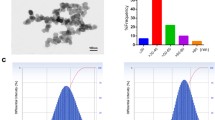
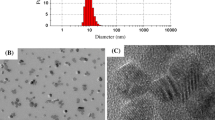
Abstract
The widespread application of lanthanoids (Lns) in manufacturing industries has raised occupational and environmental health concerns about the possible increased health risks to humans exposed to Lns in their working and living environments. Numerous studies have shown that exposures to Ln cause pulmonary injury in animals, but very little is known about the molecular mechanisms of the pulmonary inflammation caused by cerium chloride (CeCl3) exposure. In this study, we evaluated the oxidative stress and molecular mechanism underlying with the pulmonary inflammation associated with chronic lung toxicity in mice treated with nasally instilled CeCl3 for 90 consecutive days. Our findings suggest that significant cerium accumulated in the lung, leading the obvious increase of the lung indices, significant increases in inflammatory cells and levels of lactate dehydrogenase, alkaline phosphate, and total protein, overproduction of reactive oxygen species and peroxidation of lipids, reduced antioxidant capacity, and pulmonary inflammation. CeCl3 exposure also activated nuclear factor κB, increased the expression of tumor necrosis factor α, cyclooxygenase-2, heme oxygenase 1, interleukin 2, interleukin 4, interleukin 6, interleukin 8, interleukin 10, interleukin 18, interleukin 1β, and CYP1A1. However, CeCl3 reduced the expression of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB)-inhibiting factor and heat shock protein 70. These findings suggest that the pulmonary inflammation caused by CeCl3 in mice is closely associated with oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokine expression.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flachowski G (2003) Huhn und Schwein und Seltene Erden. Wirtschaft erleben 1:6–7
Ni JZ (2002) Bioinorganic chemistry of rare earth elements, 2nd edn. Science Press, Beijing, pp 1–5 (in Chinese)
Husain MH, Dick JA, Kaplan YS (1980) Rare earth pneumoconiosis. J Soc Occup Med 30:15–19
Sabbioni E, Pietra R, Gaglione R, Vocaturo G, Colombo E, Zanoni M (1982) Long term occupational risk of rare earth activation pneumoconiosis: a case report as investigated by neutron activated analysis. Sci Total Environ 26:19–32
Sulotto E, Romano C, Berra A, Botta GC, Rubino GE, Sabbioni E, Pietra R (1986) Rare earth pneumoconiosis: a new case. Am J Ind Med 9:567–575
McDonald JW, Ghio AJ, Sheehan CE, Bernhardt PF, Roggli VL (1995) Rare earth (cerium oxide) pneumoconiosis: analytical scanning electron microscopy and literature review. Mod Pathol 8(8):859–865
Porru S, Placidi D, Quarta C, Sabbioni E, Pietra R, Fortaner S (2000) The potential role of rare earths in the pathogenesis of interstitial lung disease: a case report of movie projectionist as investigated by neutron activation analysis. J Trace Elem Med Biol 14:232–236
Takaya M, Toya T, Takata A, Otaki N, Yoshida K, Kohyama N (2006) Biological effects of rare earth oxides to respiratory organs. J Aerosol Res 20:207–212
Zhu WF, Xu SQ, Shao PP, Zhang H, Wu DS, Yang WJ, Feng J (1997) Bioelectrical activity of the central nervous system among populations in a rare earth element area. Biol Trace Elem Res 57(1):71–77
Galle P, Berry JP, Galle C (1992) Role of alveolar macrophages in precipitation of mineral elements inhaled as soluble aerosols. Environ Health Perspect 97:145–147
Kawagoe M, Ishikaw K, Wan SC, Yoshikaw K, Arany S, Zhou XP, Wang JS, Ueno Y, KoizumiY KT, Koyota S, Sugiyam T (2008) Acute effects on the lung and the liver of oral administration of cerium chloride on adult, neonatal and fetal mice. J Trace Elem Med Biol 22:59–65
Windt H, Kock H, Runge F, Hübel U, Koch W (2010) Particle deposition in the lung of the Göttingen minipig. Inhalation Toxicol 22(10):828–834
Geraets L, Oomen AG, Schroeter JD, Coleman VA, Cassee FR (2012) Tissue distribution of inhaled micro- and nano-sized cerium oxide particles in rats: results from a 28-day exposure study. Toxicol Sci 127:463–473
Yoneda S, Emi N, Fujita Y, Ohmichi M, Hirano S, Suzuki KT (1995) Effects of gadolinium chloride on the rat lung following intratracheal instillation. Toxicol Sci 28(1):65–70
Marubashi K, Hirano S, Suzuki KT (1998) Effects of intratracheal pretreatment with yttrium chloride (YCl3) on inflammatory responses of the rat lung following intratracheal instillation of YCl3. Toxicol Lett 99:43–51
Li N, Wang SS, Liu J, Ma LL, Duan YM, Hong FS (2010) The oxidative damage in lung of mice caused by lanthanoide. Biol Trace Elem Res 134:68–78
Haley PJ (1991) Pulmonary toxicity of stable and radioactive lanthanides. Health Phys 61:809–820
