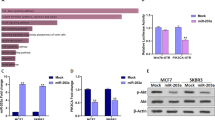
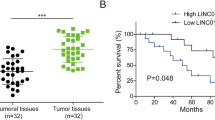
Abstract
Breast cancer (BC) is a highly aggressive tumour and one of the women’s leading causes of cancer-related deaths in worldwide. MiR-375 overexpressed in BC cells, and its biological relevance is largely unknown. Here in, we explored the function of miR-375 in BC. MicroRNA-375 targets were predicted by online target prediction tools and found that HOXA5 is one of the potential targets. MTT assay was employed to assess the effect of miR-375 on cell proliferation, where migration and invasion transwell assays were applied to detect cell migratory and invasive ability. Besides, relative expression of miR-375 and HOXA5 was measured in BC and HEK-293 cells, and its downstream gene target expressions were evaluated by qRT-PCR and western blot. In this study, we found that miR-375 expression was higher in BC cell lines than in the HEK-293 cell line, whereas HOXA5 expression was significantly lower. Our study showed that exogenous inhibition of miR-375 promoted HOXA5 expression; on the contrary, miR-375 mimics down-regulated HOXA5 expression level. Knockdown of miR-375 expression in BC cells reduces cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by inverse correlation expression of HOXA5. Our findings associated that miR-375 accelerated apoptosis evasion, proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting HOXA5. In addition, nucleolin interferes in miR-375 biogenesis while silencing of nucleolin significantly reduced miR-375 expression and increased HOXA5 expression in BC. Thus, miR-375/HOXA5 axis may represent a potential therapeutic target for BC treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., & Bray, F. (2021). Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer Journal for clinicians, 71(3), 209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Chen, C. P., Sun, Z. L., Lu, X., Wu, W. X., Guo, W. L., LU, J. J., Fang, Y. (2015). miR-340 suppresses cell migration and invasion by targeting MYO10 in breast cancer, Oncology Reports, 35(2), 709–716. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.4411
Shibuya, H., Iinuma, H., Shimada, R., Horiuchi, A., & Watanabe, T. (2010). Clinicopathological and Prognostic Value of MicroRNA-21 and MicroRNA-155 in Colorectal Cancer, Oncology,79(3–4), 313–320. https://doi.org/10.1159/000323283
Hu, J., Shan, Z., Hu, K., Ren, F., Zhang, W. E. I., Han, M., Feng, Y. (2016). miRNA-223 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric carcinoma cells via Sp1, International Journal of Oncology, 49(1), 325–335. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2016.3533
Ma, L. (2016). MicroRNA and Metastasis, Advances in Cancer Research (pp. 165–207). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.acr.2016.07.004
Braicu, C., Raduly, L., Morar-Bolba, G., Cojocneanu, R., Jurj, A., Pop, L.-A., Berindan-Neagoe, I. (2018). Aberrant miRNAs expressed in HER-2 negative breast cancers patient. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research : CR, 37(1), 257. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0920-2
Tang, W., Li, G. S., Li, J. D., Pan, W. Y., Shi, Q., Xiong, D.D., Rong, M. H. (2020). The role of upregulated miR-375 expression in breast cancer: An in vitro and in silico study, Pathology-Research and Practice,216(1), 152754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2019.152754
Guan, X., Shi, A., Zou, Y., Sun, M., Zhan, Y., Dong, Y., & Fan, Z. (2021). EZH2-Mediated microRNA-375 Upregulation Promotes Progression of Breast Cancer via the Inhibition of FOXO1 and the p53 Signaling Pathway. Frontiers in Genetics, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.633756
