Abstract
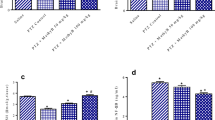
Our purpose in this study was to investigate the protective effects of selenium and vitamin E on the blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability in rats with convulsion under hyperthermic conditions. To eliminate the effect of sex on BBB, we performed our study on 4- to 5-week-old prepubertal rat pups. Evans-blue was used as a BBB tracer. Convulsions were induced by administration of i.p. pentylenetetrazol. In the selenium group, 4 ppm selenium was added to the drinking water for 4–5 weeks. Vitamin E was administered at 700 mg/kg ip. It was shown that the convulsions, both under normothermic and hyperthermic conditions, caused widespread increase in the BBB permeability (p < 0.05). In addition, a significant difference was observed among female and male rats (f [1, 102] = 6.387, p < 0.05). In convulsions under normothermic conditions, there was a further increase in the BBB permeability (F[3, 102] = 43.534, p < 0.001) and a greater increase of permeability in males compared to females (F[1, 102] = 6.387, p < 0.05). Selenium and vitamin E significantly decreased the BBB destruction caused by convulsions under hyperthermic conditions in males (p < 0.05). Treatment with selenium or vitamin E has beneficial effects on the BBB breakdown during convulsions. But gender differences are very important in BBB permeability under pathological conditions and antioxidant treatments.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang CP, Hsu YC, Lin MT (2003) Magnolol protects against cerebral ischemic injury of rat heatstroke. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 30:387–392
Sharma HS (2006) Hyperthermia influences excitatory and inhibitory amino acid neurotransmitters in the central nervous system. An experimental study in the rat using behavioral, biochemical, pharmacological, and morphological approaches. J Neural Transm 113(4):497–519
Drislane FW (2000) Presentation, Evaluation, and Treatment of Nonconvulsive Status Epilepticus. Epilepsy Behav 1(5):301–314
Shorvon S (1993) Tonic clonic status epilepticus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 56:125–134
Oztas B, Akgul S, Seker FB (2006) Influence of antioxidants on blood–brain barrier permeability during pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures in hyperthermic rat pups. In: Abstract Book of the fifth international congress of pathophysiology, Beijing, China, June 28–July 1, Abstract Book
Oztas B, Kılıc S, Dural E, Ispir T (2001) Influence of antioxidants on the blood–1brain barrier permeability during epileptic seizures. J Neurosci Res 66:674–678
Chhabra SK, Rao AR (1994) Translactational exposure of F1 mouse pups to selenium. Food Chem Toxicol 32:527–531
Emmett PM, Rogers IS (1997) Properties of human milk and their relationship with maternal nutrition. Early Hum Dev 49:7–28
Kaya M, Palanduz A, Kalayci R, Kemikler G, Simsek G, Bilgic B, Ahishali B, Arican N, Kocyildiz ZC, Elmas I, Kucuk M, Karadeniz A (2004) Effects of lipopolysaccharide on the radiation-induced changes in the blood–brain barrier and the astrocytes. Brain Res 1019(1–2):105–112
Cragg BG, Phillips SC (1981) Natural variation in the blood–brain barrier. Neurosci Lett 27:309–312
Oztas B, Camurcu S, Kaya M (1992) Influence of sex on the blood–brain barrier permeability during bicuculline-induced seizures. Int J Neurosci 65:131–139
Tarkka R (2003) Febrile seizures and mesial temporal sclerosis: no association in a long-term follow-up study. Neurology 741:1–44
Ehrenbrink G, Hakenhaar FS, Salomon TB, Petrucci AP, Sandri MR, Benfato MS (2006) Antioxidant enzymes activities and protein damage in rat brain of both sexes. Exp Gerontol 41(4):368–371
Wei EP, Ellison MD, Kontos HA, Povlishock JT (1986) O2 radicals in arachidonate-induced increased blood-brain barrier permeability to proteins. Am J Physiol 251:693–699
Schwenke DC (1998) Antioxidants and atherogenesis. J Nutr Biochem 9:424–445
Yu BP, Chung HY (2006) Adaptive mechanisms to oxidative stress during aging. Mech Ageing Dev 127:436–443
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals, antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160(1):1–40
de Vries HE, Kuiper J, de Boer AG, Van Berkel TJ, Breimer DD (1997) The blood–brain barrier in neuroinflammatory diseases. Pharmacol Rev 49:143–156
Calingasan NY, Park LCH, Calo LL, Trifiletti RR, Gandy SE, Gibson GE (1998) Induction of nitric oxide synthase and microglial responses precede selective cell death induced by chronic impairment of oxidative metabolism. Am J Pathol 153:599–610
Sherki YG, Melamed E, Offen D (2001) Oxidative stress induced-neurodegenerative diseases: The need for antioxidants that penetrate the blood–brain barrier. Neuropharmacology 40:959–975
Mahadik SP, Mukherjee S (1996) Free radical pathology and antioxidant defense in schizophrenia: a review. Schizophr Res 19(1):1–17
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Research Fund of University of Istanbul. Project number: 702/ 24032006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oztas, B., Akgul, S. & Seker, F.B. Gender Difference in the Influence of Antioxidants on the Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability During Pentylenetetrazol-Induced Seizures in Hyperthermic Rat Pups. Biol Trace Elem Res 118, 77–83 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-007-0020-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-007-0020-1