Abstract
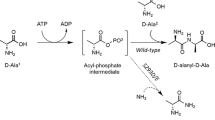
The multi-enzyme coupling reaction system has become a promising biomanufacturing platform for biochemical production. Tyr is an essential amino acid, but the limited solubility restricts its use. Tyrosyl dipeptide has been paid more attention due to its higher solubility. In this study, an efficient enzymatic cascade of Ala-Tyr synthesis was developed by a L-amino acid ligase together with polyphosphate kinase (PPK). Two L-amino acid ligases from Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus pumilus were selected and applied for Ala-Tyr synthesis. The L-amino acid ligase from B. subtilis (Bs) was selected and coupled with the PPK from Sulfurovum lithotrophicum (PPKSL) for regenerating ATP to produce Ala-Tyr in one pot. In the optimization system, 40.1 mM Ala-Tyr was produced within 3 h due to efficient ATP regeneration with hexametaphosphate (PolyP(6)) as the phosphate donor. The molar yield was 0.89 mol/mol based on the substrates added, while the productivity of Ala-Tyr achieved 13.4 mM/h, which were the highest yield and productivity ever reported about Ala-Tyr synthesis with L-amino acid ligase.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data in the manuscript are available.
References
Daabees, T. T., & Stegink, L. D. (1978). L-alanyl-L-tyrosine as a tyrosine source during intravenous nutrition of the rat. Journal of Nutrition, 108, 1104–1113.
Druml, W., Lochs, H., & Roth, E. (1995). Utilization of tyrosine-containing dipeptides and N-acetyl-tyrosine in hepatic failure. Hepatology, 21, 923–928.
Yagasaki, M., & Hashimoto, S. (2008). Synthesis and application of dipeptides; current status and perspectives. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 81, 13–22.
Tanaka, T., Takagi, K., Saddam, H. M., Takeda, Y., & Wakayama, M. (2017). Purification and Characterization of Elizabethkingia L-Amino Acid Esterase: An enzyme useful for enzymatic synthesis of the dipeptide, Valyl-Glycine. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 183, 362–373.
Gill, I., López-Fandiño, R., Jorba, X., & Vulfson, E. N. (1996). Biologically active peptides and enzymatic approaches to their production. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 18, 162–183.
Becker, M., Nikel, P., & Andexer, J. N. (2021). A multi-enzyme cascade reaction for the production of 2’3’-cGAMP. Biomolecules, 11, 590.
Sheldon, R. A., & Woodley, J. M. (2018). Role of biocatalysis in sustainable chemistry. Chemical Reviews, 118, 801–838.
Behrens, G. A., Hummel, A., Padhi, S. K., Schätzle, S., & Bornscheuer, U. T. (2011). Discovery and protein engineering of biocatalysts for organic synthesis. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 353, 2191–2215.
Rieckenberg, F., Ardao, I., Rujananon, R., & Zeng, A. P. (2014). Cell-free synthesis of 1,3-propanediol from glycerol with a high yield. Engineering in Life Sciences, 14, 380–386.
Dai, Y. W., Li, M. L., Jiang, B., Zhang, T., & Chen, J. J. (2021). Whole-cell biosynthesis of D-tagatose from maltodextrin by engineered Escherichia coli with multi-enzyme co-expression system. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 145, 109747.
Bordewick, S., Berger, R. G., & Ersoy, F. (2021). Mutagenesis of the L-Amino acid ligase RizA increased the production of bioactive dipeptides. Catalysts, 11, 1385.
Kino, H., & Kino, K. (2015). Alteration of the substrate specificity of L -amino acid ligase and selective synthesis of Met-Gly as a salt taste enhancer. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 79, 1827–1832.
Kino, K., Kotanaka, Y., Arai, T., & Yagasaki, M. (2009). A novel L-Amino acid ligase from Bacillus subtilis NBRC3134, a microorganism producing peptide antibiotic rhizocticin. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 73, 901–907.
Tabata, K., Ikeda, H., & Hashimoto, S. I. (2005). ywfE in Bacillus subtilis codes for a novel enzyme L-amino acid ligase. Journal of Bacteriology, 187, 5195–5202.
Wang, T., Zhang, Y. F., & Ning, L. X. (2020). L-amino acid ligase: A promising alternative for the biosynthesis of L-dipeptides. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 136, 109537.
