Abstract
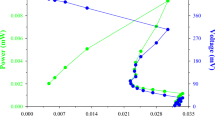
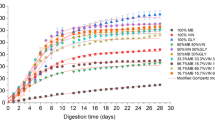
Anaerobic fermentation of excess sludge (ES) for hydrogen production is a crucial strategy for resource utilization and environmentally friendly treatment. However, the low hydrolysis efficiency of ES and the depletion of produced hydrogen have become the limiting factors for low hydrogen yield. This study innovatively applied the bio-based surfactant alkyl polyglucoside (APG) to enhance the efficiency of dark fermentation for hydrogen production from ES. When the APG content was 100 mg/g (calculated based on total suspended solids), the maximum hydrogen production reached 17.8 mL/g VSS, approximately 3.7 times that in the control group. Mechanistic analysis revealed that APG promoted the release of organic matter from ES. APG also facilitated the release of soluble protein and soluble polysaccharide, increasing the organic matter reduction rate to 34.8%, significantly higher than other groups. APG enhanced the accumulation of volatile fatty acids and promoted the proportion of small molecular carboxylic acids. Enzyme activity analysis revealed that APG promoted the activity of hydrolytic enzymes but inhibited the activity of hydrogen-consuming enzymes. The research results provide a green and environmentally friendly strategy for the efficient resource utilization of ES.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confirm that data supporting the literature of this review article are available within the article.
References
Bashar, R., Gungor, K., Karthikeyan, K. G., & Barak, P. (2018). Cost effectiveness of phosphorus removal processes in municipal wastewater treatment.Chemosphere,197, 280–290.
Yuan, Q., Zhang, H., Qin, C., Zhang, H., Wang, D., Zhang, Q., Zhang, D., & Zhao, J. (2023). Impact of emerging pollutant florfenicol on enhanced biological phosphorus removal process: Focus on reactor performance and related mechanisms. Science of the Total Environment, 859, 160316.
Fijalkowski, K., Rorat, A., Grobelak, A., & Kacprzak, M. J. (2017). The presence of contaminations in sewage sludge–the current situation. Journal of Environmental Management, 203, 1126–1136.
Buta, M., Hubeny, J., Zieliński, W., Harnisz, M., & Korzeniewska, E. (2021). Sewage sludge in agriculture–the effects of selected chemical pollutants and emerging genetic resistance determinants on the quality of soil and crops–a review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 214, 112070.
Zhao, J., Wang, Y., Guan, D., Fu, Z., Zhang, Q., Guo, L., Sun, Y., Zhang, Q., & Wang, D. (2023). Calcium hypochlorite-coupled aged refuse promotes hydrogen production from sludge anaerobic fermentation. Bioresource Technology, 370, 128534.
Zhao, J., Zhang, J., Zhang, D., Hu, Z., & Sun, Y. (2021). Effect of emerging pollutant fluoxetine on the excess sludge anaerobic digestion. Science of the Total Environment, 752, 141932.
Li, X., Sui, K., Zhang, J., Liu, X., Xu, Q., Wang, D., & Yang, Q. (2022). Revealing the mechanisms of rhamnolipid enhanced hydrogen production from dark fermentation of waste activated sludge. Science of the Total Environment, 806, 150347.
Yang, G., & Wang, J. (2019). Biohydrogen production by co-fermentation of sewage sludge and grass residue: Effect of various substrate concentrations. Fuel, 237, 1203–1208.
Fu, Z., Zhao, J., Guan, D., Wang, Y., Xie, J., Zhang, H., Sun, Y., Zhu, J., & Guo, L. (2024). A comprehensive review on the preparation of biochar from digestate sources and its application in environmental pollution remediation. Science of the Total Environment, 912, 168822.
Guan, D., Zhao, J., Wang, Y., Fu, Z., Zhang, D., Zhang, H., Xie, J., Sun, Y., Zhu, J., & Wang, D. (2024). A critical review on sustainable management and resource utilization of digestate. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 183, 339–354.
Liu, X., Liu, H., Chen, J., Du, G., & Chen, J. (2008). Enhancement of solubilization and acidification of waste activated sludge by pretreatment. Waste Management, 28(12), 2614–2622.
Nguyen, V. K., Chaudhary, D. K., Dahal, R. H., Trinh, N. H., Kim, J., Chang, S. W., Hong, Y., La, D. D., Nguyen, X., Ngo, H., Chung, W. J., & Nguyen, D. D. (2021). Review on pretreatment techniques to improve anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Fuel, 285, 119105.
Zhao, J., Yang, Q., Li, X., Wang, D., Luo, K., Zhong, Y., Xu, Q., & Zeng, G. (2015). Enhanced production of short-chain fatty acid from food waste stimulated by alkyl polyglycosides and its mechanism. Waste Management, 46, 133–139.
Wu, Y., Song, X., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Su, B., & Zhou, Y. (2023). Effects of free nitrous acid combined with alkyl polyglucoside on short-chain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge anaerobic fermentation and fermentation liquor for polyhydroxyalkanoates synthesis. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 52, 103515.
Liu, Y., Zhao, J., Li, X., Wang, D., Yang, Q., & Zeng, G. (2018). Synergistic effect of free nitrous acid integrated with biosurfactant alkyl polyglucose on sludge anaerobic fermentation. Waste Management, 78, 310–317.
