Abstract
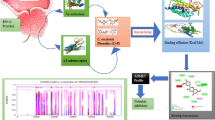
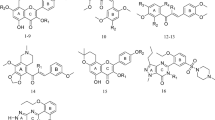
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a major challenge for men. The drugs for its treatment are associated with side effects. Hence, in phytomedicinal research, where Anonna senegalensis (A. senegalensis) is a candidate with abundant phytochemicals possessing various pharmacological properties, but the sex-enhancing phytochemical is elusive in the literature. This study aimed to understand the molecular interaction of its potent molecule mediating male sexual enhancement. A library of 69 compounds from A. senegalensis was docked against the ED-targeted proteins. Sildenafil citrate was used as the reference standard. Thereafter, the lead compound was screened for drug-likeness by applying the Lipinski rule of 5 (RO5), pharmacokinetic properties, and bioactivity using SwissADME and Molinspiration web servers, respectively. The results show catechin as the lead phytochemical compound with a stronger binding affinity for most of the proteins of ED. Also, catechin demonstrates good compliance with the RO5, great pharmacokinetic profiles, and could be said to be a polypharmacological molecule with good bioactivity scores. The research findings unravel the potential of catechin (a phytochemical belonging to the flavonoids class) from A. senegalensis leaf as a potential male sexual enhancement molecule via its high binding affinity for most erectile dysfunction-targeted proteins. They may require further toxicity and therapeutic evaluations in vivo.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Available upon request from the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- 3α-HSD :
-
3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
- AChE :
-
acetylcholinesterase
- ADA :
-
adenosine deaminase
- BBB :
-
blood-brain barrier
- Caco-2 :
-
cancer coli, “colon cancer”
- cGMP :
-
cyclic guanosine monophosphate
- CYP3A4 :
-
cytochrome P450 3A4
- DHT :
-
dihydrotestosterone
- ED :
-
erectile dysfunction
- EI :
-
enzyme inhibitor
- GI-A :
-
human gastrointestinal absorption
- GLIDE :
-
grid-based Ligand Docking with Energetics
- GPCR :
-
G protein-coupled receptors
- HERG-K+ :
-
human ether-à-go-go related gene potassium channel encoded
- IK :
-
inhibitor of kinase
- IP :
-
inhibitor protease
- Log KP :
-
human skin permeability coefficients
- MIC :
-
modulator of ion channels
- NADP :
-
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- NO :
-
nitric oxide
- NR :
-
nuclear receptor
- OGT :
-
O-GlcNAc transferase
- OPLS-3e :
-
optimized Potentials for Liquid Simulations-3e
- PDE-5 :
-
phosphodiesterase type-5
- PE :
-
penile erection
- PKC :
-
protein kinase C
- PKG :
-
protein kinase target
- RCSB PDB :
-
Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics Protein Data Bank
- RO5 :
-
lipinski rule of 5
- WS :
-
water solubility
References
Chen, L., Shi, G. R., Huang, D. D., Li, Y., Ma, C. C., Shi, M., Su, B. X., & Shi, G. J. (2019). Male sexual dysfunction: A review of literature on its pathological mechanisms, potential risk factors, and herbal drug intervention. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie, 112, 108585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.01.046
Oboh, G., Adebayo, A. A., Ademosun, A. O., & Boligon, A. A. (2017). In vitro inhibition of phosphodiesterase-5 and arginase activities from rat penile tissue by two Nigerian herbs (Hunteria umbellata and Anogeissus leiocarpus). Journal of Basic and Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology, 28(4), 393–401. https://doi.org/10.1515/jbcpp-2016-0143
Burnett, A. L. (2006). The role of nitric oxide in erectile dysfunction: Implications for medical therapy. Journal of Clinical Hypertension (Greenwich, Conn.), 8(12 Suppl 4), 53–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-6175.2006.06026.x
Kessler, A., Sollie, S., Challacombe, B., Briggs, K., & Van Hemelrijck, M. (2019). The global prevalence of erectile dysfunction: A review. BJU International, Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.14813
Ismail, E. A., & El-Sakka, A. I. (2016). Innovative trends and perspectives for erectile dysfunction treatment: A systematic review. Arab Journal of Urology, 14(2), 84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aju.2016.04.002
Saxena, A., Prakash, P., Porwal, M., Sissodia, N., & Sharma, P. (2012). Erectile dysfunction: A review and herbs used for its treatment. International Journal of Green Pharmacy (IJGP), 6(2).
