Abstract
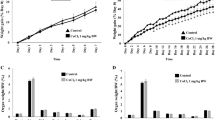
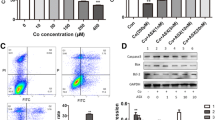
Metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty has been performed with increasing frequency throughout the world, particularly in younger and more active patients, including women of childbearing age. The potential toxicity of cobalt exposure on fetus is concerned since cobalt ions generated by metal-on-metal bearings can traverse the placenta and be detected in fetal blood and amniotic fluid. This study examined the effects of cobalt exposure on early embryonic development and the mechanisms underlying its toxicity. Zebrafish embryos were exposed to a range of cobalt concentrations (0–100 mg/L) between 1 and 144 h postfertilization. The survival and early development of embryos were not significantly affected by cobalt at concentrations <100 μg/L. However, embryos exposed to higher concentrations (>100 μg/L) displayed reduced survival rates and abnormal development, including delayed hatching, aberrant morphology, retarded growth, and bradycardia. Furthermore, this study examined oxidative stress and apoptosis in embryos exposed to cobalt at concentrations of 0–500 μg/L. Lipid peroxidation levels were increased in cobalt-treated embryos at concentrations of 100 and 500 μg/L. The mRNA levels of catalase, superoxide dismutase 2, p53, caspase-3, and caspase-9 genes were upregulated in a dose-dependent manner. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling assays also revealed abnormal apoptotic signals in the brain, trunk, and tail when treated with 500 μg/L cobalt. These data suggest that oxidative stress and apoptosis are associated with cobalt toxicity in zebrafish embryos.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stabler SP, Allen RH (2004) Vitamin B12 deficiency as a worldwide problem. Annu Rev Nutr 24:299–326
Case CP (2001) Chromosomal changes after surgery for joint replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 83(8):1093–1095
Jiang H, Liu F, Yang H, Li Y (2012) Effects of cobalt nanoparticles on human T cells in vitro. Biol Trace Elem Res 146(1):23–29
Olivieri G, Hess C, Savaskan E, Ly C, Meier F, Baysang G, Brockhaus M, Muller-Spahn F (2001) Melatonin protects SHSY5Y neuroblastoma cells from cobalt-induced oxidative stress, neurotoxicity and increased beta-amyloid secretion. J Pineal Res 31(4):320–325
De Boeck M, Kirsch-Volders M, Lison D (2003) Cobalt and antimony: genotoxicity and carcinogenicity. Mutat Res 533(1–2):135–152
Kasten U, Mullenders LH, Hartwig A (1997) Cobalt(II) inhibits the incision and the polymerization step of nucleotide excision repair in human fibroblasts. Mutat Res 383(1):81–89
IARC (2006) Cobalt in hard metals and cobalt sulphate, gallium arsenide, indium phosphide and vanadium pentoxide. In: IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans, vol. 86. Lyon, France
Anissian HL, Stark A, Gustafson A, Good V, Clarke IC (1999) Metal-on-metal bearing in hip prosthesis generates 100-fold less wear debris than metal-on-polyethylene. Acta Orthop Scand 70(6):578–582
Figgitt M, Newson R, Leslie IJ, Fisher J, Ingham E, Case CP (2010) The genotoxicity of physiological concentrations of chromium (Cr(III) and Cr(VI)) and cobalt (Co(II)): an in vitro study. Mutat Res 688(1–2):53–61
Szakmary E, Ungvary G, Hudak A, Tatrai E, Naray M, Morvai V (2001) Effects of cobalt sulfate on prenatal development of mice, rats, and rabbits, and on early postnatal development of rats. J Toxicol Environ Health A 62(5):367–386
Kimmel CB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B, Schilling TF (1995) Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn 203(3):253–310
Garbuz DS, Tanzer M, Greidanus NV, Masri BA, Duncan CP (2010) The John Charnley Award: metal-on-metal hip resurfacing versus large-diameter head metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468(2):318–325
Bozic KJ, Kurtz S, Lau E, Ong K, Chiu V, Vail TP, Rubash HE, Berry DJ (2009) The epidemiology of bearing surface usage in total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91(7):1614–1620
Ziaee H, Daniel J, Datta AK, Blunt S, McMinn DJ (2007) Transplacental transfer of cobalt and chromium in patients with metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty: a controlled study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89(3):301–305
Imanishi T, Hasegawa M, Sudo A (2010) Serum metal ion levels after second-generation metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130(12):1447–1450
Oldenburg M, Wegner R, Baur X (2009) Severe cobalt intoxication due to prosthesis wear in repeated total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 24(5):825.e15, 825.e20