Nurzadeh, M., Naemi, M., & Hasani, S. S. (2021). A comprehensive review on oncogenic miRNAs in breast cancer. Journal of Genetics, 100(1), https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-021-01265-7
Frank, A.-C., Ebersberger, S., Fink, A. F., Lampe, S., Weigert, A., Schmid, T., Brüne, B. (2019). Apoptotic tumor cell-derived microRNA-375 uses CD36 to alter the tumor-associated macrophage phenotype, Nature Communications, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08989-2
Zedan, A. H., Osther, P. J. S., Assenholt, J., Madsen, J. S., & Hansen, T. F. (2020). Circulating miR-141 and miR-375 are associated with treatment outcome in metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer. Scientific Reports, 10(1), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-57101-7
Abramovic, I., Vrhovec, B., Skara, L., Vrtaric, A., Gabaj, N. N., Kulis, T., Sincic, N. (2021). MiR-182-5p and miR-375-3p Have Higher Performance Than PSA in Discriminating Prostate Cancer from Benign Prostate Hyperplasia, Cancers,13(9), 2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092068
Xu, Y., Jin, J., Liu, Y., Huang, Z., Deng, Y., You, T., Zhuo, W. (2014). Snail-Regulated MiR-375 Inhibits Migration and Invasion of Gastric Cancer Cells by Targeting JAK2. PLoS ONE, 9(7), e99516. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099516
Jayamohan, S., Kannan, M., Moorthy, R. K., Rajasekaran, N., Jung, H. S., Shin, Y. K., & Arockiam, A. J. V. (2019). Dysregulation of miR-375/AEG-1 Axis by Human Papillomavirus 16/18-E6/E7 promotes Cellular Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Cervical Cancer. Frontiers in oncology, 9, 847. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00847
Alam, K. J., Mo, J. S., Han, S. H., Park, W. C., Kim, H. S., Yun, K. J., & Chae, S. C. (2017). MicroRNA 375 regulates proliferation and migration of colon cancer cells by suppressing the CTGF-EGFR signaling pathway. International Journal of Cancer, 141(8), 1614–1629. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30861
Xu, X., Liu, Y., Li, Y., Chen, H., Zhang, Y., Liu, J., … Ke, Y. (2021). Selective exosome exclusion of miR-375 by glioma cells promotes glioma progression by activating the CTGF-EGFR pathway. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 40(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-020-01810-9
Zhang, B., Li, Y., Hou, D., Shi, Q., Yang, S., & Li, Q. (2017). MicroRNA-375 inhibits growth and enhances radiosensitivity in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting insulin like growth factor 1 receptor. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 42(5), 2105–2117. https://doi.org/10.1159/000479913
Gehring, W. J., & Hiromi, Y. (1986). Homeotic genes and homeobox. Annual Review of Genetics, 20(1), 147–173. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001051
Anbazhagan, R., & Raman, V. (1997). Homeobox genes: molecular link between congenital anomalies and cancer. European Journal of Cancer, 33(4), 635–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-8049(97)00010-5
Zhang, H., Zhao, J., & Suo, Z. (2017). Knockdown of HOXA5 inhibits the tumorigenesis in esophageal squamous cell cancer. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, 86, 149–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.012
Peng, X., Zha, L., Chen, A., & Wang, Z. (2018). HOXA5 is a tumor suppressor gene that is decreased in gastric cancer. Oncology Reports. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6537
Wang, Y. F., Liu, F., Sherwin, S., Farrelly, M., Yan, X. G., Croft, A., Jiang, C. C. (2018). Cooperativity of HOXA5 and STAT3 Is Critical for HDAC8 Inhibition-Mediated Transcriptional Activation of PD-L1 in Human Melanoma Cells. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 138(4), 922–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2017.11.009