Li, X., Zhao, Q., Wang, J., Wang, J., Dai, H., Li, H., & Wang, B. (2018). Efficacy and safety of PDE5 inhibitors in the treatment of diabetes mellitus erectile dysfunction: Protocol for a systematic review. Medicine, 97(40), e12559. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000012559
Abdillahi, H. S., & Van Staden, J. (2012). South African plants and male reproductive healthcare: Conception and contraception. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 143(2), 475–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.06.047
Chauhan, N. S., Sharma, V., Dixit, V. K., & Thakur, M. (2014). A review on plants used for improvement of sexual performance and virility. BioMed Research International, 2014, 868062. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/868062
Adefegha, S. A., Oboh, G., Oyeleye, S. I., Dada, F. A., Ejakpovi, I., & Boligon, A. A. (2017). Cognitive enhancing and antioxidative potentials of velvet beans (Mucuna pruriens) and horseradish (Moringa oleifera) seeds extracts: A comparative study. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 41(1), e12292.
Oboh, G., Ademiluyi, A. O., Ademosun, A. O., Olasehinde, T. A., Oyeleye, S. I., Boligon, A. A., & Athayde, M. L. (2015). Phenolic extract from Moringa oleifera leaves inhibits key enzymes linked to erectile dysfunction and oxidative stress in rats’ penile tissues. Biochemistry Research International, 2015, 175950. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/175950
Akomolafe, S. F., Oboh, G., Oyeleye, S. I., & Boligon, A. A. (2016). Aqueous extract from Ficus capensis leaves inhibits key enzymes linked to erectile dysfunction and prevent oxidative stress in rats’ penile tissue. NFS Journal, 4, 15–21.
Ojo, A. B., Ojo, O. A., Okesola, M. A., Ajiboye, B. O., & Oyinloye, B. E. (2019). Garcinia kola extracts improve biochemical markers associated with erectile function: Possible applications in clinical treatment? Acta Facultatis Medicae Naissensis, 36(1), 15–26.
Ojo, O. A., Ojo, A. B., Oyinloye, B. E., Ajiboye, B. O., Anifowose, O. O., Akawa, A., Olaiya, O. E., Olasehinde, O. R., & Kappo, A. P. (2019). Ocimum gratissimum Linn. Leaves reduce the key enzymes activities relevant to erectile dysfunction in isolated penile and testicular tissues of rats. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 19(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-019-2481-0
NaAllah, A., Ayipo, Y. O., Komolafe, D. I., Solihu, S., Bamidele, B., Alabi, M. A., et al. (2021). Phytochemical screening and in silico pharmacological profiling of ethanolic extract of Aframomum melegueta for prostate carcinoma. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 11(7), 132â–1145.
Ayipo, Y. O., Osunniran, W. A., & Mordi, M. N. (2021). Metal complexes of β-carboline: Advances in anticancer therapeutics. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 432, 213746.
Skok, Ž., Zidar, N., Kikelj, D., & Ilaš, J. (2020). Dual inhibitors of human DNA topoisomerase II and other cancer-related targets. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 63(3), 884–904. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00726
Adefegha, S. A., Oboh, G., Fakunle, B., Oyeleye, S. I., & Olasehinde, T. A. (2018). Quercetin, rutin, and their combinations modulate penile phosphodiesterase-5′, arginase, acetylcholinesterase, and angiotensin-I-converting enzyme activities: A comparative study. Comparative Clinical Pathology, 27(3), 773–780.
Goswami, S. K., Inamdar, M. N., Jamwal, R., & Dethe, S. (2014). Effect of Cinnamomum cassia methanol extract and sildenafil on arginase and sexual function of young male Wistar rats. The Journal of Sexual Medicine, 11(6), 1475–1483. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsm.12535
Ademosun, A. O., Adebayo, A. A., & Oboh, G. (2019). Anogeissus leiocarpus attenuates paroxetine-induced erectile dysfunction in male rats via enhanced sexual behavior, nitric oxide level and antioxidant status. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 111, 1029–1035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.01.022
Afolabi, F., & Afolabi, O. J. (2013). Phytochemical Constituents of some medicinal plants in South West, Nigeria. IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry, 4(1), 76–78.
