Abstract
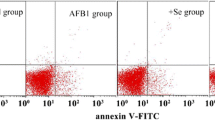
The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) exposure and sodium selenite supplementation on the histology, cell proliferation and cell cycle of jejunum in broilers. A total of 240 1-day-old male AA broilers were divided into four groups of 60 each, fed with basal diet (control group), 0.3 mg/kg AFB1 (AFB1 group), 0.4 mg/kg supplement Se (Se group), and 0.3 mg/kg AFB1 + 0.4 mg/kg supplement Se (AFB1 + Se group) for 21 days, respectively. Compared with the control group, decreased jejunal villus height, villus height/crypt ratio, and proliferation cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)-positive cells, and G2/M phase arrest and shedded epithelial cells on the tip of jejunal villus were observed in AFB1 groups at 7 and 14 days of age. However, the villus/crypt ratio, PCNA-positive cells and cell percentage of G0/G1, S, and G2/M phases had no significant differences between AFB1 group and control group at 21 days. Simultaneous supplementation with sodium selenite restored these parameters to be close to those in control group. In conclusion, 0.3 mg/kg AFB1 in the diet inhibits the development of broiler’s jejunum by reducing cellular proliferation and inducing G2/M arrest during only the first 2 weeks after hatching. Supplementation of dietary sodium selenite at the concentration of 0.4 mg/kg Se had protective action against these toxic effects of AFB1.



Similar content being viewed by others

References
Yunus AW, Razzazi-Fazeli E, Bohm J (2011) Aflatoxin B1 in affecting broiler’s performance, immunity, and gastrointestinal tract: a review of history and contemporary issues. Toxins 3(6):566–590
Hartley RD, Nesbitt BF, O'kelly J (1963) Toxic metabolites of Aspergillus flavus. Nature 198:1056–1058
Jakhar KK, Sadana JR (2004) Sequential pathology of experimental aflatoxicosis in quail and the effect of selenium supplementation in modifying the disease process. Mycopathologia 157(1):99–109
Rawal S, Kim JE, Coulombe JR (2010) Aflatoxin B1 in poultry: toxicology, metabolism and prevention. Res Vet Sci 89(3):325–331
Yunus AW, Ghareeb K, Abd-El-Fattah AAM, Twaruzek M, Bohm J (2011) Gross intestinal adaptations in relation to broiler performance during chronic aflatoxin exposure. Poult Sci 90(8):1683–1689
Guo S, Shi D, Liao S, Su R, Lin Y, Pan J et al (2012) Influence of selenium on body weights and immune organ indexes in ducklings intoxicated with aflatoxin B1. Biol Trace Elem Res 146(2):167–170
Shi D, Guo S, Liao S, Su R, Pan J, Lin Y et al (2012) Influence of selenium on hepatic mitochondrial antioxidant capacity in ducklings intoxicated with aflatoxin B1. Biol Trace Elem Res 145(3):325–329
Wan XL, Yang ZB, Yang WR, Jiang SZ, Zhang GG, Johnston SL et al (2013) Toxicity of increasing aflatoxin B1 concentrations from contaminated corn with or without clay adsorbent supplementation in ducklings. Poult Sci 92(5):1244–1253
Combs GF, Clark LC, Turnbull BW (2001) An analysis of cancer prevention by selenium. Biofactors 14(1–4):153–159
Allan CB, Lacourciere GM, Stadtman TC (1999) Responsiveness of selenoproteins to dietary selenium 1, 2. Annu Rev Nutr 19(1):1–16
Zeng H, Combs JGF (2008) Selenium as an anticancer nutrient: roles in cell proliferation and tumor cell invasion. J Nutr Biochem 19(1):1–7
McKenzie RC, Rafferty TS, Beckett GJ (1998) Selenium: an essential element for immune function. Immunol Today 19(8):342–345
Hoffmann PR, Berry MJ (2008) The influence of selenium on immune responses. Mol Nutr Food Res 52(11):1273–1280
Kumar R, Balachandran C (2009) Histopathological changes in broiler chickens fed aflatoxin and cyclopiazonic acid. Vet Arhiv 79:31–40
Kana JR, Teguia A, Tchoumboue J (2010) Effect of dietary plant charcoal from canarium schweinfurthii Engl. and maize cob on aflatoxin B1 toxicosis in broiler chickens. Adv Anim Biosci 1(2):462–463
Gaikwad SS, Pillai MM (2004) Effect of aflatoxin B1 in gastrointestine of mice. Ecophysiol Occup Health 4:153–159
Fleming SE, Youngman LD, Ames BN (1994) Intestinal cell proliferation is influenced by intakes of protein and energy, aflatoxin, and whole-body radiation. Nutr Cancer 22(1):11–30
Ledoux DR, Rottinghaus GE, Bermudez AJ, Alonso-Debolt M (1999) Efficacy of a hydrated sodium calcium aluminosilicate to ameliorate the toxic effects of aflatoxin in broiler chicks. Poult Sci 78(2):204–210
