Abstract
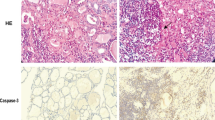
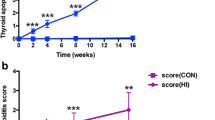
Death receptor-mediated apoptosis has been implicated in target organ destruction in patients with chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. Several apoptosis signaling pathways, such as Fas ligand and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), have been shown to be active in thyroid cells and may be involved in destructive thyroiditis. Thyroid toxicity of iodide excess has been demonstrated in animals fed with an iodide-rich diet, but its pathogenic role remains unclear. The effects of excessive iodine on TRAIL and its death receptor expression in thyroid were investigated. Experimental autoimmune thyroiditis (EAT) was induced by excessive iodine and thyroglobulin (Tg) in non-obese diabetic mice. The expression of TRAIL and its death receptor DR5 was detected by immunofluorescence staining. Following administration of excessive iodine alone, Tg, and excessive iodine combined with Tg, TRAIL-positive cells appear not only in follicular cells but also in lymphocytes infiltrated in the thyroid, whereas DR5-positive cells appear only in follicular cells. Large numbers of CD3-positive cells and a few CD22-positive cells were detected in thyroid. A great amount of follicular cells were labeled specifically by terminal deoxynucleotide transferase-mediated deoxynucleotide triphosphate nick-end labeling assay. Taken together, our results suggest that excessive iodine could induce TRAIL and DR5 abnormal expression in thyroid. TRAIL band with DR5 to promote follicular cells apoptosis thus mediate thyroid destruction in EAT.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ng HP, Kung AW (2006) Induction of autoimmune thyroiditis and hypothyroidism by immunization of immunoactive T cell epitope of thyroid peroxidase. Endocrinology 147:3085–3092
Bindra A, Braunstein GD (2006) Thyroiditis. Am Fam Phys 73:1769–1776
Rose NR, Bonita R, Burek CL (2002) Iodine: an environmental trigger of thyroiditis. Autoimmun Rev 1:97–103
Stagnaro-Green A (2002) Clinical review 152: postpartum thyroiditis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:4042–4047
Baker DH (2004) Iodine toxicity and its amelioration. Exp Biol Med 229:473–478
Fountoulakis S, Philippou G, Tsatsoulis A (2007) The role of iodine in the evolution of thyroid disease in Greece: from endemic goiter to thyroid autoimmunity. Hormones 6:25–35
Teng W, Shan Z, Teng X, Guan H, Li Y, Teng D, Jin Y, Yu X, Fan C, Chong W et al (2006) Effect of iodine intake on thyroid diseases in China. N Engl J Med 354:2783–2793
Yu S, Sharp GC, Braley-Mullen H (2002) Dual roles for IFN-gamma, but not for IL-4, in spontaneous autoimmune thyroiditis in NOD.H-2h4 mice. J Immunol 169:3999–4007
Rudin CM, Thompson CB (1997) Apoptosis and disease: regulation and clinical relevance of programmed cell death. Annu Rev Med 48:267–281
Scaffidi C, Kirchoff S, Krammer PH, Peter ME (1999) Apoptosis signaling in lymphocytes. Curr Opin Immunol 11:277–285
Vaux DL, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) Cell death in development. Cell 96:245–254
Bretz JD, Mezosi E, Giordano TJ, Gauger PG, Thompson NW, Baker JR Jr (2002) Inflammatory cytokine regulation of TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in thyroid epithelial cells. Cell Death Differ 9:274–286
French LE, Tschopp J (1997) Thyroiditis and hepatitis: Fas on the road to disease. Nat Med 3:387–388
Giordano C, Stassi G, De Maria R, Todaro M, Richiusa P, Papoff G, Ruberti G, Bagnasco M, Testi R, Galluzzo A (1997) Potential involvement of Fas and its ligand in the pathogenesis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Science 275:960–963
Borgerson KL, Bretz JD, Baker JR Jr (1999) The role of Fas-mediated apoptosis in thyroid autoimmune disease. Autoimmunity 30:251–264