Li, Q., Huang, Y., Wen, D., Fu, R., & Feng, L. (2020). Application of alkyl polyglycosides for enhanced bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil using Sphingomonas changbaiensis and Pseudomonas stutzeri. Science of the Total Environment, 719, 137456.
Jiang, R., Ren, F., & Yao, J. (2022). Alkyl polyglycosides enhanced the dark fermentation of excess sludge and plant waste to produce hydrogen: Performance and mechanism. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(45), 68087–68095.
Luo, J., Feng, L., Chen, Y., Sun, H., Shen, Q., Li, X., & Chen, H. (2015). Alkyl polyglucose enhancing propionic acid enriched short-chain fatty acids production during anaerobic treatment of waste activated sludge and mechanisms. Water Research, 73, 332–341.
Zhao, J., Yuan, Q., Sun, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, D., & Bian, R. (2021). Effect of fluoxetine on enhanced biological phosphorus removal using a sequencing batch reactor. Bioresource Technology, 320, 124396.
Qin, X., Tao, R., Cheng, S., Xing, B., Meng, W., Nie, Y., Zhang, C., & Yu, J. (2024). Microwave-assisted one-pot method preparation of ZnO decorated biochar for levofloxacin and Cr (VI) removal from wastewater.Industrial Crops and Products, 208, 117863.
Feng, L., Yuan, F., Xie, J., Duan, X., Zhou, Q., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., Fei, Z., Yan, Y., & Wang, F. (2022). Sulfadiazine inhibits hydrogen production during sludge anaerobic fermentation by affecting pyruvate decarboxylation. Science of the Total Environment, 838, 156415.
Wang, Y., Zhao, J., Fu, Z., Guan, D., Zhang, D., Zhang, H., Zhang, Q., Xie, J., Sun, Y., & Wang, D. (2024). Innovative overview of the occurrence, aging characteristics, and ecological toxicity of microplastics in environmental media. Environmental Pollution, 123623.
Zhao, J., Zhang, H., Guan, D., Wang, Y., Fu, Z., Sun, Y., Wang, D., & Zhang, H. (2023). New insights into mechanism of emerging pollutant polybrominated diphenyl ether inhibiting sludge dark fermentation. Bioresource Technology, 368, 128358.
Cheng, S., Zhao, S., Xing, B., Shi, C., Meng, W., Zhang, C., & Bo, Z. (2022). Facile one-pot green synthesis of magnetic separation photocatalyst-adsorbent and its application. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 47, 102802.
Li, X., Xie, H., Sun, Y., Liu, F., Yang, Y., Liu, G., & Wang, K. (2022). Hydrolyzation characteristics of waste actived sludge and antibiotics release when improved with alkyl polyglycoside. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(3), 107552.
Stein, U. H., Wimmer, B., Ortner, M., Fuchs, W., & Bochmann, G. (2017). Maximizing the production of butyric acid from food waste as a precursor for ABE-fermentation. Science of the Total Environment, 598, 993–1000.
Yu, P., Tu, W., Wu, M., Zhang, Z., & Wang, H. (2021). Pilot-scale fermentation of urban food waste for volatile fatty acids production: The importance of pH. Bioresource Technology, 332, 125116.
Zhang, H., Zhao, J., Fu, Z., Wang, Y., Guan, D., Xie, J., Zhang, Q., Liu, Q., Wang, D., & Sun, Y. (2023). Metagenomic approach reveals the mechanism of calcium oxide improving kitchen waste dry anaerobic digestion. Bioresource Technology, 387, 129647.
Chen, Y., Yin, Y., & Wang, J. (2021). Recent advance in inhibition of dark fermentative hydrogen production. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 46(7), 5053–5073.
Cheng, S., Xing, B., Shi, C., Nie, Y., & Xia, H. (2021). Efficient and selective removal of pb (II) from aqueous solution by modification crofton weed: Experiment and density functional theory calculation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 280, 124407.
Jain, R., Panwar, N. L., Jain, S. K., Gupta, T., Agarwal, C., & Meena, S. S. (2022). Bio-hydrogen production through dark fermentation: An overview. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 1–26.
Wong, Y. M., Wu, T. Y., & Juan, J. C. (2014). A review of sustainable hydrogen production using seed sludge via dark fermentation. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 34, 471–482.
Rafieenia, R., Lavagnolo, M. C., & Pivato, A. (2018). Pre-treatment technologies for dark fermentative hydrogen production: Current advances and future directions. Waste Management, 71, 734–748.
Wang, D., Duan, Y., Yang, Q., Liu, Y., Ni, B. J., Wang, Q., Zeng, G., Li, X., & Yuan, Z. (2018). Free ammonia enhances dark fermentative hydrogen production from waste activated sludge. Water Research, 133, 272–281.
Wang, Y., Zhao, J., Wang, D., Liu, Y., Wang, Q., Ni, B. J., Chen, F., Yang, Q., Li, X., Zeng, G., & Yuan, Z. (2018). Free nitrous acid promotes hydrogen production from dark fermentation of waste activated sludge. Water Research, 145, 113–124.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the project of Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (No. 152208318).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xuemei Yang: writing—original draft. Tiantian Yang: writing—review and editing. Yazhou Xu: writing—review and editing, project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This is an experimental paper.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for Publication
The authors provided informed consent for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Yang, T. & Xu, Y. Novel Insights into Alkyl Polyglucoside Biosurfactant Promoting Anaerobic Dark Fermentation for Hydrogen Production in Sludge. Appl Biochem Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-024-04923-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-024-04923-5