Tadao T, Ayako T, Noriko O, Mitsutoshi T, Fumio S, Yasushi S, Mariko O, Katsumi Y, Norihiko K (2005) Chronic pulmonary effects of rare-earth oxides particles instilled intratracheally into rats. Rare Earths 46:84–85
Yoon HK, Moon HS, Park SH, Song JS, Lim Y, Kohyama N (2005) Dendriform pulmonary ossification in patient with rare earth pneumoconiosis. Thorax 60:701–703
Mitsutoshi T, Tadao T, Ayko T, Noriko K, Katsumi Y, Norihiko K (2005) Biological effects of rare earth oxides to respiratory organs. J Aerosol Res 20(3):207–212
Toya T, Takata A, Otaki N, Takaya M, Serita F, Yoshida K, Kohyama N (2010) Pulmonary toxicity induced by intratracheal instillation of coarse and fine particles of cerium dioxide in male rats. Ind Health 48:3–11
Ma JY, Zhao H, Mercer RR, Barger M, Rao M, Meighan T, Schwegler-Berry D, Castranova V, Ma JK (2011) Cerium oxide nanoparticle-induced pulmonary inflammation and alveolar macrophage functional change in rats. Nanotoxicol 5(3):312–325
Srinivas A, Rao PJ, Selvam G, Murthy PB, Reddy PN (2011) Acute inhalation toxicity of cerium oxide nanoparticles in rats. Toxicol Lett 205:105–115
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2008) Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 132:344–362
Karin M, Yamamoto Y, Wang QM (2004) The IKK NF-kappa B system: a treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:17–26
Fei M, Li N, Liu J, Wang SS, Gong XL, Duan YM, Zhao XY, Wang H, Hong FS (2011) The mechanism of liver injury in mice caused by lanthanoids. Biol Trace Elem Res 140(3):317–329
Li N, Cheng J, Cheng Z, Hu RP, Cai JW, Gao GD, Cui YL, Wang L, Hong FS (2013) Molecular mechanism of inflammatory response in mouse liver caused by exposure to CeCl3. Environ Toxicol 28:349–358
Wang XC, Su JJ, Zhu LY, Guan N, Sang XZ, Ze YG, Zhao XY, Sheng L, Gui SX, Sun QQ, Wang L, Hong FS (2013) Hippocampal damage and alterations of inflammatory cytokines expression in mice caused by exposure to cerium chloride. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 64:545–553
Liu J, Li N, Ma LL, Duan YM, Wang J, Zhao XY, Hong FS (2010) Oxidative injury in the mouse spleen caused by lanthanides. J Alloy Compound 489:708–713
Cheng J, Li N, Cheng Z, Hu RP, Cai JW, Si WH, Hong FS (2011) Splenocyte apopotic pathway in mice following exposure to cerium chloride. Chemosphere 8:612–617
Cheng Z, Li N, Cheng J, Hu RP, Gao GD, Cui YL, Gong XL, Wang L, Hong FS (2012) Signal pathway of hippocampal apoptosis and cognitive impairment of mice caused by cerium chloride. Environ Toxicol 27(12):701–717
Zhu WF, Xu SQ, Shao PP, Zhang H, Feng J, Wu DL, Yang WJ (1997) Investigation on intake allowance of rare earth—a study on bio-effect of rare earth in South Jiangxi. Chin Environ Sci 17(1):64–66
Zhang H, Feng J, Zhu WF (1999) Characteristic of rare earth distribution in biologic chains of rare earth-rich background regions. J Rare Earths 17(4):356–358
Chen ZY (1999) Reflection on the biological effects of rare earth and the cumulative impacts of its agricultural application. Rural Eco-Environ 15(3):44–48
Cheng J, Fei M, Sang XZ, Cheng Z, Gui SX, Zhao XY, Sheng L, Sun QQ, Hu RP, Wang L, Hong FS (2012) Gene expression profile in chronic mouse liver injury caused by long-term exposure to CeCl3. Environ Toxicol. doi:10.1002/tox
Sang XZ, Ze X, Gui SX, Wang XC, Hong J, Ze YG, Zhao XY, Sheng L, Sun QQ, Yu XH, Wang L, Hong FS (2013) Kidney injury and alterations of inflammatory cytokine expressions in mice following long-term exposure to cerium chloride. Environ Toxicol. doi:10.1002/tox
Yuan BJ, Liao MY, Li B (2007) Drug toxicological method and technic. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, pp 215–217, Abstract in English
AshaRani PV, Mun GLK, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S (2009) Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. Acs Nano 3:279–290
Tarabishy AB, Aldabagh B, Sun Y, Imamura Y, Mukherjee PK, Lass JH, Ghannoum MA, Pearlman E (2008) MyD88 regulation of Fusarium keratitis is dependent on TLR4 and IL-1R1 but not TLR2. J Immunol 181:593–600
Liu WH, Saint AD (2002) Validation of a quantitative method for real time PCR kinetics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 294:347–353
Park GY, Christman JW (2006) Involvement of cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandins in the molecular pathogenesis of inflammatory lung diseases. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 290:L797–L805
Li N, Wang M, Oberley TD, Sempf JM, Nel AE (2002) Comparison of the pro-oxidative and proinflammatory effects of organic diesel exhaust particle chemicals in bronchial epithelial cells and macrophages. J Immunol 169(8):4531–4541
