Abstract
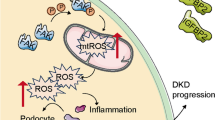
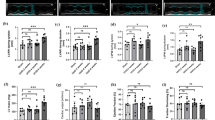
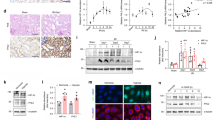
Emerging evidences suggested that circular RNAs (circRNAs) are involved in diabetic nephropathy (DN). Accumulating evidence had suggested that the degree of podocyte is a major prognostic determinant of DN progression. However, the function and in-depth mechanisms of hsa_circ_0001162 in podocyte injury of DN remain unclear. Hsa_circ_0001162 expression was detected by real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in peripheral blood of DN patients and high glucose-induced podocytes injury model. The cell counting kit 8, 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine, flow cytometry with Annexin V-FITC/PI staining, caspase-3 activity assay Kit, enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), RT-qPCR and western blotting were used to evaluate the effect of hsa_circ_0001162 / miR-149-5p / MMP9 axis on high glucose-induced podocyte injury. Mechanistically, dual luciferase reporter was used to confirm the relationship of miR-149-5p and hsa_circ_0001162 or MMP9. Furthermore, RNA-pull down and immunoprecipitation assay were implemented to verify the potential regulatory effects of EIF4A3 on biogenesis of hsa_circ_0001162. Our results showed that hsa_circ_0001162 was highly expressed in peripheral blood of DN patients and high glucose-induced podocytes injury model, and the knockdown of hsa_circ_0001162 increased the proliferation, inhibited the apoptosis, and suppressed inflammatory response in high glucose-induced podocytes injury. Mechanism studies demonstrated that EIF4A3 bound with flanking sequences of hsa_circ_0001162 to promote hsa_circ_0001162 expression, upregulated hsa_circ_0001162 increased the MMP9 expression via sponging miR-149-5p, thus aggravating the high glucose-induced podocytes injury. Overall, our data demonstrated that knockdown of hsa_circ_0001162 inhibited high glucose-induced podocytes injury by regulating miR-149-5p/MMP9 axis, and intervention of hsa_circ_0001162/miR-149-5p/MMP9 axis may be a potentially promising therapeutic strategy for podocyte injury in DN patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
References
Maezawa, Y., Takemoto, M., & Yokote, K. (2015). Cell biology of diabetic nephropathy: Roles of endothelial cells, tubulointerstitial cells and podocytes. Journal of diabetes investigation, 6, 3–15.
Suneja, M. (2021). Diabetic Nephropathy and Diabetic Kidney Disease. Journal of Diabetes Mellitus, 11, 359–377.
Jiang, L., Liu, X., Hu, X., Gao, L., Zeng, H., Wang, X., Huang, Y., Zhu, W., Wang, J., Wen, J., Meng, X., & Wu, Y. (2022). METTL3-mediated m(6)A modification of TIMP2 mRNA promotes podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy. Molecular therapy : The journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy, 30, 1721–1740.
Ram, C., Jha, A. K., Ghosh, A., Gairola, S., Syed, A. M., Murty, U. S., Naidu, V. G. M., & Sahu, B. D. (2020). Targeting NLRP3 inflammasome as a promising approach for treatment of diabetic nephropathy: Preclinical evidences with therapeutic approaches. European Journal of Pharmacology, 885, 173503.
Klessens, C. Q. F., Zandbergen, M., Wolterbeek, R., Bruijn, J. A., Rabelink, T. J., Bajema, I. M., & DHT, I. J. (2017). Macrophages in diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 32, 1322–1329.
Tang, S. C. W., & Yiu, W. H. (2020). Innate immunity in diabetic kidney disease. Nature Reviews. Nephrology, 16, 206–222.
Lu, Z., Liu, H., Song, N., Liang, Y., Zhu, J., Chen, J., Ning, Y., Hu, J., Fang, Y., Teng, J., Zou, J., Dai, Y., & Ding, X. (2021). METTL14 aggravates podocyte injury and glomerulopathy progression through N(6)-methyladenosine-dependent downregulating of Sirt1. Cell death & disease, 12, 881.
