Abstract
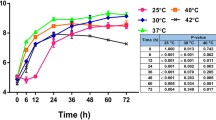
The toxic effects of artesunate and dihydroartemisinin on the growth metabolism of Tetrahymena thermophila BF5 were studied by microcalorimetry. The results showed that: (1) low concentrations of artesunate (≤1 mg L−1) and dihydroartemisinin (≤ 2 mg L−1) promoted the growth metabolism of T. thermophila BF5, whereas high concentrations of artesunate (1–60 mg L−1) and dihydroartemisinin (2–60 mg L−1) inhibited its growth; (2) the half inhibition concentrations IC50 of artesunate and dihydroartemisinin were 17.5817 and 9.5089 mg L−1, respectively. It was concluded that the inhibition of dihydroartemisinin was stronger than that of artesunate.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dhingra V, Rao KV, Narasu ML (1999) Current status of artemisinin and its derivatives as antimalarial drugs. Life Sci 66:279–300. doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(99)00356-2
Li Y, Shana F, Wua J-M, Wua G-S (2001) Novel antitumor artemisinin derivatives targeting G1 phase of the cell cycle. Bioorgan Med Chem 11:5–8
Krishna S, Bustamante L, Haynes RK, Staines HM (2008) Artemisinins: their growing importance in medicine. Trends Pharmacol Sci 29:520–527
Li H-R, Ku Z-J, Qin C-Q, Zhang Z-H, Liu Y (2007) Microcalorimetric investigation of influence of fungicide SYP-L190 on growth metabolism of Tetrahymena thermophila and Bacillus thuringiensis. Chin J Chem 25:1798–1801
Gonzalez AM, Benitez L, Soto T, De Lecea JR, Gutierrez JC (1997) A rapid bioassay to detect mycotoxins using a melanin precursor overproducer mutant of the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila. Cell Biol Int 21(4):213–216
Sauvant MP, Pepin D, Piccinni E (1999) Tetrahymena pyriformis: a tool for toxicological studies. A review. Chemosphere 38:1631–1641
Nunez-Regueira L, Rodriguez-Anon JA, Proupin-Castineiras J, Nunez-Fernandez O (2006) Soil Biol Biochem 38:115
Barros N, Gallego M, Feijoo S (2004) Chem Biodivers 1:1560
Wadsö I (2002) Thermochim Acta 394:305
Zheng D, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Chen XJ, Shen YF (2006) Microcalorimetric investigation of the toxic action of Cr(VI) on the metabolism of Tetrahymena thermophila BF5 during growth. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 22:121–127
Holzel R, Motzkus C, Lamprechet I (1994) Kinetic investigation of microbial metabolism. Thermochim Acta 239:17–24
McGulnness MS, Barisas BG (1991) Acute toxicity measurements on aquatic pollutants using microcalorimetry on tissue-cultured cells. Environ Sci Technol 25:1092–1098
Calabrese EJ (2005) Toxicological awakenings: the rebirth of hormesis as a central pillar of toxicology. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 204:1–8
Calabrese EJ, Blain R (2005) The occurrence of hormetic dose responses in the toxicological literature, the hormesis database: an overview. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 202:289–299
Vilas-Boas GT, Lemos MVF (2004) Can J Microbiol 50:605
Liu CL (2000) International conference on pests and diseases, England
Acknowledgment
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (no. 0728227).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, XS., Su, Q., Qiu, Zp. et al. Effects of Artemisinin Derivative on the Growth Metabolism of Tetrahymena thermophila BF5 Based on Expression of Thermokinetics. Biol Trace Elem Res 136, 117–125 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8527-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8527-2