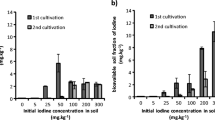
Abstract
Iodine-enhanced vegetable has been proven to be an effective way to reduce iodine deficiency disorders in many regions. However, the knowledge about what mechanisms control plant uptake of iodine and where iodine is stored in plants is still very limited. A series of controlled experiments, including solution culture, pot planting, and field experiments were carried out to investigate the uptake mechanism of iodine in different forms. A new methodology for observing the iodine distribution within the plant tissues, based on AgI precipitation reaction and transmission electron microscope techniques, has been developed and successfully applied to Chinese cabbage. Results show that iodine uptake by Chinese cabbage was more effective when iodine was in the form of IO3 − than in the form of I− if the concentration was low (<0.5 mg L−1), but the trend was opposite if iodine concentration was 0.5 mg L−1 or higher. The uptake was more sensitive to metabolism inhibitor in lower concentration of iodine, which implies that the uptake mechanism transits from active to passive as the iodine concentration increases, especially when the iodine is in the form of IO3 −. The inorganic iodine fertilizer provided a quicker supply for plant uptake, but the higher level of iodine was toxic to plant growth. The organic iodine fertilizer (seaweed composite) provided a more sustainable iodine supply for plants. Most of the iodine uptake by the cabbage is intercepted and stored in the fibrins in the root while the iodine that is transported to the above-ground portion (shoots and leaves) is selectively stored in the chloroplasts.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rose NR, Bonita R, Burek CL (2002) Iodine: an environmental trigger of thyroiditis. Autoimmun Rev 1:97–103
Zaichick V, Zaichick S (1997) Normal human intrathyroidal iodine. Sci Total Environ 206(18):39–56
Upadhyay G, Singh R, Sharma R, Balapure AK, Godbole MM (2002) Differential action of iodine on mitochondria from human tumoral- and extra-tumoral tissue in inducing the release of apoptogenic proteins. Mitochondrion 2:199–210
Hetzel BS (1983) Iodine deficiency disorders (IDD) and their eradication. Lancet 2:1126–1129
Huang YZ, Zhu YG, Hu Y, Liu YX, Dai JL (2003) Iodine in soil–plant systems and prevention of iodine deficiency disorders. Ecol Environ 12:228–231 (in Chinese)
Xu WM, Wang GH, Jin DF (1999) Investigation on the incidence of hyperthyroidism among iodine supplied population of low grade iodine deficiency area. Chin J Endemiol 18:453–456 (in Chinese)
Yu ZH (2001) Problems of prevention and cure of IDD in China concluded from the IDD monitoring reports in China since 1999. Chin J Endemiol 20:70–71 (in Chinese)
Wang FJ, Xu M, Wu SX (2003) The relation between USI and toxic nodular goiter. J Surg Concepts Practice 8:333–334
Horvatic G, Skreb F, Kusacic KS, Bracic I, Dodig D (1998) Echographic thyroid changes in iodine deficiency and excess. Eur J Ultrasound 7(S1):26–26 (1)
Peng YM (2002) Iodine and thyroid autoimmune disease. Mod Med Health 18:864–865 (in Chinese)
Hong FG, Cao YX, Liu HT (1997) Distribution of high fluorin and high iodine water in Binzhou region and the research on its harm. Prev Med Tribune 3:341–342 (in Chinese)
Liu GY (2001) Exploitation of deep groundwater in northern Shandong plain and environmental problems. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 3:43–45 (in Chinese)
Longvah T, Deosthale YG (1998) Iodine content of commonly consumed foods and water from the goitre-endemic northeast region of India. Food Chem 61(5):327–331
Shi L, Zhou RH, Wang GY (1998) Effect of iodine lose under different cooking method. J Hygiene Res 27:412–414
Zhang LJ, Chen ZW, Wang JY, Bao JM (2000) Iodine loss from iodized salt during processing, sale and consumption. Zhejiang J Prev Med 12:32–34 (in Chinese)
Zhu YG, Huang YZ, Hu Y, Liu YX (2002) Iodine uptake by spinach (Spinacia oleracea L) plants grown in solution culture: effects of iodine species and solution concentration. Environ Int 984:1–5
Zhou YL, Jiang QY, Wu MY (2003) Influence of salt iodization on hospitalization rate of hyperthyroid ism in mild iodine deficiency areas. Chin J Endemiol 22:530–531
Peterson S, Legue F, Tylleskar T (1995) Improved cassava-processing can help reduce iodine deficiency disorders in the Central African Republic. Nutr Res 15:803–812
Zheng BS, Wang BB (2001) Environmental geochemistry of iodine in atmosphere and plant review and a hypothesis. Earth Sci Front 8:359–365 (in Chinese)
Lian Z-H (1995) Theory and technology of soilless culture, chapter III nutritional liquid. Huazhong Agriculture University, 32 pp (in Chinese)
Weng HX, Cai QX (1998) A manufacture method of iodine composite fertilizer. Invention Patent in China (Grant no. ZL 94108836.7) (in Chinese)
GB/T 13882-92 (1992) Colorimetric method with ferric thiocyanate and sodium nitrite (measurement of iodine in feed). Standards Press of China, Beijing
Wang JF, Duan LZ, Liu NH (1999) Determination of micro amounts of iodine in soil by amplified reaction colorimetric method. Anal Lab 18:71–74 (in Chinese)
Hans JW, Hans JJ (1980) Subcellular distribution and chemical form of cadmium in bean plant. Plant Physiol 65:480–482
Foster RC, Sands R (1987) Response of radiata pine to salt stress. II. Localization of chloride. Aust J Plant Physiol 4:863–875
Jiang TH, Zheng SJ, Shi JQ (1995) Several considerations in kinetic research on nutrients uptake by plants. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 1:11–16
Muramatsu Y, Yoshida S (1995) Volatilization of methyl iodide from the soil–plant system. Atmos Environ 29:21–25
Ashmore CB, Gwyther JR, Sims HE (1996) Some effects of pH on inorganic iodine volatility in containment. Nucl Eng Des 166:347–355
Yan A-L, Weng H-X, Hong C-L, Song X-H, Xie L-L (2007) Biogeochemistry transportation and dynamic behavior of 125I in soil–vegetable ecosystem. Geochimica 36:525–532 (in Chinese)
Whitehead DC (1975) Uptake by perennial ryegrass of iodide, elemental iodine and iodate added to soil as influenced by various amendments. J Sci Food Agric 26:361–367
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 40373043). Thanks are due to Qinshi Pan for her editing review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, HX., Hong, CL., Yan, AL. et al. Mechanism of Iodine Uptake by Cabbage: Effects of Iodine Species and Where It is Stored. Biol Trace Elem Res 125, 59–71 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-008-8155-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-008-8155-2