Yang, X. H., Feng, S. Y., Yu, Y., & Liang, Z. (2018). Study on the relationship between the methylation of the MMP-9 gene promoter region and diabetic nephropathy. Endokrynologia Polska, 69, 269–275.
Cakirca, G., & Turgut, F. H. (2018). Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase-9, Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9/ Neutrophil Gelatinase-associated Lipocalin Complex Levels in Patients With Early-stage Diabetic Nephropathy. Iranian Journal of Kidney Diseases, 12, 299–304.
Ling, L., Chen, L., Zhang, C., Gui, S., Zhao, H., & Li, Z. (2018). High glucose induces podocyte epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by demethylation-mediated enhancement of MMP9 expression. Molecular Medicine Reports, 17, 5642–5651.
Qing-Hua, G., Ju-Ming, L., Chang-Yu, P., Zhao-Hui, L., Xiao-Man, Z., & Yi-Ming, M. (2008). The kidney expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in the diabetic nephropathy of Kkay mice. Journal of Diabetes and Its Complications, 22, 408–412.
Li, G., Zhang, J., Liu, D., Wei, Q., Wang, H., Lv, Y., Ye, Z., Liu, G., & Li, L. (2021). Identification of Hub Genes and Potential ceRNA Networks of Diabetic Nephropathy by Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis. Frontiers in Genetics, 12, 767654.
Zhang, L., Zhao, S., & Zhu, Y. (2020). Long noncoding RNA growth arrest-specific transcript 5 alleviates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by downregulating matrix metalloproteinase 9 through recruitment of enhancer of zeste homolog 2. The FASEB Journal, 34, 2703–2714.
Cortés-López, M., & Miura, P. (2016). Emerging Functions of Circular RNAs. The Yale Journal of Biology and Medicine, 89, 527–537.
Tu, C., Wang, L., Wei, L., & Jiang, Z. (2022). The role of circular RNA in Diabetic Nephropathy. International Journal of Medical Sciences, 19, 916–923.
Fang, R., Cao, X., Zhu, Y., & Chen, Q. (2022). Hsa_circ_0037128 aggravates high glucose-induced podocytes injury in diabetic nephropathy through mediating miR-31-5p/KLF9. Autoimmunity, 55, 254–263.
Yao, T., Zha, D., Hu, C., & Wu, X. (2020). Circ_0000285 promotes podocyte injury through sponging miR-654-3p and activating MAPK6 in diabetic nephropathy. Gene, 747, 144661.
Wang, R., Zhang, S., Chen, X., Li, N., Li, J., Jia, R., Pan, Y., & Liang, H. (2018). EIF4A3-induced circular RNA MMP9 (circMMP9) acts as a sponge of miR-124 and promotes glioblastoma multiforme cell tumorigenesis. Molecular cancer, 17, 166.
Pan, G., Hu, T., Chen, X., & Zhang, C. (2019). Upregulation Of circMMP9 Promotes Osteosarcoma Progression Via Targeting miR-1265/CHI3L1 Axis. Cancer Manag Res, 11, 9225–9231.
Xia, B., Hong, T., He, X., Hu, X., & Gao, Y. (2019). A circular RNA derived from MMP9 facilitates oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through regulation of MMP9 mRNA stability. Cell Transplantation, 28, 1614–1623.
Li, S. Y., Huang, P. H., Yang, A. H., Tarng, D. C., Yang, W. C., Lin, C. C., Chen, J. W., Schmid-Schönbein, G., & Lin, S. J. (2014). Matrix metalloproteinase-9 deficiency attenuates diabetic nephropathy by modulation of podocyte functions and dedifferentiation. Kidney international, 86, 358–369.
Li, Y., Ren, S., Xia, J., Wei, Y., & Xi, Y. (2020). EIF4A3-Induced circ-BNIP3 Aggravated Hypoxia-Induced Injury of H9c2 Cells by Targeting miR-27a-3p/BNIP3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 19, 533–545.
