Abstract
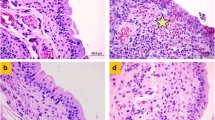
Cyclophosphamide (CP) is a widely used antineoplastic drug, which could cause toxicity of the normal cells due to its toxic metabolites. Its urotoxicity may cause dose-limiting side effects like hemorrhagic cystitis. Overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) during inflammation is one of the reasons of the urothelial injury. Selenoproteins play crucial roles in regulating ROS and redox status in nearly all tissues; therefore, in this study, the urotoxicity of CP and the possible protective effects of seleno-l-methionine (SLM) on urinary bladder of rats were investigated. Intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of 50, 100, or 150 mg/kg CP induced cystitis, in a dose-dependent manner, as manifested by marked congestion, edema and extravasation in rat urinary bladder, a marked desquamative damage to the urothelium, severe inflammation in the lamina propria, focal erosions, and polymorphonuclear (PMN) leukocytes associated with occasional lymphocyte infiltration determined by macroscopic and histopathological examination. In rat urinary bladder tissue, a significant decrease in the endogenous antioxidant compound glutathione, and elevation of lipid peroxidation were also noted. Pretreatment with SLM (0.5 or 1 mg/kg) produced a significant decrease in the bladder edema and caused a marked decrease in vascular congestion and hemorrhage and a profound improvement in the histological structure. Moreover, SLM pretreatment decreased lipid peroxide significantly in urinary bladder tissue, and glutathione content was greatly restored. These results suggest that SLM offers protective effects against CP-induced urinary bladder toxicity and could be used as a protective agent against the drug toxicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Selvakumar E, Prahalathan C, Sudharsan PT, Varalakshmi P (2006) Chemoprotective effect of lipoic acid against cyclophosphamide-induced changes in the rat sperm. Toxicology 217:71–78
Alfieri B, Gardner CJ (1997) The NK1 antagonist, GR203040, inhibits cyclophosphamide-induced damage in the rat and ferret bladder. Br J Pharmacol 29:245–250
Frasier LU, Sarathchandra K, Kehrer JP (1991) Cyclophosphamide toxicity: characterising and avoiding the problem. Drugs 42:781–795
West NJ (1997) Prevention and treatment of hemorrhagic cystitis. Pharmacother 17(4):696–706
Özcan A, Korkmaz A, Oter S, Coskun O (2005) Contribution of flavonoid antioxidants to the preventive effect of MESNA in cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis in rats. Arch Toxicol 79:461–465
Premila A, Indirani K, Preethi K (2008) Alterations in antioxidant enzyme activities and increased oxidative stress in cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in the rat. J Cancer Therapy 6:563–570
Virag L, Szabo E, Gergely P, Szabo C (2003) Peroxynitrite-induced cytotoxicity: mechanism and opportunities for intervention. Toxicol Let 141:113–124
Das UB, Mallick M, Debnath JM, Ghosh D (2002) Protective effect of ascorbic acid on cyclophosphamide-induced testicular gametogenic and androgenic disorders in male rats. Asian J Androl 4:201–207
Manda K, Bhatia AI (2003) Prophylactic action of melatonin against Cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress in mice. Cell Biol Toxicol 19:367–372
Mates JM, Perez-Gomez P, Nunez de Castro I (1999) Antioxidant enzymes and human disease. Clin Biochem 32:595–603
Cuzzocrea S, Reiter RJ (2001) Pharmacological action of melatonin in shock, inflammation, and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Eur J Pharmacol 426:1–10
Gouaze V, Mirault ME, Carpenter S, Salvayre R, Levade T, Andrieu-Abadie N (2001) Glutathione peroxidase-1 overexpression prevent ceramide production and partially inhibits apoptosis in doxorubicin-treated human breast carcinoma cells. Mol Pharmacol 60:488–496
Hoffmann PR, Berry MJ (2008) The influence of selenium on immune responses. Mol Nut Res 52:1273–1280
Cao S, Durrani FA, Rustum YM (2004) Selective modulation of the therapeutic efficacy of anticancer drugs by selenium containing compounds against human tumor xenografts. Clinical Cancer Research 10:2561–2569