Bretz JD, Arscott PL, Myc A, Baker JR Jr (1999) Inflammatory cytokine regulation of Fas-mediated apoptosis in thyroid follicular cells. J Biol Chem 274:25433–25438
Aqqarwal BB, Bhardwai U, Takada Y (2004) Regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by ectopic expression of antiapoptotic factors. Vitam Horm 67:453–483
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, Sutherland GR, Smith TD, Rauch C, Smith CA, Goodwin RG (1995) Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity 3:673–682
Song K, Chen Y, Göke R, Wilmen A, Seidel C, Göke A, Hilliard B, Chen Y (2000) Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is an inhibitor of autoimmune inflammation and cell cycle progression. J Exp Med 191:1095–1103
Izeradjene K, Douglas L, Delaney A, Houghton JA (2004) Influence of casein kinase II in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 10:6650–6660
Söderström TS, Poukkula M, Holmström TH, Heiskanen KM, Erikson JE (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling in activated T cells abrogates TRAIL-induced apoptosis upstream of the mitochondrial amplification loop and caspase-8. J Immunol 169:2851–2860
Mezosi E, Wang SH, Utsugi S, Bajnok L, Bretz JD, Gauger PG, Thompson NW, Baker JR Jr (2004) Interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α sensitize human thyroid epithelial cells to TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis through increases in procaspase-7 and Bid, and the down-regulation of p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:250–257
Nesterov A, Nikrad M, Johnson T, Kraft AS (2004) Oncogenic Ras sensitizes normal human cells to tumor necrosis factor-α-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 64:3922–3927
Drosopoulos KG, Roberts ML, Cermak L, Sasazuki T, Shirasawa S, Andera L, Pintzas A (2005) Transformation by oncogenic RAS sensitizes human colon cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by up-regulating death receptor 4 and death receptor 5 through a MEK-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 280:22856–22867
Gura T (1997) How TRAIL kills cancer cells, but not normal cells. Science 277:768
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S, Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, Blackie C, Chang L, McMurtrey AE, Hebert A, DeForge AL, Koumenis IL, Lewis D, Harris L, Bussiere J, Koeppen H, Shahrokh Z, Schwall RH (1999) Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest 104:155–162
Bonavida B, Ng CP, Jazirehi A, Schiller G, Mizutani Y (1999) Selectivity of TRAIL-mediated apoptosis of cancer cells and synergy with drugs: the trail to non-toxic cancer therapeutics. Int J Oncol 15:793–802
Kim K, Fisher MJ, Xu SQ, El-Deiry WS (2000) Molecular determinants of response to TRAIL in killing of normal and cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 6:335–346
Nieda M, Nicol A, Koezuka Y, Kikuchi A, Lapteva N, Tanaka Y, Tokunaga K, Suzuki K, Kayagaki N, Yagita H, Hirai H, Juji T (2001) TRAIL expression by activated human CD4(+) V α 24NKT cells induces in vitro and in vivo apoptosis of human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 97:2067–2074
Takeda K, Hayakawa Y, Smyth MJ, Kayagaki N, Yamaguchi N, Kakuta S, Iwakura Y, Yagita H, Okumura K (2001) Involvement of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in surveillance of tumor metastasis by liver natural killer cells. Nat Med 7:94–100
Cretney E, Takeda K, Yagita H, Glaccum M, Pschon JJ, Smyth MJ (2002) Increased susceptibility to tumor initiation and metastasis in TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-deficient mice. J Immunol 168:1356–1361
Wang SH, Cao Z, Wolf JM, Van Antwerp M, Baker JR Jr (2005) Death ligand tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand inhibits experimental autoimmune thyroiditis. Endocrinology 146:4721–4726
