Abstract
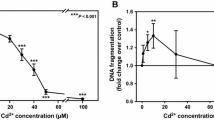
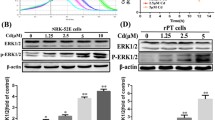
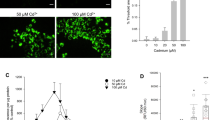
Cadmium (Cd) is a known nephrotoxic element. In this study, the primary cultures of rat proximal tubular (rPT) cells were treated with low doses of cadmium acetate (2.5 and 5 µM) to investigate its cytotoxic mechanism. A progressive loss in cell viability, together with a significant increase in the number of apoptotic and necrotic cells, were seen in the experiment. Simultaneously, elevation of intracellular [Ca2+]i and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, significant depletion of mitochondrial membrane potential(Δ Ψ) and cellular glutathione (GSH), intracellular acidification, and inhibition of Na+, K+-ATPase and Ca2+-ATPase activities were revealed in a dose-dependent manner during the exposure, while the cellular death and the apoptosis could be markedly reversed by N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC). Also, the calcium overload and GSH depletion were significantly affected by NAC. In conclusion, exposure of rPT cells to low-dose cadmium led to cellular death, mediated by an apoptotic and a necrotic mechanism. The apoptotic death might be the chief mechanism, which may be mediated by oxidative stress. Also, a disorder of intracellular homeostasis induced by oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction is a trigger of apoptosis in rPT cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waisberg M, Joseph P, Hale B, Beyersmann D (2003) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicology 192:95–117
Klaassen CD, Liu J, Choudhuti S (1999) Metallothionein: an intracellular protein to protect against cadmium toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 39:267–294
Ohta H, Yamauchi Y, Nakakita M, Tanaka H, Asami S, Seki Y, Yoshikawa H (2000) Relationship between renal dysfunction and bone metabolism disorder in male rats after long-term oral quantitative cadmium administration. Ind Health 38:339–355
Morales AI, Vicente-Sánchez C, Sandoval JM, Egido J, Mayoral P, Arévalo MA, Fernández-Tagarro M, López-Novoa JM, Pérez-Barriocanal F (2006) Protective effect of quercetin on experimental chronic cadmium nephrotoxicity in rats is based on its antioxidant properties. Food Chem Toxicol 44:2092–2100
Thévenod F, Friedmann JM (1999) Cadmium-mediated oxidative stress in kidney proximal tubule cells induces degradation of Na+/K+-ATPase through proteasomal and endo-/lysosomal proteotic pathway. FASEB J 13:1751–1761
Pari L, Murugavel P (2007) Diallyl tetrasulfide improves cadmium induced alterations of acetylcholinesterase, ATPases and oxidative stress in brain of rats. Toxicology 234:44–50
Thévenod F (2003) Nephrotoxicity and the proximal tubule. Insights from cadmium. Nephron Physiol 93:87–93
Alvarez-Barrientos A, O’Connor JE, Nieto Castillo R, Moreno Moreno AB, Prieto P (2001) Use of flow cytometry and confocal microscopy techniques to investigate early CdCl2-induced nephrotoxicity in vitro. Toxicol in Vitro 15:407–412
Lemarié A, Lagadic-Gossmann D, Morzadec C, Allain N, Fardel O, Vernhet L (2004) Cadmium induces caspase-independent apoptosis in liver Hep3B cells: role for calcium in signaling oxidative stress-related impairment of mitochondria and relocation of endonuclease G and apoptosis-inducing factor. Free Radic Biol Med 36:1517–1531
Li M, Kondo T, Zhao QL, Li FJ, Tanabe K, Arai Y, Zhou ZC, Kasuya M (2000) Apoptosis induced by cadmium in human lymphoma U937 cells through Ca2+-calpain and caspase-mitochondria-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem 275:39702–39709
Lühe A, Hildebrand H, Bach U, Dingermann T, Ahr HJ (2003) A new approach to studying ochratoxin A (OTA)-induced nephrotoxicity: expression profiling in vivo and in vitro employing cDNA microarrays. Toxicol Sci 73:315–328
Nouwen EJ, Dauwe S, van der Biest I, De Broe ME (1993) Stage- and segment- specific expression of cell-adhesion molecules N-CAM, A-CAM, and L-CAM in the kidney. Kidney Int 44:147–158
Scaduto RC, Grotyohann LW (1999) Measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential using fluorescent rhodamine derivatives. Biophys J 76:469–477
Hirpara JL, Clément MV, Pervaiz S (2001) Intracellular acidification triggered by mitochondrial-derived hydrogen peroxide is an effector mechanism for drug-induced apoptosis in tumor cells. J Biol Chem 276:514–521