Jada, M., Usman, W., & Olabisi, A. (2015). Crude flavonoids isolated from the stem bark of annona senegalensis have antimicrobial activity. Journal of Advances in Biology & Biotechnology, 2(1), 24–29. https://doi.org/10.9734/JABB/2015/11884
Lall, N., Kishore, N., Bodiba, D., More, G., Tshikalange, E., Kikuchi, H., & Oshima, Y. (2017). Alkaloids from aerial parts of Annona senegalensis against Streptococcus mutans. Natural Product Research, 31(16), 1944–1947. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2016.1263847
Jiofack, T., Fokunang, C., Guedje, N., Kemeuze, V., Fongnzossie, E., Nkongmeneck, B., Mapongmetsem, P., et al. (2009). Ethnobotanical uses of some plants of two ethnoecological regions of cameroon. African Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 3(13), 664–684.
Faleyimu, O., Ahmad, I., & Akinyemi, O. (2010). Herbal approach to the treatment of chicken pox: A case study of Giwa Local Government, Kaduna State, Nigeria. International Journal of Biomedical and Health Sciences, 6(1), 13–18.
Nanti, G. G. C. G., Bi, S. A. N., Zahoui, O. S., & Traore, F. (2018). Comparative study of Annona senegalensis (Annonaceae) and Hallea ledermannii (Rubiacaceae) effects on glycemia in rats. Journal of Complementary Medicine Research, 7(1), 1–1. https://doi.org/10.5455/jice.20170909091946
Madièye, S., Firmin, S. B., Abdou, S., Dominique, T. O., Alassane, W., Emmanuel, B., & Guata, Y. S. Y. (2017). Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of methanolic fraction of total ethereal leaf extract of Annona senegalensis Pers. (Annonaceae). African Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 11(8), 120–124. https://doi.org/10.5897/ajpp2017.4735
Dandjesso, C., Klotoé, J. R., Dougnon, T. V., Sègbo, J., Atègbo, J. M., Gbaguidi, F., et al. (2012). Phytochemistry and hemostatic properties of some medicinal plants sold as anti-hemorrhagic in Cotonou markets (Benin). Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 5(8), 3105–3109. https://doi.org/10.17485/IJST/2012/V5I8.10
Ajboye, T. O., Yakubu, M. T., Salau, A. K., Oladiji, A. T., Akanji, M. A., & Okogun, J. I. (2010). Antioxidant and drug detoxification potential of aqueous extract of Annona senegalensis leaves in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatocellular damage. Pharmaceutical Biology, 48(12), 1361–1370. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2010.483247
Okoye, T. C., Akah, P. A., Ezike, A. C., & Nwoye, J. C. (2011). Studies on the effects of Annona senegalensis root bark extract on acute and chronic inflammation in rats. Journal of Pharmacy Research, 4(5), 1443–1444.
Konate, A., Sawadogo, W. R., Dubruc, F., Caillard, O., & Guissou, I. P. (2012). Anticonvulsant effects of the stem bark extract of Annona senegalensis Pers. Molecular & Clinical Pharmacology, 3(1), 62–72.
Michael, O. G., Abimbade, F. I., & Ade, O. M. (2014). Effect of aqueous extract of Annonasenegalensis leaves on the spermiogram of male albino rats. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 3(8), 409–418.
Nwonuma, C., Irokanulo, E., Jolaiya, A., & Ore, A. (2015). Effect of aqueous leaf extract of annona senegalensis on selected testicular function indices of wistar rats. American Journal of Life Sciences, 3(3), 203–212. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajls.20150303.21
Poroikov, V. V., Filimonov, D. A., Gloriozova, T. A., Lagunin, A. A., Druzhilovskiy, D. S., Rudik, A. V., et al. (2019). Computer-aided prediction of biological activity spectra for organic compounds: The possibilities and limitations. Russian Chemical Bulletin, 68(12), 2143–2154.
Ameen, O. M., Usman, L. A., Oganija, F. S., Hamid, A. A., Muhammed, N. O., Zubair, M. F., & Adebayo, S. A. (2011). Chemical composition of leaf essential oil of Annona senegalensis Pers.(Annonaceae) growing in North Central Nigeria. International Journal of Biological and Chemical Sciences, 5(1).