Applegate TJ, Schatzmayr G, Pricket K, Troche C, Jiang Z (2009) Effect of aflatoxin culture on intestinal function and nutrient loss in laying hens. Poult Sci 88(6):1235–1241
Chen KJ, Shu G, Peng X, Fang J, Cui HM, Chen J et al (2013) Protective role of sodium selenite on histopathological lesions, decreased T-cell subsets and increased apoptosis of thymus in broilers intoxicated with aflatoxin B1. Food Chem Toxicol 59:446–454
Perozo F, Rivera S (2003) Effect of aflatoxin B1 exposure and selenium supplementation on immune response in broilers. Indian Vet J 80(12):1218–1221
Wang FY, Shu G, Peng X, Fang J, Chen KJ, Cui HM et al (2013) Protective effects of sodium selenite against aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in broiler spleen. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10(7):2834–2844
Fang J, Cui HM, Peng X, Chen ZL, He M, Tang L (2011) Developmental changes in cell proliferation and apoptosis in the normal duck thymus. Anat Histol Embryol 40(6):457–465
Chen T, Cui H, Cui Y, Bai C, Gong T, Peng X (2011) Cell-cycle blockage associated with increased apoptotic cells in the thymus of chickens fed on diets high in fluorine. Human Exp Toxicol 30(7):685–692
Zitnan R, Kuhla S, Nurnberg K, Schonhusen U, Ceresnakova Z, Sommer A et al (2003) Influence of the diet on the morphology of ruminal and intestinal mucosa and on intestinal carbohydrase levels in cattle. Vet Med 48(7):177–182
Wang YH, Xu M, Wang FN, Yu ZP, Yao JH, Zan LS et al (2009) Effect of dietary starch on rumen and small intestine morphology and digesta pH in goats. Livest Sci 122(1):48–52
De Conto C, Oevermann A, Burgener IA, Doherr MG, Blum JW (2010) Gastrointestinal tract mucosal histomorphometry and epithelial cell proliferation and apoptosis in neonatal and adult dogs. J Anim Sci 88(7):2255–2264
Kurki P, Vanderlaan M, Dolbeare F, Gray J, Tan EM (1986) Expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)/cyclin during the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res 166(1):209–219
Bravo R, Frank R, Blundell PA, Macdonald-Bravo H (1987) Cyclin/PCNA is the auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase-δ. Nature 326:515–517
Uni Z, Platin R, Sklan D (1988) Cell proliferation in chicken intestinal epithelium occurs both in the crypt and along the villus. J Comp Physiol B 168(4):241–247
Wang L, Li J, Li Q, Zhang J, Duan XL (2003) Morphological changes of cell proliferation and apoptosis in rat jejunal mucosa at different ages. World J Gastroenterol 9(9):2060–2064
Ahnen DJ (1992) Proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression normal, preneoplastic, and neoplastic colonic epithelium of the rat. Gastroenterology 103:160–167
Sarraf CE, Mccormick CSF, Brown GR, Price YE, Hall PA, Lane DP et al (1991) Proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunolocalization in gastro-intestinal epithelia. Digestion 50(2):85–91
Pines J (1995) Cyclins, CDKs and cancer. In: Seminars in cancer biology, 6(2). Academic, London, pp 63-72.
Scott TR, Rowland SM, Rodgers RS, Bodine AB (1991) Genetic selection for aflatoxin B1 resistance influences chicken T-cell and thymocyte proliferation. Dev Comp Immunol 15(4):383–391
Ricordy R, Gensabella G, Cacci E, Augusti-Tocco G (2002) Impairment of cell cycle progression by aflatoxin B1 in human cell lines. Mutagenesis 17(3):241–249
Yang H, Chung DH, Kim YB, Choi YH, Moon Y (2008) Ribotoxic mycotoxin deoxynivalenol induces G2/M cell cycle arrest via p21Cip/WAF1 mRNA stabilization in human epithelial cells. Toxicology 243(1):145–154
Maga G, Hübscher U (2003) Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA): a dancer with many partners. J Cell Sci 116(15):3051–3060
Zeng H (2009) Selenium as an essential micronutrient: roles in cell cycle and apoptosis. Molecules 14(3):1263–1278
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the program for Changjiang scholars and university Innovative Research Team (IRT 0848) and the Education Department of Sichuan Province (2012FZ0066).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Shengqiang Zhang and Xi Peng contributed equally in this study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Peng, X., Fang, J. et al. Effects of Aflatoxin B1 Exposure and Sodium Selenite Supplementation on the Histology, Cell Proliferation, and Cell Cycle of Jejunum in Broilers. Biol Trace Elem Res 160, 32–40 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0009-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0009-5