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Tietze F (1969) Enzymatic methods for quantitative determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized glutathione: Application to mammalian blood and other tissue. Anal Biochem 27:502–522
Hervouet E, Simonnet H, Godinot C (2007) Mitochondria and reactive oxygen species in renal cancer. Biochimie 89:1080–1088
Fleury C, Mignotte B, Vayssière JL (2002) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cell death signaling. Biochimie 84:131–141
Wallace DC (2005) A mitochondrial paradigm of metabolic and degenerative diseases, aging, and cancer: a dawn for evolutionary medicine. Annu Rev Genet 39:359–407
Wang Y, Fang J, Leonard SS, Rao KM (2004) Cadmium inhibits the electron transfer chain and induces reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med 36:1434–1443
Foster KA, Galeffi F, Gerich FJ, Turner DA, Müller M (2006) Optical and pharmacological tools to investigate the role of mitochondria during oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Prog Neurobiol 79:136–171
Chen F, Vallyathan V, Castranova V, Shi X (2001) Cell apoptosis induced by carcinogenic metals. Mol Cell Biochem 222:183–188
Matsuyama S, Llopis J, Deveraux QL, Tsien RY, Reed JC (2000) Changes in intramitochondrial and cytosolic pH: early events that modulate caspase activation during apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 2:318–325
Clément MV, Ponton A, Pervaiz S (1998) Apoptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide is mediated by decreased superoxide anion concentration and reduction of intracellular milieu. FEBS Lett 440:13–18
Grammatopoulos TN, Johnson V, Moore SA, Andres R, Weyhenmeyer JA (2004) Angiotensin type 2 receptor neuroprotection against chemical hypoxia is dependent on the delayed rectifier K+ channel, Na+/Ca2+ exchanger and Na+/K+ ATPase in primary cortical cultures. Neurosci Res 50:299–306
Orrenius S, Mccabe MJ, Nicotera P (1992) Ca2+-dependent mechanisms of cytotoxicity and programmed cell death. Toxicol Lett 64:357–364
McConkey DJ, Orrenius S (1997) The role of calcium in the regulation of apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 239:357–366
Fujita T, Inoue H, Kitamura T, Sato N, Shimosawa T, Maruyama N (1998) Senescence marker protein-30 (SMP30) rescues cell death by enhancing plasma membrane Ca2+-pumping activity in HepG2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 250:374–380
Wang XQ, Xiao AY, Sheline C, Hyrc K, Yang A, Goldberg MP, Choi DW, Yu SP (2003) Apoptotic insults impair Na+, K+-ATPase activity as a mechanism of neuronal death mediated by concurrent ATP deficiency and oxidant stress. J Cell Sci 116:2099–2110
Qin XJ, Li YN, Liang X, Wang P, Hai CX (2008) The dysfunction of ATPases due to impaired mitochondrial respiration in phosgene-induced pulmonary edema. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 367:150–155
Moran LK, Guteridge JM, Quinlan GJ (2001) Thiols in cellular redox signaling and control. Curr Med Chem 8:763–772
Schafer FQ, Buettner GR (2001) Redox environment of the cell as viewed through the redox state of the glutathione disulfide/glutathione couple. Free Radic Biol Med 30:1191–1212
Masella R, Benedetto R, Varì R, Filesi C, Giovannini C (2005) Novel mechanisms of natural antioxidant compounds in biological systems: involvement of glutathione and glutathione-related enzymes. J Nutr Biochem 16:577–586
Lavrentiadou SN, Chan C, Kawcak T, Ravid T, Tsaba A, Der Vliet AV, Rasooly R, Goldkorn T (2001) Ceramide-mediated apoptosis in lung epithelial cells is regulated by glutathione. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 25:676–684
Nigam D, Shukla GS, Agarwal AK (1999) Glutathione depletion and oxidative damage in mitochondria following exposure to cadmium in rat liver and kidney. Toxicol Lett 106:151–157
Valko M, Morris H, Cronin MTD (2005) Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem 12:1161–1208
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (no. 30440050 and 30571364).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Cao, J., Chen, D. et al. Role of Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, and Intracellular Homeostasis in Primary Cultures of Rat Proximal Tubular Cells Exposed to Cadmium. Biol Trace Elem Res 127, 53–68 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-008-8223-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-008-8223-7