Calabrese EJ, Baldwin LA (2003) Inorganics and hormesis. Crit Rev Toxicol 33(3–4):215–304
Yamagani K (1988) Mechanisms of hatching in fish. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ (eds) Fish physiology, vol. 11a. Academic, New York, pp 447–449
Dave G, Xiu RQ (1991) Toxicity of mercury, copper, nickel, lead, and cobalt to embryos and larvae of zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 21(1):126–134
Naziroglu M (2009) Role of selenium on calcium signaling and oxidative stress-induced molecular pathways in epilepsy. Neurochem Res 34(12):2181–2191
Kovacic P, Somanathan R (2008) Unifying mechanism for eye toxicity: electron transfer, reactive oxygen species, antioxidant benefits, cell signaling and cell membranes. Cell Membr Free Radic Res 1(2):56–69
Ozkaya MO, Naziroglu M (2010) Multivitamin and mineral supplementation modulates oxidative stress and antioxidant vitamin levels in serum and follicular fluid of women undergoing in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril 94(6):2465–2466
Ozkaya MO, Naziroglu M, Barak C, Berkkanoglu M (2011) Effects of multivitamin/mineral supplementation on trace element levels in serum and follicular fluid of women undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF). Biol Trace Elem Res 139(1):1–9
Ray G, Husain SA (2002) Oxidants, antioxidants and carcinogenesis. Indian J Exp Biol 40(11):1213–1232
Pi J, Zhang Q, Fu J, Woods CG, Hou Y, Corkey BE, Collins S, Andersen ME (2010) ROS signaling, oxidative stress and Nrf2 in pancreatic beta-cell function. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 244(1):77–83
Kubrak OI, Husak VV, Rovenko BM, Storey JM, Storey KB, Lushchak VI (2011) Cobalt-induced oxidative stress in brain, liver and kidney of goldfish Carassius auratus. Chemosphere 85(6):983–989
Rodriguez C, Mayo JC, Sainz RM, Antolin I, Herrera F, Martin V, Reiter RJ (2004) Regulation of antioxidant enzymes: a significant role for melatonin. J Pineal Res 36(1):1–9
Christova TY, Gorneva GA, Taxirov SI, Duridanova DB, Setchenska MS (2003) Effect of cisplatin and cobalt chloride on antioxidant enzymes in the livers of Lewis lung carcinoma-bearing mice: protective role of heme oxygenase. Toxicol Lett 138(3):235–242
Fleury C, Petit A, Mwale F, Antoniou J, Zukor DJ, Tabrizian M, Huk OL (2006) Effect of cobalt and chromium ions on human MG-63 osteoblasts in vitro: morphology, cytotoxicity, and oxidative stress. Biomaterials 27(18):3351–3360
Pulido MD, Parrish AR (2003) Metal-induced apoptosis: mechanisms. Mutat Res 533(1–2):227–241
Wolf BB, Green DR (1999) Suicidal tendencies: apoptotic cell death by caspase family proteinases. J Biol Chem 274(29):20049–20052
Masumura M, Hata R, Nishimura I, Uetsuki T, Sawada T, Yoshikawa K (2000) Caspase-3 activation and inflammatory responses in rat hippocampus inoculated with a recombinant adenovirus expressing the Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 80(2):219–227
Araya J, Maruyama M, Inoue A, Fujita T, Kawahara J, Sassa K, Hayashi R, Kawagishi Y, Yamashita N, Sugiyama E, Kobayashi M (2002) Inhibition of proteasome activity is involved in cobalt-induced apoptosis of human alveolar macrophages. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 283(4):L849–L858
Zou W, Zeng J, Zhuo M, Xu W, Sun L, Wang J, Liu X (2002) Involvement of caspase-3 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in cobalt chloride-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. J Neurosci Res 67(6):837–843
Tyner SD, Venkatachalam S, Choi J, Jones S, Ghebranious N, Igelmann H, Lu X, Soron G, Cooper B, Brayton C, Hee Park S, Thompson T, Karsenty G, Bradley A, Donehower LA (2002) p53 mutant mice that display early ageing-associated phenotypes. Nature 415(6867):45–53
Sheikh MS, Fornace AJ Jr (2000) Role of p53 family members in apoptosis. J Cell Physiol 182(2):171–181
Wang T, Chen F, Chen Z, Wu YF, Xu XL, Zheng S, Hu X (2004) Honokiol induces apoptosis through p53-independent pathway in human colorectal cell line RKO. World J Gastroenterol 10(15):2205–2208
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 81171705 and 81101381). The authors would like to thank Jiye He, Xiaoquan Li, Jiwen Bu, Shanye Gu, and Xufei Du for their technical help and writing assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, G., Zhu, J., Shen, C. et al. The Effects of Cobalt on the Development, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis in Zebrafish Embryos. Biol Trace Elem Res 150, 200–207 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-012-9506-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-012-9506-6