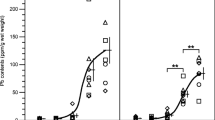
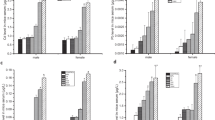
Abstract
Due to increasing applications of lanthanides (Ln) in industry and daily life, numerous studies confirmed that Ln exposure may result in organ damages in mice and rats, while very few studies focused on several organs damages simultaneously. In order to compare the toxicity of Ln on organs, mice were exposed to LaCl3, CeCl3, and NdCl3 of a dose of 20 mg/kg body weight for consecutive 60 days, respectively, then histopathological changes of liver, kidney, and heart, and their function were investigated. The results showed that long-term exposure to Ln caused cell necrosis and basophilia of liver, ambiguity of renal tubule architecture, congestion of blood vessel and capillary of kidney, and heart hemorrhage. The histopathological changes of liver, kidney, and heart in mice caused by Ce3+ was most severe; the effect by Nd3+ was slighter than Ce3+ but more severe than La3+. The assay of serum biochemical parameters suggested that Ln exposure severely impaired the functions of liver, kidney, and myocardium in mice. These findings suggested that long-term exposure to Ln resulted in histopathological changes of liver, kidney, and heart, and their function damages. Therefore, we thought that long-term application of the products containing Ln on human should be cautious.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsuchiya T, Taketsugu T, Nakano H, Hirao K. (1999) Theoretical study of electronic and geometric structures of a series of lanthanide trihalides LnX3 (Ln = La–Lu; X = Cl, F). J Mol Struc-Theochem 203–222.
Ni JZ (2002) Bioinorganic chemistry of rare earth elements. Academic, Beijing (in Chinese)
Arnd V, Horst K (2006) Excited state properties of lanthanide complexes: beyond ff states. Inorg Chim Acta 359:4130–4138
Shimada H, Nagano M, Funakoshi T, Kojima S (1996) Pulmonary toxicity of systemic terbium chloride in mice. J Toxicol Environ Health 48(1):81–92
Zhu WF, Xu SQ, Zhang H, Shao PP, Wu DS, Yang WJ, Feng J (1996) Investigation on the intelligence quotient of children in the areas with high REE background (I)–REE bio-effects in the REE-high areas of southern Jiangxi province. Chin Sci Bull 41:1977–1981
Feng J, Zhang H, Zhu WF, Liu CQ, Xu SQ, Wu DS (2000) Bio-effect of rare earths in RE-high background region I. Some blood biochemical indices from population resided in light REE district. J Rare Earths 18(4):356–358
Clayton TA, Lindon JC, Everett JR, Charuel C, Hanton G, Net JLL, Provost JP, Nicholson JK (2003) An hypothesis for a mechanism underlying hepatotoxin-induced hypercreatinuria. Arch Toxicol 77:208–217
Feng JH, Li XJ, Pei FK, Chen X, Li SL, Nie YX (2002) 1H NMR analysis for metabolites in serum and urine from rats administrated chronically with La(NO3)3. Anal Biochem 301:1–7
Kawagoe M, Hirasawa F, Wang SC, Liu Y, Ueno Y, Sugiyama T (2005) Orally administrated rare earth element cerium induces metallothionein synthesis and increases glutathione in the mouse liver. Life Sci 77:922–937
Wu H, Li XI, Li ZF, Liao PQ, Wu YI, Pei FK (2006) Comparison of biochemical effects induced by “Changle” between male and female rats using NMR and ICP-MS techniques. J Rare Earths 24:108–114
Liu J, Li N, Ma LL, Duan YM, Wang J, Zhao XY, Hong FS (2010) Oxidative injury in the mouse spleen caused by lanthanides. J Alloy Compound 489:708–713
Li N, Wang SS, Liu J, Ma LL, Duan YM, Hong FS (2010) The oxidative damage in lung of mice caused by lanthanides. Biol Trace Elem Res 134:68–78
Fei M, Li N, Liu J, Gong XL, Duan YM, Zhao XY, Wang H, Hong FS (2011) Oxidative stress in the liver of mice caused by lanthanoides. Biol Trace Elem Res 139:72–80
Fei M, Li N, Liu J, Wang SS, Gong XL, Duan YM, Zhao XY, Wang H, Hong FS (2011) The mechanism of liver injury in mice caused by lanthanides. Biol Trace Elem Res 140:317–329
