Abstract
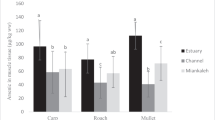
Concentration of heavy metals (lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), and copper (Cu)) was determined in the liver, gills, kidneys, and muscles of eight edible fish species (Channa punctata, Cirrhinus reba, Labeo rohita, Heteropneustes fossilis, Mystus cavasius, Oreochromis niloticus, Puntius sophore, and Wallago attu) from upstream and downstream zones of the Nullah Aik and Palkhu tributaries of the River Chenab located in the Sialkot district known for its tanning industries worldwide. The pattern of metal accumulation in studied organs was in the order: Cr > Pb > Cu > Cd. Liver showed greater metal accumulation, followed by gills, kidneys, and muscles. Accumulation of Pb and Cr was significantly different in organs between upstream and downstream zones. Accumulation was greater in fish species dwelling downstream, indicating impairment of ambient stream water due to untreated discharge of industrial and municipal effluents into studied streams. Highest concentration of Pb and Cr and lowest of Cd was detected in H. fossilis whereas Cu showed higher concentration and Cr lowest concentration in P. sophore. In contrast, lower concentration of Pb and Cu was recorded in M. cavasius, O. niloticus, and W. attu. Mean concentrations of Cd, Cr, and Cu were higher in pre-monsoon compared to post-monsoon season. Measured concentrations of Pb, Cd, and Cr in muscles of species such as C. punctata, W. attu, L. rohita, P. sophore, and O. niloticus were above permissible limits of heavy metals for human consumption, indicating potential health risks. Therefore, these fish species from studied locations should be avoided for human diet.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kotze P, du Preez HH, van Vuren JHJ (1999) Bioaccumulation of copper and zinc in Oreochromis mossambicus and Clarias gariepinus from the Olifants River, Mpumalanga, South Africa. Water SA 25:99–110
Qadir A, Malik RN, Husain SZ (2008) Spatio-temporal variations in water quality of Nullah Aik-tributary of the river Chenab, Pakistan. Environ Monit Assess 140:43–59
Malik RN, Zeb N (2009) Assessment of environmental contamination using feathers of Bubulcus ibis as a biomonitor of heavy metal pollution Pakistan. Ecotoxicology 8:522–536
Wright DA, Welbourn P (2002) Environmental toxicology (Cambridge environmental chemistry series 11). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Canli M, Atli G (2003) The relationships between heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) levels and the size of six Mediterranean fish species. Environ Pollut 121:129–136
Avenant-Oldewage A, Marx HM (2000) Bioaccumulation of chromium, copper and iron in the organs and tissues of Clarias gariepinus in the Olifants River, Kruger National Park. Water Sanit 26:569–582
Sesli E, Tuzen M, Soylak M (2008) Evaluation of trace metal contents of some wild edible mushrooms from Black sea region, Turkey. J Hazard Mater 160:462–467
Atchison GJ, Henry MG, Sandheinrich MB (1987) Effects of metals on fish behavior: a review. Environ Biol Fish 18:11–25
Langston WJ (1990) Toxic effects of metals and the incidence of marine ecosystems. In: Furness RW, Rainbow PS (eds) Heavy metals in the marine environment. CRC Press, New York
Jezierska B, Witeska M (2007) The metal uptake and accumulation in fish living in polluted waters. NATO 69:1568–1238
Besser JM, Brumbaugh WG, May TW, Schmitt CJ (2007) Biomonitoring of lead, zinc and cadmium in streams draining lead-mining and non-mining areas, Southeast Missouri, USA. Environ Monit Assess 129:227–241
Kojadinovic J, Potier M, Le Corre R, Cosson P, Bustamante P (2007) Bioaccumulation of trace elements in pelagic fish from the Western Indian Ocean. Environ Pollut 146:548–566
