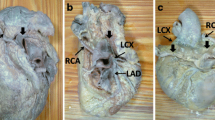
Abstract
To elucidate compositional changes of the arteries with aging, the authors investigated age-related changes of elements in the splenic and pulmonary arteries, which supplied blood to contractile organs. After ordinary dissection by medical students at Nara Medical University was finished, the splenic and pulmonary arteries were resected from the subjects, ranging in age from 58 to 94 years. The element contents were determined by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. It was found that a moderate accumulation of Ca and P occurred in the splenic artery with aging, but it hardly occurred in the pulmonary artery with aging. Regarding the relationship among elements, the finding that there were significant direct correlations among the contents of Ca, P, Mg, and Na was commonly obtained in both the splenic and pulmonary arteries. The accumulation of Ca and P in the splenic artery with aging occurred independently of that in the pulmonary artery. Histologic observation indicated that a major part of Ca deposits was seen in the middle tunica, but not in the internal tunica. Therefore, the calcification occurring in the splenic artery belonged to middle sclerosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tohno Y, Tohno S, Minami T et al (1996) Age-related changes of mineral contents in the human thoracic aorta and in the cerebral artery. Biol Trace Elem Res 54:23–31
Tohno Y, Tohno S, Minami T et al (1998) Age-related changes of mineral contents in the human aorta and internal thoracic artery. Biol Trace Elem Res 61:219–226
Tohno S, Tohno Y (1998) Age-related differences in calcium accumulation in human arteries. Cell Mol Biol 44:1253–1263
Tohno Y, Tohno S, Mahakkanukrauh P et al (2001) Simultaneous accumulation of magnesium with calcium and phosphorus in aorta and iliac arteries of Thai. Biol Trace Elem Res 84:19–35
Tohno S, Mahakkanukrauh P, Tohno Y et al (2002) High accumulation of calcium and phosphorus in the coronary artery of the Thai in comparison with the Japanese. Biol Trace Elem Res 87:69–82
Naganuma T, Tohno Y, Yamasaki M et al (2004) High accumulation of calcium in human uterine artery with aging. Biol Trace Elem Res 101:203–210
Mahakkanukrauh P, Tohno S, Tohno Y et al (2004) Accumulation of calcium and phosphorus accompanied by inevitable accumulation of magnesium in human arteries. Biol Trace Elem Res 100:205–214
Tohno Y, Tohno S, Mahakkanukrauh P et al (2006) Earlier accumulation of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium in the coronary artery in comparison with the ascending aorta, aortic valve, and mitral valve. Biol Trace Elem Res 112:31–42
Ongkana N, Prieto Payo IM, Tohno S et al (2007) Age-related changes and relationships among the element contents in the thoracic and abdominal aortas and the coronary, common carotid, pulmonary, splenic, common iliac, and uterine arteries. Biol Trace Elem Res (in press)
Sinzinger H, Schmiedl R, Reisinger L et al (1974) Lange, Verlauf und Gewicht der Arteria lienalis des Menschen in verschiedenen Abschnitten in Relation zu makroskopisch faszbaren arteriosklerotischen Veranderungen. Acta Morphol Neerl-Scand 12:123–144
Okuda K, Kobayashi S, Hayashi H et al (2002) Case-control study of calcification of the hepatic artery in chronic hemodialysis patients: comparison with abdominal aorta and splenic artery. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17:91–95
Philp T (1972) Pulmonary artery calcification. Scott Med J 17:104–107
Parameswaran R, Maranhao V, Ablaza SGG et al (1970) Calcification of the pulmonary artery: a complication of the banding procedure. Chest 57:577–579
Pochaczevsky R, Dunst ME (1972) Coexistent pulmonary artery and aortic arch calcification. Its significance and association with patent ductus arteriosus. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 116:141–145
Gutierrez FR, Moran CJ, Ludbrook PA et al (1980) Pulmonary arterial calcification with reversible pulmonary hypertension. Am J Radiol 135:177–178
Yigla M, Keidar Z, Safadi I et al (2004) Pulmonary calcification in hemodialysis patients: correlation with pulmonary artery pressure values. Kidney Int 66:806–810
Bakovic D, Valic Z, Eterovic D et al (2003) Spleen volume and blood flow response to repeated breath-hold apneas. J Appl Physiol 95:1460–1466
Acknowledgment
Portions of this work were supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research no. 17200032 from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prieto Payo, I.M., Ongkana, N., Tohno, S. et al. Moderate Accumulation of Calcium and Phosphorus in the Splenic Artery with Aging and Low Accumulation of Those in the Pulmonary Artery with Aging. Biol Trace Elem Res 119, 103–110 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-007-0052-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-007-0052-6