Ma, H. M., Cui, N., & Zheng, P. S. (2020). HOXA5 inhibits the proliferation and neoplasia of cervical cancer cells via downregulating the activity of the Wnt/ß-catenin pathway and transactivating TP53. Cell Death and Disease, 11(6), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2629-3
Kim, D.-S., Kim, M.-J., Lee, J.-Y., Lee, S.-M., Choi, J.-Y., Yoon, G.-S., … Park, J.-Y. (2009). Epigenetic inactivation of Homeobox A5 gene in nonsmall cell lung cancer and its relationship with clinicopathological features. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 48(12), 1109–1115. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.20561
Jeannotte, L., Gotti, F., & Landry-Truchon, K. (2016). Hoxa5: a key player in Development and Disease. Journal of Developmental Biology, 4(2), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb4020013
Henderson, G. S., van Diest, P. J., Burger, H., Russo, J., & Raman, V. (2006). Expression pattern of a homeotic gene, HOXA5, in normal breast and in breast tumors. Analytical Cellular Pathology, 28(5–6), 305–313. https://doi.org/10.1155/2006/974810
Raman, V., Martensen, S. A., Reisman, D., Evron, E., Odenwald, W. F., Jaffee, E., Sukumar, S. (2000). Compromised HOXA5 function can limit p53 expression in human breast tumours. Nature, 405(6789), 974–978. https://doi.org/10.1038/35016125
Godfrey, T. C., Wildman, B. J., Beloti, M. M., Kemper, A. G., Ferraz, E. P., Roy, B., Hassan, Q. (2018). The microRNA-23a cluster regulates the developmental HoxA cluster function during osteoblast differentiation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 293(45), 17646–17660. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.ra118.003052
Wang, H., Wei, H., Wang, J., Li, L., Chen, A., & Li, Z. (2020). MicroRNA-181d-5p-Containing exosomes derived from CAFs promote EMT by regulating CDX2/HOXA5 in breast Cancer. Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids, 19, 654–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2019.11.024
Ferlay, J., Colombet, M., Soerjomataram, I., Parkin, D. M., Piñeros, M., Znaor, A., & Bray, F. (2021). Cancer statistics for the year 2020: an overview. International Journal of Cancer, 149(4), 778–789. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.33588
Kannan, M., Jayamohan, S., Moorthy, R. K., Chabattula, S. C., Ganeshan, M., & Arockiam, A. J. V. (2022). Dysregulation of miRISC Regulatory Network promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911300
Moorthy, R. K., Srinivasan, C., Jayamohan, S., Kannan, M. K., Thirugnanam, S. S., Ganesh, J. S., & Arockiam, A. J. V. (2021). Knockdown of microRNA-375 suppresses cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 14(43), 3199–3209. https://doi.org/10.17485/IJST/v14i43.1719
Moorthy, R. K., Jayamohan, S., Kannan, M. K., & Arockiam, A. J. V. (n.d.). Parthenolide Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest by the Suppression of miR-375 Through Nucleolin in Prostate Cancer. .Journal of Pharmaceutical Research International, 33(45A), 215–227, https://doi.org/10.9734/jpri/2021/v33i45A32736
Zhang, Z. W., Men, T., Feng, R. C., Li, Y. C., Zhou, D., & Teng, C. B. (2013). miR-375 inhibits proliferation of mouse pancreatic progenitor cells by targeting YAP1. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 32(6), 1808–1817. https://doi.org/10.1159/000356614
Vickers, N. J. (2017). Animal Communication: when I’m calling you, will you answer too? Current Biology, 27(14), R713–R715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.05.064.