Agarwal R, Kumar R, Behari JR (2007) Mercury and lead content in fish species from the River Gomti, Lucknow, India, as biomarkers of contamination. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 78:108–112
Rauf A, Javed M, Ubaidullah M (2009) Heavy metal levels in three major carps (Catla catla, Labeo rohita and Cirrhina mrigala) from the river Ravi, Pakistan. Pak Vet J 29:24–26
Javed M (2005) Heavy metal contamination of freshwater fish and bed sediments in the river Ravi stretch and related tributaries. Pak J Biol Sci 8(10):1337–1341
Tariq J, Jaffar M, Ashraf M (1994) Trace metal concentration, distribution and correlation in water, sediment and fish from the Ravi River, Pakistan. Fish Res 19:131–139
Nawaz S, Nagra SA, Saleem Y, Priydarshi A (2009) Determination of heavy metals in fresh water fish species of the River Ravi, Pakistan compared to farmed fish varieties. Environ Monit Assess 167:461–471
Tariq J, Ashraf M, Jaffar M (2009) Metal pollution status of the river Chennab, Pakistan through fish, water and sediment analysis. Toxicol Environ Chem 38:175–181
Qadir A, Malik RN (2009) Assessment of an index of biological integrity (IBI) to quantify the quality of two tributaries of River Chenab, Sialkot, Pakistan. Hydrobiology 621:127–153
Mirza MR (2003) Check list of fresh water fishes of Pakistan. Pak J Zool 3:1–30
Mirza MR, Bhatti MN (1993) Pakistan Ki Machlian aur Mahi Parwari, Part-1. Ferozsons (Pvt.) Ltd, Lahore
Talwar PK, Jhingran A (1991) Inland fishes of India and adjacent countries. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi
Malik RN, Jadoon W (2009) Metal contamination of surface soils of industrial city Sialkot Pakistan: a multivariate and GIS approach. Environ Geochem Health. doi:10.1007/s10653-009-9274-1
El-Shaikh K, Nada AS, Yousief ZA (2005) Assessment of cadmium and lead in water, sediment and different organs of Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) in the river Nile. Med J Isl Worl Acad Sci 15:161–167
Kargin F (1998) Metal concentrations in tissues of the freshwater fish Capoeta barroisi from the Seyhan River (Turkey). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 60:822–828
Mendil M, UluÖzlÜ ÖD, Hasdemir E, TÜzen M, Sari H, Suiçmez M (2005) Determination of trace metal levels in seven fish species in lakes in Tokat, Turkey. Food Chem 90:175–179
Pickering QH, Brungs WA, Gast MH (1977) Effect of exposure time and copper concentration on reproduction of the fathead minnow (Pimepkales promelas). Water Res 11:1079–1983
Bajc ZKŠ, Gačnik JV, Doganoc DZ (2005) The contents of Cu, Zn, Fe and Mn in Slovenian Freshwater. Fish Slov Vet Res 42:15–21
McCarter JA, Roch M (1983) Hepatic metallothionein and resistance to copper in juvenile coho salmon. Comp Biochem Physiol 74:133–137
Van Aardt WJ, Erdmann R (2004) Heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Cu, Zn) in mudfish and sediments from three hard-water dams of the Mooi River catchment, South Africa. Water SA 2:211–218
Tryfonas AE, Tuckerb JK, Brunkow PE, Johnson KA, Hussein HS, Lin Z (2006) Metal accumulation in eggs of the red-eared slider (Trachemys scripta elegans) in the Lower Illinois River. Chemosphere 63:39–40
Van Eeden PH (2003) Metal concentrations in selected organs and tissues of five Red-knobbed Coot (Fulica cristata) populations. Water SA 29:313–322
Campbell KR (1995) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fish living in storm water treatment ponds. Technical Publication SJ95-1. St. Johns River Water Management District, Palatka, Florida
Tekin-Özan S, Kir I (2007) Seasonal variations of heavy metals in some organs of carp (Cyprinus carpio L., 1758) from Beyşehir Lake (Turkey). Environ Monit Assess 138:201–206
Nussey G, van Vuren JHJ, du Preez HH (2000) Bioaccumulation of chromium, manganese, nickel and lead in the tissues of the moggel, Labeo umbratus (Cyprinidae), from Witbank Dam, Mpumalanga. Water SA 26:269–284