Xu X, Malave A (2001) Protective effect of berberin on cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in rats. Pharmacol Toxicol 88:232–237
Abd-Allah ARA, Gado AM, Al-Majed A, Al-Yahya AA, Al-Shabanah OA (2004) Protective effect of taurine against cyclophosphamide-induced urinary bladder toxicity in rats. Clin and Exp Pharmacology and Physiology 31:167–172
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Gray KJ, Engelmann UH, Fishman IJ (1986) Evaluation of misoprostol cytoprotection of the bladder with cyclophosphamide (cytoxan) therapy. J Urol 133:497–500
Brock N, Pohl J, Stekar J (1981) Studies on the urotoxicity of oxazaphosphorine cytostatics and its prevention. 1. Experimental studies on the urotoxicity of alkylating compounds. Eur J Cancer 17:595–601
Korkmaz A, Topal T, Oter S (2007) Pathophysiological aspects of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide induced hemorrhagic cystitis; implication of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species as well as PARP activation. Cell Biol Toxicol 23:303–312
Lundberg J (1996) Airbone nitric oxide: Inflammatory marker and aereocrine messenger in man. Acta Physiol Scand 157:1–27
Ribeiro RA, Feritas HC, Campos MC, Santos CC, Figueiredo FC, Brito GA (2002) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta mediate the production of nitric oxide involved in the pathogenesis of ifosfamide induced hemorrhagic cystitis in mice. Jurol 167(5):2229–2234
Davis L, Kuttan G (2000) Effect of Withania somnifera on cyclophosphamide-induced urotoxicity. Cancer Letter 148:9–17
Yuan M, Smith PB, Brundrett RB, Colvin M, Fenselau C (1991) Glutathione conjugation with phospharamide mustard and Cyclophosphamide. A mechanistic study using tandem mass spectrometry. Drug Metab Dispos 19:625–629
Lee IM (1999) Antioxidant vitamins in the prevention of cancer. Proc Assoc Am Physicians 111:10–15
Batista CK, Mota JM, Souza ML, Brito GA, Cunha FQ, Ribeiro RA (2007) Amifostine and glutathione prevent ifosfamide and acrolein-induced hemorrhagic cystitis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 59:71–77
Navarova J, Ujhazy E, Dubovicky M (1999) Protective effect of the antioxidant stobadineagainst Cyclophosphamide and irradiation induced oxidative stress. Gen Physiol Biophys 18:112–119
Aruoma OI, Halliwell B, Hoey BM, Butler J (1988) The antioxidant action of taurine, hypotaurine and their metabolic precursors. Biochem J 256:251–255
Whanger PD (1981) Selenium and heavy metal toxicity. JE, In Spallholz JL, Martin HE (eds), Ganther: Selenium in Biology and Medicine. AVI Westport Conn 230-255
Diplock AT, Watkins WJ, Heurson M (1986) Selenium and heavy metals. Ann Clin Res 18:55–60
Ip C (1986) Selenium and experimental cancer. Ann Clin Res 18:22–29
Jamba L, Nehru B, Bansal MP (1997) Selenium Supplementation During Cadmium Exposure: Changes in Antioxidant Enzymes and the Ultrastructure of the Kidney. The Journal of Trace Elements in Experimental Medicine 10:233–242
Furst A (2002) Can nutrition affect chemical toxicity? Int J Toxicol 21:419–424
Olas B, Wachowicz B (1997) Selenium in the cytotoxicity of cisplatin. Postepy Hyg Med Dos 51:95–108
Weijl NI, Elsendoorn TJ, Lentjes EG, Hopman GD, Viking-Bakker A, Zwinderman AH, Cleton FJ, Osanto S (2004) Supplementation with antioxidant micronutrients and chemotherapy-induced toxicity in cancer patients treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur J Cancer 40:1713–1723
Zeng H, Combs GF (2008) Selenium as an anticancer nutrient: roles in cell proliferation and tumor cell invasion. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 19:1–7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayhanci, A., Yaman, S., Sahinturk, V. et al. Protective Effect of Seleno-l-Methionine on Cyclophosphamide-Induced Urinary Bladder Toxicity in Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 134, 98–108 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8458-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8458-y