Chen, L., Li, X., Zhao, Y., Liu, W., Wu, H., Liu, J., Wu, H. (2017). Down-regulated microRNA-375 expression as a predictive biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer brain metastasis and its prognostic significance. Pathology - Research and Practice, 213(8), 882–888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2017.06.012
Hu, C., Lv, L., Peng, J., Liu, D., Wang, X., Zhou, Y., & Huo, J. (2017). MicroRNA-375 suppresses esophageal cancer cell growth and invasion by repressing metadherin expression. Oncology Letters, 13(6), 4769–4775. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6098
Wong, J. J. M., Ginter, P. S., Tyryshkin, K., Yang, X., Nanayakkara, J., Zhou, Z., Renwick, N. (2020). Classifying Lung Neuroendocrine Neoplasms through MicroRNA Sequence Data Mining. Cancers, 12(9), 2653. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092653
Yang, X., Nanayakkara, J., Claypool, D., Saghafinia, S., Wong, J. J. M., Xu, M., Renwick, N. (2021). A miR-375/YAP axis regulates neuroendocrine differentiation and tumorigenesis in lung carcinoid cells. Scientific Reports, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-89855-4
Wu, Y., Sun, X., Song, B., Qiu, X., & Zhao, J. (2017). MiR-375/SLC7A11 axis regulates oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and invasion. Cancer Medicine, 6(7), 1686–1697. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1110
He, S., Shi, J., Mao, J., Luo, X., Liu, W., Liu, R., & Yang, F. (2019). The expression of miR-375 in prostate cancer: a study based on GEO, TCGA data and bioinformatics analysis. Pathology - Research and Practice, 215(6), 152375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2019.03.004
Costa-Pinheiro, P., Ramalho-Carvalho, J., Vieira, F. Q., Torres-Ferreira, J., Oliveira, J., Gonçalves, C. S., Jerónimo, C. (2015). MicroRNA-375 plays a dual role in prostate carcinogenesis. Clinical epigenetics, 7(1), 42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-015-0076-2
De Souza Rocha Simonini, P., Breiling, A., Gupta, N., Malekpour, M., Youns, M., Omranipour, R., Riazalhosseini, Y. (2010). Epigenetically Deregulated microRNA-375 Is Involved in a Positive Feedback Loop with Estrogen Receptor alpha in Breast Cancer Cells, Cancer Research, 70(22), 9175–9184. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-10-1318
Montavon, T., & Soshnikova, N. (2014). Hox gene regulation and timing in embryogenesis. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 34, 76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.06.005
Mallo, M., & Alonso, C. R. (2013). The regulation of hox gene expression during animal development. Development, 140(19), 3951–3963. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.068346
Abramovich, C., & Humphries, R. K. (2005). Hox regulation of normal and leukemic hematopoietic stem cells. Current Opinion in Hematology, 12(3), 210–216. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.moh.0000160737.52349.aa
Moens, C. B., & Selleri, L. (2006). Hox cofactors in vertebrate development. Developmental Biology, 291(2), 193–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.10.032
Sample, J., Brooks, L., Sample, C., Young, L., Rowe, M., Gregory, C., Kieff, E. (1991). Restricted Epstein-Barr virus protein expression in Burkitt lymphoma is due to a different Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 transcriptional initiation site. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 88(14), 6343–6347. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.88.14.6343
Pai, P., Wang, G., Teo, W. W., Raez-Rodriguez, D., Gabrielson, K. L., Győrffy, B., … Sukumar, S. (2022). HOXA5-Mediated Stabilization of IκBα Inhibits the NF-κB Pathway and Suppresses Malignant Transformation of Breast Epithelial Cells. Cancer Research, 82(20), 3802–3814. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-4277
Chen, H., Chung, S., & Sukumar, S. (2004). HOXA5-Induced apoptosis in breast Cancer cells is mediated by caspases 2 and 8. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 24(2), 924–935. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.24.2.924-935.2004
Stasinopoulos, I. A., Mironchik, Y., Raman, A., Wildes, F., Winnard, P., & Raman, V. (2005). HOXA5-Twist Interaction alters p53 homeostasis in breast Cancer cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280(3), 2294–2299. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m411018200
Teo, W. W., Merino, V. F., Cho, S., Korangath, P., Liang, X., Wu, R., Sukumar, S. (2016). HOXA5 determines cell fate transition and impedes tumor initiation and progression in breast cancer through regulation of E-cadherin and CD24. Oncogene, 35(42), 5539–5551. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.95