Okhale, S. E., Akpan, E., Fatokun, O. T., Esievo, K. B., & Kunle, O. F. (2016). Annona senegalensis Persoon (Annonaceae): A review of its ethnomedicinal uses, biological activities and phytocompounds. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 5(2), 211.
Harder, E., Damm, W., Maple, J., Wu, C., Reboul, M., Xiang, J. Y., Wang, L., Lupyan, D., Dahlgren, M. K., Knight, J. L., Kaus, J. W., Cerutti, D. S., Krilov, G., Jorgensen, W. L., Abel, R., & Friesner, R. A. (2016). OPLS3: A force field providing broad coverage of drug-like small molecules and proteins. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 12(1), 281–296. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00864
Inyang, O. K., Omotuyi, O. I., Ogunleye, A. J., Eniafe, G. O., Adewumi, B., & Metibemu, D. S. (2017). Molecular interaction and inhibitory potential of polyphenol on DNA repair pathway in small cell lung cancer: A computational study. Journal of Analytical & Pharmaceutical Research, 6, 00178–00186.
Ehigiator, B. E., Adesida, A. S., & Omotuyi, I. O. (2020). Chicoric acid, a phytochemical compound of Solenostemon monostachyus: Possible drug candidate for the relief of erectile dysfunction. International Journal in Applied Science and Engineering Technology, 4, 509–518. https://doi.org/10.33564/Ijeast.2020.V04i11.091
Omotuyi, I. O., Nash, O., Ajiboye, B. O., Olumekun, V. O., Oyinloye, B. E., Osuntokun, O. T., Olonisakin, A., Ajayi, A. O., Olusanya, O., Akomolafe, F. S., & Adelakun, N. (2021). Aframomum melegueta secondary metabolites exhibit polypharmacology against SARS-CoV-2 drug targets: In vitro validation of furin inhibition. Phytotherapy research: PTR, 35(2), 908–919. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6843
David, T. I., Adelakun, N. S., Omotuyi, O. I., Metibemu, D. S., Ekun, O. E., Eniafe, G. O., Inyang, O. K., Adewumi, B., Enejoh, O. A., Owolabi, R. T., & Oribamise, E. I. (2018). Molecular docking analysis of phyto-constituents from Cannabis sativa with pfDHFR. Bioinformation, 14(9), 574–579. https://doi.org/10.6026/97320630014574
Daina, A., Michielin, O., & Zoete, V. (2017). SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Scientific Reports, 7, 42717. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42717
Lipinski, C. A. (2004). Lead- and drug-like compounds: The rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discovery Today: Technologies, 1(4), 337–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddtec.2004.11.007
Mishra, S. S., Kumar, N., Singh, H. P., Ranjan, S., & Sharma, C. S. (2018). In silico pharmacokinetic, bioactivity and toxicity study of some selected anti-asthmatic agents. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Drug Research, 10(4), 278–282. https://doi.org/10.25004/ijpsdr.2018.100411
Abd, N., Salam, E., & El, S. (2017). Virtual screening, drug likeness, bioavailability and docking studies of small molecules of heterocyclic. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 6(3), 1145–1160. https://doi.org/10.20959/wjpps20173-8821
Atere, T. G., Akinloye, O. A., Ugbaja, R. N., Ojo, D. A., & Metibemu, D. S. (2017). Molecular interactions and docking studies of the phytochemical constituents of costus afer against therapeutic targets of type 2 diabetes. Journal of Applied Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, 6(2), 2. https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-9533.1000139
Metibemu, D. S., Akinloye, O. A., Akamo, A. J., Okoye, J. O., Ojo, D. A., Morifi, E., & Omotuyi, I. O. (2020). Carotenoid isolates of Spondias mombin demonstrate anticancer effects in DMBA-induced breast cancer in Wistar rats through X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) antagonism and anti-inflammation. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 44(12), e13523. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.13523
Metibemu, D. S., Akinloye, O. A., Akamo, A. J., Okoye, J. O., Ojo, D. A., Morifi, E., & Omotuyi, I. O. (2021). VEGFR-2 kinase domain inhibition as a scaffold for anti-angiogenesis: Validation of the anti-angiogenic effects of carotenoids from Spondias mombin in DMBA model of breast carcinoma in Wistar rats. Toxicology Reports, 8, 489–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.02.011
