohydrate on the growth performance, immune response, hepatic antioxidant abilities and heat shock protein 70 expression of Wuchang bream, Megalobrama amblycephala. J Appl Ichthyol 29:1348–1356
Zhou Y, Diao QY, Tu Y, Yun Q (2010) Effects of yeast β-glucan on growth performance, serum biochemical and gastrointestinal characteristics in pre-ruminant calves. Chin J Anim Sci 46:47–51
Sarlin PJ, Philip R (2011) Efficacy of marine yeasts and baker’s yeast as immunostimulants in Fenneropenaeus indicus: a comparative study. Aquaculture 321:173–178
Ostrakhovitch EA, Lordnejad MD, Schliess F, Sies H, Klotz LO (2002) Copper ions strongly activate the phosphoinositide–3–kinase/Akt pathway independent of the generation of reactive oxygen species. Arch Biochem Biophys 397:232–239
Boveris A, Musacco-Sebio R, Ferrarotti N, Saporito-Magriñá C, Torti H, Massot F, Repetto MG (2012) The acute toxicity of iron and copper: biomolecule oxidation and oxidative damage in rat liver. J Inorg Biochem 116:63–69
Arnal N, de Alaniz MJ, Marra CA (2012) Cytotoxic effects of copper overload on human-derived lung and liver cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820:931–939
Wang H, Liu YM, Qi ZM, Wang SY, Liu SX, Li X, Wang HJ, Xia XC (2013) An overview on natural polysaccharides with antioxidant properties. Curr Med Chem 20:2899–2913
Twomey PJ, Viljoen A, House IM, Reynolds TM, Wierzbicki AS (2005) Relationship between serum copper, ceruloplasmin, and non-ceruloplasmin-bound copper in routine clinical practice. Clin Chem 51:1558–1559
Jones DG, Suttle NF (1981) Some effects of copper deficiency on leukocyte function in sheep and cattle. Res Vet Sci 31:151–156
Virit O, Selek S, Bulut M, Savas HA, Celik H, Erel O, Herken H (2008) High ceruloplasmin levels are associated with obsessive compulsive disorder: a case control study. Behav Brain Funct 4:52
Mohan M, Taneja TK, Sahdev S, Mohareer K, Begum R, Athar M, Sah NK, Hasnain SE (2003) Antioxidants prevent UV-induced apoptosis by inhibiting mitochondrial cytochrome c release and caspase activation in Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf9) cells. Cell Biol Int 27:483–490
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516
El-Sayyad HI, Ismail MF, Shalaby FM, Abou-El-Magd RF, Gaur RL, Fernando A, Raj MH, Ouhtit A (2009) Histopathological effects of cisplatin, doxorubicin and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) on the liver of male albino rats. Int J Biol Sci 5:466–473
Liu XJ, Luo Z, Xiong BX, Liu X, Zhao YH, Hu GF, Lv GJ (2010) Effect of waterborne copper exposure on growth, hepatic enzymatic activities and histology in Synechogobius hasta. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1286–1291
Acknowledgments
The financial supports from the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (No. 201303040) and Central Public Interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (No. 1610322013003) are greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xuezhi Wang and Hui Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, H., Li, J. et al. Evaluation of Bioaccumulation and Toxic Effects of Copper on Hepatocellular Structure in Mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 159, 312–319 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9970-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9970-2