Jiang, Z., Tai, Q., Xie, X., Hou, Z., Liu, W., Yu, Z., Liang, Z., & Chen, S. (2021). EIF4A3-induced circ_0084615 contributes to the progression of colorectal cancer via miR-599/ONECUT2 pathway. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 40, 227.
Liu, Q., & Dong, H. (2021). EIF4A3-mediated hsa_circ_0088088 promotes the carcinogenesis of breast cancer by sponging miR-135-5p. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 35, e22909.
Wei, Y., Lu, C., Zhou, P., Zhao, L., Lyu, X., Yin, J., Shi, Z., & You, Y. (2021). EIF4A3-induced circular RNA ASAP1 promotes tumorigenesis and temozolomide resistance of glioblastoma via NRAS/MEK1/ERK1-2 signaling. Neuro-Oncology, 23, 611–624.
Dudekula, D. B., Panda, A. C., Grammatikakis, I., De, S., Abdelmohsen, K., & Gorospe, M. (2016). CircInteractome: A web tool for exploring circular RNAs and their interacting proteins and microRNAs. RNA biology, 13, 34–42.
Cheng, Q., Pan, J., Zhou, Z. L., Yin, F., Xie, H. Y., Chen, P. P., Li, J. Y., Zheng, P. Q., Zhou, L., Zhang, W., Liu, J., & Lu, L. M. (2021). Caspase-11/4 and gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis contributes to podocyte injury in mouse diabetic nephropathy. Acta pharmacologica Sinica, 42, 954–963.
Liu, H., Wang, X., Wang, Z. Y., & Li, L. (2020). Circ_0080425 inhibits cell proliferation and fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy via sponging miR-24-3p and targeting fibroblast growth factor 11. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 235, 4520–4529.
Sun, Z., Xu, Q., Ma, Y., Yang, S., & Shi, J. (2021). Circ_0000524/miR-500a-5p/CXCL16 axis promotes podocyte apoptosis in membranous nephropathy. European Journal of Clinical Investigation, 51, e13414.
Jin, J., Wang, Y., Zheng, D., Liang, M., & He, Q. (2022). A Novel Identified Circular RNA, mmu_mmu_circRNA_0000309, Involves in Germacrone-Mediated Improvement of Diabetic Nephropathy Through Regulating Ferroptosis by Targeting miR-188-3p/GPX4 Signaling Axis. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 36, 740–759.
Pagtalunan, M. E., Miller, P. L., Jumping-Eagle, S., Nelson, R. G., Myers, B. D., Rennke, H. G., Coplon, N. S., Sun, L., & Meyer, T. W. (1997). Podocyte loss and progressive glomerular injury in type II diabetes. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 99, 342–348.
Su, J., Li, S. J., Chen, Z. H., Zeng, C. H., Zhou, H., Li, L. S., & Liu, Z. H. (2010). Evaluation of podocyte lesion in patients with diabetic nephropathy: Wilms’ tumor-1 protein used as a podocyte marker. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 87, 167–175.
Siu, B., Saha, J., Smoyer, W. E., Sullivan, K. A., & Brosius, F. C., 3rd. (2006). Reduction in podocyte density as a pathologic feature in early diabetic nephropathy in rodents: Prevention by lipoic acid treatment. BMC Nephrology, 7, 6.
Kristensen, L. S., Andersen, M. S., Stagsted, L. V. W., Ebbesen, K. K., Hansen, T. B., & Kjems, J. (2019). The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nature Reviews Genetics, 20, 675–691.
Jin, J., Wang, Y., Zheng, D., Liang, M., & He, Q. (2021). A novel identified circular RNA, mmu_mmu_circRNA_0000309 involves in Germacrone-mediated the improvement of diabetic nephropathy through regulating ferroptosis by targeting miR-188-3p/GPX4 signaling axis. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2021.0063
Fang, R., Cao, X., Zhu, Y., & Chen, Q. (2022). Hsa_circ_0037128 aggravates high glucose-induced podocytes injury in diabetic nephropathy through mediating miR-31-5p/KLF9. Autoimmunity. https://doi.org/10.1080/08916934.2022.2037128,1-10
Zhou, J., Zhang, S., Chen, Z., He, Z., Xu, Y., & Li, Z. (2019). CircRNA-ENO1 promoted glycolysis and tumor progression in lung adenocarcinoma through upregulating its host gene ENO1. Cell death & disease, 10, 885.
