Abstract
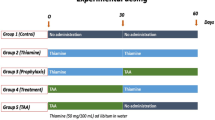
An increase in hepatic iron concentration might exacerbate liver injury. However, it is unknown whether hepatic iron overload may exacerbate acute liver injury from various toxins. Therefore, we evaluated how manipulations to increase hepatic iron concentration affected the extent of acute liver injury from thioacetamide. In this study, we used rats with either “normal” or increased hepatic iron concentration. Iron overload was induced by either providing excess iron in the diet or by injecting iron subcutaneously. Both routes of providing excess iron induced an increase in hepatic iron overload. Meanwhile, the subcutaneous route induced both hepatocellular and sinusoidal cell iron deposition; the oral route induced lesser degree of hepatic iron concentration and only hepatocellular iron overload. Thioacetamide administration to the rats with “normal” hepatic iron concentration induced hepatic cell necrosis and apoptosis associated with a remarkable increase in serum aminotransaminases and depletion of hepatic glutathione and other antioxidative indices. Thioacetamide administration to the iron-overloaded rats exacerbated the extent of liver injury only in the rats orally induced with iron overload. In the rats subcutaneously induced with iron overload, the extent of liver injury from thioacetamide was not different from that observed in the rats with “normal” iron overload. It was concluded that the outcome of thioacetamide-induced acute liver injury may depend on both the level of hepatic iron concentration and on the cellular distribution of iron. While isolated hepatocellular iron overload may exacerbate thioacetamide-induced acute liver injury, a combined hepatocellular and sinusoidal cell iron deposition, even at high hepatic iron concentration, had no such an effect.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galaris D, Pantopoulos K (2008) Oxidative stress and iron homeostasis: mechanistic and health aspects. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 45:1–23
Jomova K, Valko M (2011) Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology 283:65–87
Ishizaka N, Saito K, Noiri E, Sata M, Ikeda H, Ohno A, Ando J, Mori I, Ohno M, Nagai R (2005) Administration of ANG II induces iron deposition and upregulation of TGF-beta1 mRNA in the rat liver. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 288:R1063–R1070
Xiong S, She H, Zhang AS, Wang J, Mkrtchyan H, Dynnyk A, Gordeuk VR, French SW, Enns CA, Tsukamoto H (2008) Hepatic macrophage iron aggravates experimental alcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 295:G512–G521
Uchiyama A, Kim JS, Kon K, Jaeschke H, Ikejima K, Watanabe S, Lemasters JJ (2008) Translocation of iron from lysosomes into mitochondria is a key event during oxidative stress-induced hepatocellular injury. Hepatology 48:1644–1654
Rauen U, Petrat F, Sustmann R, de Groot H (2004) Iron-induced mitochondrial permeability transition in cultured hepatocytes. J Hepatol 40:607–615
Moon MS, Richie JP, Isom HC (2010) Iron potentiates acetaminophen-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in cultured mouse hepatocytes. Toxicol Sci 118:119–127
Pietrangelo A (2004) Hereditary hemochromatosis—a new look at an old disease. N Engl J Med 350:2383–2397
Peretz G, Link G, Pappo O, Bruck R, Ackerman Z (2006) Effect of hepatic iron concentration reduction on hepatic fibrosis and damage in rats with cholestatic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 12:240–245
Ackerman Z, Pappo O, Ben-Dov IZ (2011) The prognostic value of changes in serum ferritin levels during therapy for hepatitis C virus infection. J Med Virol 83:1262–1268
Lambrecht RW, Sterling RK, Naishadham D, Stoddard AM, Rogers T, Morishima C, Morgan TR, Bonkovsky HL (2011) Iron levels in hepatocytes and portal tract cells predict progression and outcomes of patients with advanced chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 140:1490–1500
Dey A, Cederbaum AI (2006) Alcohol and oxidative liver injury. Hepatology 43(2 Suppl 1):S63–S74
Imeryuz N, Tahan V, Sonsuz A, Eren F, Uraz S, Yuksel M, Akpulat S, Ozcelik D, Haklar G, Celikel C, Avsar E, Tozun N (2007) Iron preloading aggravates nutritional steatohepatitis in rats by increasing apoptotic cell death. J Hepatol 47:851–859
O’Brien J, Powell LW (2011) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: is iron relevant? Hep Intl 6:332–341
Otogawa K, Ogawa T, Shiga R, Nakatani K, Ikeda K, Nakajima Y, Kawada N (2008) Attenuation of acute and chronic liver injury in rats by iron-deficient diet. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294:R311–R320
Shapiro H, Ashkenazi M, Weizman N, Shahmurov M, Aeed H, Bruck R (2006) Curcumin ameliorates acute thioacetamide-induced hepatotoxicity. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 21:358–366
Gualdi R, Casalgrandi G, Montosi G, Ventura E, Pietrangelo A (1994) Excess iron into hepatocytes is required for activation of collagen type I gene during experimental siderosis. Gastroenterology 107:1118–1124