Johnson I (1988) The effects of combinations of heavy metals, hypoxia and salinity on ion-regulation in Crangon crangon (L.) and Carcinus means (L.). Comp Biochem Physiol C 91:459–463
Simkiss K, Mason AZ (1983) Metal ions metabolic and toxic effects. In: Biology of Mollusca. Academic Press, New York
Roesijadi G, Robinson WE (1994) In: Malins DC, Ostrander GK (eds) Aquatic toxicology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Grobler E, Du Preez HH, Van Vuren JHJ (1989) Toxic effects of zinc and iron on the routine oxygen consumption of Tilapia sparrmanii (Cichlidae). Comp Biochem Physiol 94:207–214
Burger J, Gaines KF, Boring CS, Warren L, Jr S, Snodgrass J, Gochfeld M (2001) Mercury and selenium in fish from the Savannah River: species, trophic level and locational differences. Environ Res Section A 87:108–118
Vicente-Martorell JJ, Galindo-Riaño MD, García-Vargas M et al (2009) Bioavailability of heavy metals monitoring water, sediments and fish species from a polluted estuary. J Hazard Mater 162:823–836
USEPA (1980) Ambient water quality criteria for chromium. EPA 440/5-80-035. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC
Terra BF, Araújo FG, Calza CF, Lopes RT, Teixeira TP (2008) Heavy metal in tissues of three fish species from different trophic levels in a tropical Brazilian River. Water Air Soil Pollut 187:275–284
USEPA (1999) Biological assessment of the Idaho water quality standards for numeric water quality criteria for toxic pollutants. U.S. EPA, Region 10, Seattle Washington, DC
Eisler R (1988) Lead hazards to fish, wildlife and invertebrate: a synoptic review. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Patuxent Wildlife Research Center, Laurel
Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (1999) Canadian environmental quality guidelines, Publication No. 1299; ISBN 1- 896997-34–1
Sastry BF, Shukla V (1994) Acute and chronic toxic effects of cadmium on some haematological, biochemical and enzymological parameters in the fresh water teleost fish, Channa punctatus. Acta Hydroch Hydrob 22:171–176
Hontela A, Daniel C, Ricard AC (1996) Effects of acute and subacute exposures to cadmium on the internal and thyroid function in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquat Toxicol 35:171–182
Eisler R (1986) Chromium hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: a synoptic review. Biological Report, 85. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Washington, DC
Buhl KJ, Hamilton SJ (1996) Toxicity of inorganic contaminants, individually and in environmental mixtures, to three endangered fishes (Colorado squawfish, bony-tail, and razorback sucker). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 30:84–92
Van den Broek JL, Gledhill KS, Morgan DG (2002) Heavy metal concentrations in the mosquito fish, Gambusia holbrooki, in the Manly Lagoon catchment. In: UTS Freshwater Ecology Report 2002, Department of Environmental Sciences, University of Technology, Sydney Australia
FDA (1993) Guidance document for lead in shellfish. FDA, Washington, DC
WHO (1985) Guidelines for drinking water quality. Vol 1. Recommendations. WHO, Geneva
Acknowledgments
The first author thanks the Higher Education Commission (HEC), Pakistan for their financial support during the study period and also recognizes the kind support rendered by Professor Dr Tahira Ahmed during the development of methodology. Thanks are due to Muhammad Hussain (Fisherman), Allah ditta (Fisherman), Arshed Makhdoom Sabir, and Abdul Rehman for their assistance in the field work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qadir, A., Malik, R.N. Heavy Metals in Eight Edible Fish Species from Two Polluted Tributaries (Aik and Palkhu) of the River Chenab, Pakistan. Biol Trace Elem Res 143, 1524–1540 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9011-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9011-3