Fang Y, Sharp GC, Yagita H, Braley-Mullen H (2008) A critical role for TRAIL in resolution of granulomatous experimental autoimmune thyroiditis. J Pathol 216:505–513
Wang SH, Bretz JD, Phelps E, Mezosi E, Arscott PL, Utsugi S, Baker JR Jr (2002) A unique combination of inflammatory cytokines enhances apoptosis of thyroid follicular cells and transforms nondestructive to destructive thyroiditis in experimental autoimmune thyroiditis. J Immunol 168:2470–2474
Wang SH, Van Antwerp M, Kuick R, Kuick R, Gauger PG, Doherty GM, Fan YY, Baker JR Jr (2007) Microarray analysis of cytokine activation of apoptosis pathways in the thyroid. Endocrinology 148:4844–4852
Mezosi E, Wang SH, Utsugi S, Bajnok L, Bretz JD, Gauger PG, Thompson NW, Baker JR Jr (2005) Induction and regulation of Fas-mediated apoptosis in human thyroid epithelial cells. Mol Endocrinol 19:804–811
Tani J, Mori K, Hoshikawa S, Nakazawa T, Satoh J, Nakagawa Y, Ito S, Yoshida K (2002) Prevention of lymphocytic thyroiditis in iodide-treated non-obese diabetic mice lacking interferon regulatory factor-1. Eur J Endocrinol 147:809–814
Chen K, Wei Y, Sharp GC, Braley-Mullen H (2005) Balance of proliferation and cell death between thyrocytes and myofibroblasts regulates thyroid fibrosis in granulomatous experimental autoimmune thyroiditis (G-EAT). J Leukoc Biol 77:166–172
McLachlan SM, Braley-Mullen H, Chen CR, Aliesky H, Pichurin PN, Rapoport B (2005) Dissociation between iodide-induced thyroiditis and antibody-mediated hyperthyroidism in NOD.H-2h4 mice. Endocrinology 146:294–300
Yu S, Sharp GC, Braley-Mullen H (2006) Thyrocytes responding to IFN-γ are essential for development of lymphocytic spontaneous autoimmune thyroiditis and inhibition of thyrocyte hyperplaisia. J Immunol 176:1259–1265
Dai YD, Rao VP, Carayanniotis G (2002) Enhanced iodination of thyroglobulin facilitates processing and presentation of a cryptic pathogenic peptide. J Immunol 168:5907–5911
Barin JG, Talor MV, Sharma RB, Rose NR, Burek CL (2005) Iodination of murine thyroglobulin enhances autoimmune reactivity in the NOD.H2h4 mouse. Clin Exp Immunol 142:251–259
Poncin S, Gérard AC, Boucquey M, Senou M, Calderon PB, Knoops B, Lengelé B, Many MC, Colin IM (2008) Oxidative stress in the thyroid gland: from harmlessness to hazard depending on the iodine content. Endocrinology 149:424–433
Bretz JD, Baker JR Jr (2001) Apoptosis and autoimmune thyroid disease: following a TRAIL to thyroid destruction? Clin Endocrinol 55:1–11
Cretney E, Shanker A, Yagita H, Smyth MJ, Sayers TJ (2006) TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand as a therapeutic agent in autoimmunity and cancer. Immunol Cell Biol 84:87–98
Wang SH, Chen GH, Fan Y, Van Antwerp M, Baker JR Jr (2009) Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand inhibits experimental autoimmune thyroiditis by the expansion of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Endocrinology 150:2000–2007
Nakahara M, Nagayama Y, Saitoh O, Sogawa R, Tone S, Abiru N (2009) Expression of immunoregulatory molecules by thyrocytes protects nonobese diabetic-H2h4 mice from developing autoimmune thyroiditis. Endocrinology 150:1545–1551
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Council of Tianjin (grant no. 05YFGDSF02700) for scientific research. The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that would prejudice the impartiality of this scientific work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Li, L., Li, Q. et al. TRAIL and DR5 Promote Thyroid Follicular Cell Apoptosis in Iodine Excess-Induced Experimental Autoimmune Thyroiditis in NOD Mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 143, 1064–1076 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8941-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8941-5