Bonkovsky HL (1991) Iron and the liver. Am J Med Sci 301:32–43
Powell EE, Ali A, Clouston AD, Dixon JL, Lincoln DJ, Purdie DM, Fletcher LM, Powell LW, Jonsson JR (2005) Steatosis is a cofactor in liver injury in hemochromatosis. Gastroenterology 129:1937–1943
Pietrangelo A (2007) Hemochromatosis: an endocrine liver disease. Hepatology 46:1291–1301
Valenti L, Fracanzani AL, Bugianesi E, Dongiovanni P, Galmozzi E, Vanni E, Canavesi E, Lattuada E, Roviaro G, Marchesini G, Fargion S (2010) HFE genotype, parenchymal iron accumulation, and liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 138:905–912
Valenti L, Dongiovanni P, Piperno A, Fracanzani AL, Maggioni M, Rametta R, Loria P, Casiraghi MA, Suigo E, Ceriani R, Remondini E, Trombini P, Fargion S (2006) Alpha 1-antitrypsin mutations in NAFLD: high prevalence and association with altered iron metabolism but not with liver damage. Hepatology 44:857–864
Nelson JE, Wilson L, Brunt EM, Yeh MM, Kleiner DE, Unalp-Arida A, Kowdley KV, Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network (2011) Relationship between the pattern of hepatic iron deposition and histological severity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 53:448–457
Wood JC, Aguilar M, Otto-Duessel M, Nick H, Nelson MD, Moats R (2008) Influence of iron chelation on R1 and R2 calibration curves in gerbil liver and heart. Magn Reson Med 60:82–89
Galleano M, Aimo L, Puntarulo S (2002) Ascorbyl radical/ascorbate ratio in plasma from iron overloaded rats as oxidative stress indicator. Toxicol Lett 133:193–201
Torrance JD, Bothwell TH (1968) A simple technique for measuring storage iron concentrations in formalinized liver samples. S Afr J Med Sci 33:9–11
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Gottfried SP, Rosenberg B (1973) Improved manual spectrophotometric procedure for determination of triglycerides. Clin Chem 19:1077–1078
Taylor RP, Broccoli AV, Grisham CM (1978) Enzymatic and colorimetric determination of total serum cholesterol. An undergraduate biochemistry laboratory experiment. J Chem Educ 55:63–64
Baker H, Frank O, DeAngelis B, Feingold S (1980) Plasma tocopherol in man at various times after ingesting free and acetylated tocopherol. Nutr Rep Int 21:531–536
Akerboom TP, Sies H (1981) Assay of glutathione, glutathione disulfide, and glutathione mixed disulfides in biological samples. Methods Enzymol 77:373–382
Gan KN, Smolen A, Eckerson HW, La Du BN (1991) Purification of human serum paraoxonase/arylesterase. Evidence for one esterase catalyzing both activities. Drug Metab Dispos 19:100–106
Beutler E (1975) Glutathione peroxidase. In: Beutler E (ed) Red cell metabolsim: a manual of biochemical methods, 2nd edn. Grune and Strottan, New York, pp 71–73
Carlberg I, Mannervik B (1985) Glutathione reductase. Methods Enzymol 113:484–490
Stookey L (1970) Ferrozine—a new spectrophotometric reagent for iron. Anal Chem 42:779–781
Deugnier YM, Turlin B, Powell LW, Summers KM, Moirand R, Fletcher L, Loréal O, Brissot P, Halliday JW (1993) Differentiation between heterozygotes and homozygotes in genetic hemochromatosis by means of a histological hepatic iron index: a study of 192 cases. Hepatology 17:30–34
Matot I, Cohen K, Pappo O, Barash H, Abramovitch R (2008) Liver response to hemorrhagic shock and subsequent resuscitation: MRI analysis. Shock 29:16–24
Olynyk JK, Clarke SL (2001) Iron overload impairs pro-inflammatory cytokine responses by Kupffer cells. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:438–444
Zhang Y, Crichton RR, Boelaert JR, Jorens PG, Herman AG, Ward RJ, Lallemand F, de Witte P (1998) Decreased release of nitric oxide (NO) by alveolar macrophages after in vivo loading of rats with either iron or ethanol. Biochem Pharmacol 55:21–25
Ledda-Columbano GM, Coni P, Curto M, Giacomini L, Faa G, Oliverio S, Piacentini M, Columbano A (1991) Induction of two different modes of cell death, apoptosis and necrosis, in rat liver after a single dose of thioacetamide. Am J Pathol 139:1099–1109
Sun F, Hayami S, Ogiri Y, Haruna S, Tanaka K, Yamada Y, Tokumaru S, Kojo S (2000) Evaluation of oxidative stress based on lipid hydroperoxide, vitamin C and vitamin E during apoptosis and necrosis caused by thioacetamide in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 500:181–185
Kishioka T, Iida C, Fujii K, Nagae R, Onishi Y, Ichi I, Kojo S (2007) Effect of dimethyl sulphoxide on oxidative stress, activation of mitogen activated protein kinase and necrosis caused by thioacetamide in the rat liver. Eur J Pharmacol 564:190–195
Financial Support
None
Conflict of Interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ackerman, Z., Pappo, O., Link, G. et al. Liver Toxicity of Thioacetamide is Increased by Hepatocellular Iron Overload. Biol Trace Elem Res 163, 169–176 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0110-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0110-9