Hansen, T. B., Jensen, T. I., Clausen, B. H., Bramsen, J. B., Finsen, B., Damgaard, C. K., & Kjems, J. (2013). Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature, 495, 384–388.
Panda, A. C. (2018). Circular RNAs Act as miRNA Sponges. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1087, 67–79.
Zhou, D., Lin, X., Wang, P., Yang, Y., Zheng, J., & Zhou, D. (2021). Circular RNA circ_0001162 promotes cell proliferation and invasion of glioma via the miR-936/ERBB4 axis. Bioengineered, 12, 2106–2118.
Ghafouri-Fard, S., Khoshbakht, T., Hussen, B. M., Kadkhoda, S., Taheri, M., Tafrishinejad, A. (2021). A Review on the Role of miR-149–5p in the Carcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 23.
Ren, F. J., Yao, Y., Cai, X. Y., Cai, Y. T., Su, Q., & Fang, G. Y. (2021). MiR-149-5p: An Important miRNA Regulated by Competing Endogenous RNAs in Diverse Human Cancers. Frontiers in Oncology, 11, 743077.
Ye, Z. M., Yang, S., Xia, Y. P., Hu, R. T., Chen, S., Li, B. W., Chen, S. L., Luo, X. Y., Mao, L., Li, Y., Jin, H., Qin, C., & Hu, B. (2019). LncRNA MIAT sponges miR-149-5p to inhibit efferocytosis in advanced atherosclerosis through CD47 upregulation. Cell Death & Disease, 10, 138.
Law, Y. Y., Lee, W. F., Hsu, C. J., Lin, Y. Y., Tsai, C. H., Huang, C. C., Wu, M. H., Tang, C. H., & Liu, J. F. (2021). miR-let-7c-5p and miR-149-5p inhibit proinflammatory cytokine production in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Aging (Albany NY), 13, 17227–17236.
Wang, W., Feng, J., Zhou, H., & Li, Q. (2020). Circ_0123996 promotes cell proliferation and fibrosisin mouse mesangial cells through sponging miR-149-5p and inducing Bach1 expression. Gene, 761, 144971.
Wang, W., Feng, J., Zhou, H., & Li, Q. (2020). Circ_0123996 promotes cell proliferation and fibrosis in mouse mesangial cells through sponging miR-149-5p and inducing Bach1 expression. Gene, 761, 144971.
Qiu, D., Zhao, N., Chen, Q., & Wang, M. (2022). Knockdown of circ_CDYL Contributes to Inhibit Angiotensin II-Induced Podocytes Apoptosis in Membranous Nephropathy via the miR-149-5p/TNFSF11 Pathway. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology, 79, 887–895.
Chan, C. C., Dostie, J., Diem, M. D., Feng, W., Mann, M., Rappsilber, J., & Dreyfuss, G. (2004). eIF4A3 is a novel component of the exon junction complex. RNA, 10, 200–209.
Huang, W. H., Yang, Q., & Zhang, C. (2022). eIF4A3-induced circWAC promotes breast cancer progression through mediating miR-599/E2F3 axis. Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences, 38, 321–335.
Funding
This work was supported by Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission Fund of 2022 (grant number: JCYJ20220530141600002) and Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission Fund of 2021 (grant number: JCYJ20210324112408022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ling Ye and Shenglang Zhu contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection and analysis were performed by Jiehui Chen, Dandan Xu, Ling Ye, Shenglang Zhu, Yun Yang, and Mingpei Shi. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Ling Ye and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Huazhong University of Science and Technology Union Shenzhen Hospital (No. LW-2022–004) and peforemed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to Participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, L., Chen, Jh., Zhu, Sl. et al. Hsa_circ_0001162 Inhibition Alleviates High Glucose-Induced Human Podocytes Injury by the miR-149-5p/MMP9 Signaling Pathway. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 7255–7276 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04431-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04431-y