Iwaloye, O., Elekofehinti, O. O., Babatomiwa, K., & Fadipe, T. M. (2020). In silico molecular studies of selected compounds as novel inhibitors for phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) in the management of erectile dysfunction. J Comput Sci Syst Biol, 13(307), 2. https://doi.org/10.37421/jcsb.2020.13.307
Ojo, O. A., Ojo, A. B., Okolie, C., Nwakama, M. A. C., Iyobhebhe, M., Evbuomwan, I. O., Nwonuma, C. O., Maimako, R. F., Adegboyega, A. E., Taiwo, O. A., Alsharif, K. F., & Batiha, G. E. S. (2021a). Deciphering the interactions of bioactive compounds in selected traditional medicinal plants against alzheimer’s diseases via pharmacophore modeling, auto-QSAR, and molecular docking approaches. Molecules, 26(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071996
Ojo, O. A., Ojo, A. B., Maimako, R. F., Rotimi, D., Iyobhebhe, M., Alejolowo, O. O., Nwonuma, C. O., & Elebiyo, T. C. (2021). Exploring the potentials of some compounds from Garcinia kola seeds towards identification of novel PDE-5 inhibitors in erectile dysfunction therapy. Andrologia, 53(7), e14092. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.14092
Selvaraj, G., Kaliamurthi, S., & Thiruganasambandam, R. (2016). Molecular docking studies of rutin on matrix metalloproteinase. Insights Biomed, 1(1).
Gurung, A. B., Ali, M. A., Lee, J., Farah, M. A., & Al-Anazi, K. M. (2021). Molecular docking and dynamics simulation study of bioactive compounds from Ficus carica L. with important anticancer drug targets. PLoS One, 16(7), e0254035. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0254035
Wopara, I., Mobisson, S. K., Pius, E. A., Uwakwe, A. A., & Wegwu, M. O. (2020). Inhibition of phosphodiesterase 5 enzyme by Pterine-6 carboxylic acid from Baphia nitida–related to erectile dysfunction: Computational kinetic. European Journal of Medicinal Plants, 31, 49–55. https://doi.org/10.9734/EJMP/2020/v31i430231
Ismail, S. Y., Uzairu, A., Sagagi, B., & Suleiman, M. S. (2018). In silico molecular docking and pharmacokinetic study of selected phytochemicals with estrogen and progesterone receptors as anticancer agent for breast cancer. Journal of the Turkish Chemical Society, Section A: Chemistry, 5(3), 1337–1350. https://doi.org/10.18596/jotcsa.449778
Dar, A. M., & Mir, S. (2017). Molecular docking: Approaches, types, applications and basic challenges. Journal of Analytical & Bioanalytical Techniques, 08(02), 8–10. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9872.1000356
Abdullahi, S. M., Musa, A. M., Abdullahi, M. I., Sani, Y. M., & Atiku, I. (2017). Catechin from the leaf extract of Ziziphus mucronata Willd.(Rhamnaceae). Nigerian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 16(2), 01–05.
Reddy, G. L., Dar, M. I., Hudwekar, A. D., Mahajan, P., Nargotra, A., Baba, A. M., Nandi, U., Wazir, P., Singh, G., Vishwakarma, R. A., Syed, S. H., & Sawant, S. D. (2019). Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of pyrazolopyrimidinone based potent and selective PDE5 inhibitors for treatment of erectile dysfunction. Bioorganic Chemistry, 89, 103022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103022
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The conception and design of the study were carried out by FMA, AAF, TIA, and OIO, data collection and analysis were performed by FMA, AAF, and OIO. The first draft of the manuscript was written by FMA, AFO, BE, and all other authors made adequate contributions thereafter so as to improve the first draft which give birth to the final manuscript that was read and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable. This is an in silico study.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors read and approved the manuscript for publication
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Folawiyo, M.A., Omotuyi, I.O., Ajao, F.O. et al. Catechin from Anonna senegalensis is a Potential Inhibitor of Erectile Dysfunction: Implication for Its Use in Male Sexual Enhancement. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 4936–4964 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04557-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04557-z