Abstract
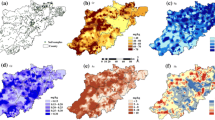
The relationship between the mortality of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and soil trace elements of 29 regions of China was investigated. A total of 29 elements (i.e., Mn, Na, K, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Hg, Pb, Se, In, Yb, Lu, Th, U, Sn, Ti, Zr, Hf, Bi, Ta, Te, Br, I, As, Cr, Cu, Fe, and Zn) were considered. A hybrid strategy called genetic algorithm-partial least squares was used to screen out important elements. As a result, only six elements, i.e., Mn, Ti, Mg, K, Na, and I, were picked out, based on which, a PLS model containing two latent variables exhibited the best performance. According to whether the mortality is larger than 2/100,000 (2 × 10−5), all the 29 regions were divided into the low-mortality group with 23 regions and the high-mortality group with six regions. Based on the optimal PLS model, all high-mortality regions were successfully classified while only two low-mortality regions were misclassified, i.e., an accuracy of 93%, implying that the selected six elements are effective and successful for predicting the NPC mortality of a region.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chien YC, Chen JY, Liu MY, Yang HI, Hsu MM, Chen CJ, Yang CS (2001) Serologic markers of Epstein–Barr virus infection and nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Taiwanese men. N EngI J Med 345:1877–1882
Tiwawech D, Srivatanakul P, Karalak A, Ishida T (2005) Cytochrome P450 2A6 polymorphism in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Lett 241:135–141
William CC (2007) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: molecular biomarker discovery and progress. Molecular Cancer 6:1–9
Xia LW, Liang SX, Jiang JW, Zhou XJ, Li J (1988) Trace element content in drinking water of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Cancer Lett 41:91–97
Tannenbaum SR, Bishop W, Yu MC, Henderson BE (1985) Attempts to isolate N-nitroso compounds from Chinese-style salted fish. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 69:209–211
Man CK, Zheng YH, Mak PK (1996) Trace element profiles in the hair of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients. J Radioanal Nucl Chem Lett 212:151–160
Wold S, Sjöström M, Eriksson L (2001) PLS-regression: a basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom Intel Lab Syst 58:109–130
Höskuldsson A (1988) PLS regression methods. J Chemometr 2:211–228
Leardi R, González AL (1998) Genetic algorithms applied to feature selection in PLS regression: how and when to use them. Chemom Intel Lab Syst 41:195–207
Lavine BK, Davidson CE, Moores AJ (2002) Genetic algorithms for spectral pattern recognition. Vib Spectrosc 28:83–95
Leardi R, Seasholtz MB, Pell RJ (2002) Variable selection for multivariate calibration using a genetic algorithm: prediction of additive concentrations in polymer films from Fourier transform-infrared spectral data. Anal Chim Acta 461:189–200
Ding Q, Small GW (1998) Genetic algorithm-based wavelength selection for the near-infrared determination of glucose in biological matrixes: initialization strategies and effects of spectral resolution. Anal Chem 70:4472–4479
China Environmental Monitoring Centre (1990) Chinese soil element background values. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, pp 330–483, in Chinese
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Sichuan Province Science Foundation for Youths (09ZQ026-066) and Scientific Research Startup Fund for Doctor, Yibin University (2008B06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, C., Chen, H., Wu, T. et al. The Prediction of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Mortality Based on Soil Element Levels in China. Biol Trace Elem Res 138, 139–147 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8632-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8632-2