Gendronneau, G., Lemieux, M., Morneau, M., Paradis, J., Têtu, B., Frenette, N., Jeannotte, L. (2010). Influence of Hoxa5 on p53 Tumorigenic Outcome in Mice. The American Journal of Pathology, 176(2), 995–1005. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2010.090499
Yu, T., Chen, D., Zhang, L., & Wan, D. (2019). microRNA-26a-5p promotes Proliferation and Migration of Osteosarcoma cells by targeting HOXA5 in vitro and in vivo. OncoTargets and therapy, 12, 11555–11565. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S232100
Shen, W. C., & Shi, Y. W. (2021). Effect of MiR-142-3p Targeting HOXA5 on proliferation, cycle arrest and apoptosis of Acute B lymphocytic leukemia cells. Zhongguo shi yan xue ye xue za zhi, 29(4), 1085–1092. https://doi.org/10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2021.04.011
Liu, X., Lu, K., Wang, K., Sun, M., Zhang, E., Yang, J., Wang, Z. (2012). MicroRNA-196a promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion through targeting HOXA5. BMC Cancer, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-12-348
Wan, N., & Zheng, J. (2021). MicroRNA–891a–5p is a novel biomarker for non–small cell lung cancer and targets HOXA5 to regulate tumor cell biological function. Oncology Letters, 22(1), https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2021.12768
Liu, Y., Lin, C., Wang, D., Wen, S., Wang, J., Chen, Z., Feng, D. (2020). MicroRNA-224 Promotes Cell Migration and Invasion by Targeting HOXA5 expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. bioRxiv, https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.27.269654
Lu, X., Duan, J., Zhou, R., & Xu, Y. (2021). MiR-301b-3p promotes the occurrence and development of breast Cancer cells via Targeting HOXA5. Critical Reviews in Eukaryotic Gene Expression, 31(3), 35–44. https://doi.org/10.1615/critreveukaryotgeneexpr.2021038215
Wolfson, E., Solomon, S., Schmukler, E., Goldshmit, Y., & Pinkas-Kramarski, R. (2018). Nucleolin and ErbB2 inhibition reduces tumorigenicity of ErbB2-positive breast cancer. Cell Death and Disease, 9(2), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0067-7
Suzuki, H. I., Yamagata, K., Sugimoto, K., Iwamoto, T., Kato, S., & Miyazono, K. (2009). Modulation of microRNA processing by p53. Nature, 460(7254), 529–533. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08199
Davis, B. N., Hilyard, A. C., Lagna, G., & Hata, A. (2008). SMAD proteins control DROSHA-mediated microRNA maturation. Nature, 454(7200), 56–61. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07086
Blahna, M. T., & Hata, A. (2012). Smad-mediated regulation of microRNA biosynthesis. FEBS Letters, 586(14), 1906–1912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2012.01.041
Li, J., Pu, W., Sun, H.-L., Zhou, J.-K., Fan, X., Zheng, Y., … Peng, Y. (2018). Pin1 impairs microRNA biogenesis by mediating conformation change of XPO5 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death and Differentiation, 25(9), 1612–1624. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0065-z
Kawai, S., & Amano, A. (2012). BRCA1 regulates microRNA biogenesis via the DROSHA microprocessor complex. Journal of Cell Biology, 197(2), 201–208. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201110008
Pickering, B. F., Yu, D., & Van Dyke, M. W. (2011). Nucleolin protein interacts with microprocessor complex to affect biogenesis of microRNAs 15a and 16. The Journal of biological chemistry, 286(51), 44095–44103. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.265439
Pichiorri, F., Palmieri, D., Luca, L. De, Consiglio, J., You, J., Rocci, A., Croce, C. M. (2013). In vivo NCL targeting affects breast cancer aggressiveness through miRNA regulation. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 210(5), 951–968. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20120950
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the University Grant Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India for providing financial assistance for this project (F.No.41-1274/2012/(SR) dt:26.7.2012) and DST for providing funds for the improvement of the infrastructure facility (FIST) to the Department of Biochemistry, Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli- 620 024, Tamilnadu, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the study conception, design, and execution.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to Participate
all authors agreed to participate.
Consent for Publication
all authors agreed for the publication of their work.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Moorthy, R.K., Srinivasan, C., Kannan, M. et al. Deregulation of miR-375 Inhibits HOXA5 and Promotes Migration, Invasion, and Cell Proliferation in Breast Cancer. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 4503–4523 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04375-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04375-3