Zhao HQ, Cheng Z, Hu RP, Cheng J, Hong MM, Zhou M, Gong XL, Wang L, Hong FS (2011) Oxidative injury in the brain of mice caused by lanthanid. Biol Trace Elem Res 142:174–189
Zhao HQ, Cheng J, Cai JW, Cheng Z, Cui YL, Gao GD, Hu RP, Gong XL, Wang L, Hong FS (2012) Liver injury and its molecular mechanisms in mice caused by exposure to cerium chloride. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 62:154–164
Dubois CM, Bissonnette E, Rola-Pleszczynski M (1989) Asbestos fibers and silica particles stimulate rat alveolar macrophages to release tumor necrosis factor. Autoregulatory role of leukotriene B4. Am Rev Respir Dis 139(5):1257–1264
Davis GS, Pfeiffer LM, Hemenway DR (1998) Persistent overexpression of interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in murine silicosis. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 17(2):99–114
Srivastava KD, Rom WN, Jagirdar J, Yie TA, Gordon T, Tchou-Wong KM (2002) Crucial role of interleukin-1beta and nitric oxide synthase in silica-induced inflammation and apoptosis in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165(4):527–533
Israel A, Le Bai O, Hatat D, Piette J, Kieran M, Logeat F, Wallach D, Fellous M, Kourilsky P (1989) TNF stimulates expression of mouse MHC class I genes by inducing an NF kappa B-like enhancer binding activity which displaces constitutive factors. EMBO J 8(12):3793–3800
Osborn L, Kunkel S, Nabel GJ (1989) Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86(7):2336–2340
Piguet PF, Collart MA, Grau GE, Sappino AP, Vassalli P (1990) Requirement of tumour necrosis factor for development of silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Nature 344(6263):245–247
Kida Y, Kobayashi M, Suzuki T, Takeshita A, Okamatsu Y, Hanazawa S, Yasui T, Hasegawa K (2005) Interleukin-1 stimulates cytokines, prostaglandin E2 and matrix metalloproteinase-1 production via activation of MAPK/AP-1 and NF-kappaB in human gingival fibroblasts. Cytokine 29(4):159–168
Brennan P, O'Neil LA (1995) Effects of oxidants and antioxidants on nuclear factor kappa B activation in three different cell lines: evidence against a universal hypothesis involving oxygen radicals. Biochim Biophys Acta 1260(2):167–175
Rahman I, Mulier B, Gilmour PS, Watchorn T, Donaldson K, Jeffery PK, MacNee W (2001) Oxidant-mediated lung epithelial cell tolerance: the role of intracellular glutathione and nuclear factor-kappaB. Biochem Pharmacol 62(6):787–794
Hehner SP, Breitkreutz R, Shubinsky G, Unsoeld H, Schulze-Osthoff K, Schmitz ML, Dröge W (2000) Enhancement of T cell receptor signaling by a mild oxidative shift in the intracellular thiol pool. J Immunol 165(8):4319–4328
Schreck R, Rieber P, Baeuerle PA (1991) Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J 10(8):2247–2258
Janssen-Heininger YM, Macara I, Mossman BT (1999) Cooperativity between oxidants and tumor necrosis factor in the activation of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB: requirement of Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinases in the activation of NF-kappaB by oxidants. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 20(5):942–952
Alessandrini F, Beck-Speier I, Krappmann D, Weichenmeier I, Takenaka S, Karg E, Kloo B, Schulz H, Jakob T, Mempel M, Behrendt H (2009) Role of oxidative stress in ultrafine particle–induced exacerbation of allergic lung inflammation. Am J Resp Critical Care Med 179(11):984–991
58. Lodovici M, Bigagli E (2011) Oxidative stress and air pollution exposure. J Toxicol. 1–9
Beere HM, Wolf BB, Cain K, Mosser DD, Mahboubi A, Mahboubi A, Kuwana T, Tailor P, Morimoto RI, Cohen GM, Green DR (2000) Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol 2:469–475
Li HM, Niki T, Taira T, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Ariga H (2005) Association of DJ-1 with chaperones and enhanced association and colocalization with mitochondrial Hsp70 by oxidative stress. Free Radic Res 39:1091–1099
Hong HN, Kim HN, Park KS, Lee SK, Gu MB (2007) Analysis of the effects diclofenac has on Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) using real-time PCR. Chemosphere 67:2115–2121
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81273036, 30901218), a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, and the “Chun-Tsung scholar” Foundation of Soochow University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jie Hong, Xiaohong Yu, Xiaoyu Pan, and Xiaoyang Zhao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, J., Yu, X., Pan, X. et al. Pulmonary Toxicity in Mice Following Exposure to Cerium Chloride. Biol Trace Elem Res 159, 269–277 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9953-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9953-3