Zhao HQ, Cheng Z, Hu RP, Cheng J, Hong MM, Zhou M, Gong XL, Wang L, Hong FS (2011) Oxidative injury in the brain of mice caused by lanthanides. Biol Trace Elem Res 142:174–189
Zhu WF, Xu SQ, Shao PP, Zhang H, Feng J, Wu DL, Yang WJ (1997) Investigation on intake allowance of rare earth—a study on bio-effect of rare earth in South Jiangxi. Chin Environ Sci 17(1):64–66
Zhang H, Feng J, Zhu WF (1999) Characteristic of rare earth distribution in biologic chains of rare earth-rich background regions. J Rare Earths 17(4):356–358
Chen ZY (1999) Reflection on the biological effects of rare earth and the cumulative impacts of its agricultural application. Rural Eco-Environment 15(3):44–48
Yuan BJ, Liao MY, Li B (2007) Drug toxicological methods and techniques. Chemical Industry, Beijing, pp 215–217 (in Chinese)
Liu Y, Chen D, Chen AJ, Liu B, Sun SY, Nie YX (2001) Subchronic toxicity of lanthanum nitrate on liver of rats. J Chin Rare Earth Soc 19:167–170 (abstract in English)
Shen ZG, Lei HY, Wei Q, Yang XF, Zuang ZX, Yang YS (2001) Effect of Ce3+ on the activities of ATPase of hepatocytes. Chin Rare Earths 22(1):35–37 (abstract in English)
Yang WD, Wang T, Lei HY, Yang YS (1999) Effect of cerium nitrate on the activity of ATPase in rat tissues. J Hyg Res 29(6):329–355 (abstract in English)
Liu C, Hong FS, Zheng L, Tang P, Wang ZG (2004) Effects of rare earth elements on vigor enhancement of aged spinach seeds. J Rare Earths 22:547–551
Xia Q, Chen D, Liu YR, Chen AJ (2006) Effect of mixed rare earth oxide “Changle” on rat liver. Chin Rare Earths 27(3):76–78 (abstract in English)
Wu HF, Zhang XY, Liao PQ, Li ZF, Li WH, Li XJ, Wu YJ, Pei FK (2005) NMR spectroscopic-based metabonomic investigation on the acute biochemical effects induced by Ce(NO3)3 in rats. J Inorg Biochem 99:2151–2160
Tu HM, Yang YS, Li Y, Wang ED (2000) Effect of rare earth ions on kinetic properties of Escherichia coli leucyl-tRNA synthetase. J Rare Earths 18(3):224–228
Arvela P (1979) Toxicity of rare earths. Prog Pharm 2(3):69–112
Lu R, Ni JZ (2002) Mechanism of rare earth effect on liver. J Chin Rare Earth Soc 20(3):193–198 (abstract in English)
Grajewski O, Lehmann BV, Arntz HR, Arvela P, Oberdiss E (1977) Alteration of rat serum lipoproteins and lecithin-cholesterol-acyltransferase activity in praseodymium-induced liver damage. N-S Arch Pharm 301(1):65–73
Glenn JL, Tischer K, Stein A (1962) Rare earth fatty liver I. Octanoate oxidation and energy production. Biochim Biophys Acta 62(1):35–40
Lenmann BV, Oberdisse E, Grajewski O, Arntz HR (1975) Subcellular distribution of phospholipids during liver damage induced by rare earth. Arch Toxicol 34(2):89–101
Kyker GC, Cress EA (1957) Acute toxicity of yttrium, lanthanum and other rare earths. Am Med Assoc Arch Ind Health 16:475–479
Gold P, Freedman SC (1965) Demonstration of tumor-specific antigens in human colonic carcinomata by immunological tolerance and absorption techniques. J Exp Med 121:439–445
Mizejewski GJ, Allen RP (1978) Alpha-fetopotein: studies of tumor-associated antigen cytotoxicity in mouse hepatoma BW7756. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 11(3):307–317
Schmidt LE, Dalhoff K (2005) Alpha-fetoprotein is a predictor of outcome in acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Hepatology 41:26–31
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 30901218), the “Chun-Tsung scholar” Foundation of Soochow University, and the New Ideas Foundation of Student of Soochow University (grant no. 57315927).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jie Cheng, Na Li, Jingwei Cai, and Zhe Cheng contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, J., Li, N., Cai, J. et al. Organ Histopathological Changes and its Function Damage in Mice Following Long-term Exposure to Lanthanides Chloride. Biol Trace Elem Res 145, 361–368 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9193-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9193-8