Iwamoto, S., Motomura, K., Shinoda, Y., Urata, M., Kato, J., Takiguchi, N., Ohtake, H., Hirota, R., & Kuroda, A. (2007). Use of an Escherichia coli recombinant producing thermostable polyphosphate kinase as an ATP regenerator to produce fructose1,6-diphosphate. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 73, 5676–5678.
Zhang, X., Wu, H., Huang, B., Li, Z. M., & Ye, Q. (2017). One-pot synthesis of glutathione by a two-enzyme cascade using a thermophilic ATP regeneration system. Journal of Biotechnology, 241, 163–169.
Huang, C., & Yin, Z. (2020). Highly efficient synthesis of glutathione via a genetic engineering enzymatic method coupled with yeast ATP generation. Catalysts, 10, 33.
Li, Z., Ning, X., Zhao, Y., Zhang, X., Xiao, C., & Li, Z. (2020). Efficient one-pot synthesis of cytidine-5-monophosphate using an extremophilic enzyme cascade system. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 68, 9188–9194.
Yan, B., Ding, Q., Ou, L., & Zou, Z. (2014). Production of glucose-6-phosphate by glucokinase coupled with an ATP regeneration system. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 30, 1123–1128.
Li, Z., Shen, S., & Li, Z. (2020). Towards the conversion of CO2 into optically pure N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate and orotate by an in vitro multi-enzyme cascade. Green Chemistry, 22, 5798–5805.
Sun, C., Li, Z., Ning, X., Xu, W., & Li, Z. (2021). In vitro biosynthesis of ATP from adenosine and polyphosphate. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 8, 117.
Tavanti, M., Hosford, J., Lloyd, R. C., & Brown, M. (2021). ATP regeneration by a single polyphosphate kinase powers multigram-scale aldehyde synthesis in vitro. Green Chemistry, 23, 828–837.
Zhang, X., Cui, X. W., & Li, Z. M. (2020). Characterization of two polyphosphate kinase 2 enzymes used for ATP synthesis. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 191, 881–892.
Nocek, B. P., Khusnutdinova, A. N., Ruszkowski, M., Flick, R., Burda, M., & Batyrova, K. (2018). Structural insights into substrate selectivity and activity of bacterial polyphosphate kinases. ACS Catalysis, 8, 10746–10760.
Mordhorst, S., & Andexer, J. N. (2020). Round, round we go - strategies for enzymatic cofactor regeneration. Natural Products Reports, 37, 1316–1333.
Parnell, A. E., Mordhorst, S., Kemper, F., Giurrandino, M., Prince, J. P., & Schwarzer, N. J. (2018). Substrate recognition and mechanism revealed by ligand-bound polyphosphate kinase 2 structures. PNAS, 115, 3350–3355.
Cui, X. W., Wang, Z., Li, Z. L., Zhang, X., & Li, Z. M. (2021). Programming integrative multienzyme systems and ionic strength for recyclable synthesis of glutathione. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 69, 3887–3894.
Cui, X. W., Li, Z. M. (2021). High production of glutathione by in vitro enzymatic cascade after thermostability enhancement. AIChE Journal, 67, e17055.
Cao, H., Nie, K., Li, C., Xu, H., Wang, F., & Tan, T. (2017). Rational design of substrate binding pockets in polyphosphate kinase for use in cost-effective ATP-dependent cascade reactions. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 101, 5325–5332.
Adams, J. A. (2001). Kinetic and catalytic mechanisms of protein kinases. Chemical Reviews, 101, 2271–2290.
Endicott, J. A., Noble, M. E. M., & Johnson, L. N. (2012). The structural basis for control of eukaryotic protein kinases. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 81, 587–613.
Zhang, Y., Lyu, F., Ge, J., & Liu, Z. (2014). Ink-jet printing an optimal multi-enzyme system. Chemical Communications, 50, 12919–12922.
Bordewick, S., Mast, T. A., Berger, R., & Ersoy, F. (2021). Recombinant production of arginyl dipeptides by L-amino acid ligase RizA coupled with ATP regeneration. Catalysts, 11, 1290.
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Support Plan for Youth Innovation of Colleges and Universities of Shandong Province (2021KJ109) and the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2019MC066).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation and data collection were performed by X. W. Cui, X. X. Du, Q. Zhao, and Y. Y. Hu. Data analysis was performed by C. H. Tian. The first draft of the manuscript was written by W. L. Song, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The authors affirm that consent for publication of all the images.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, X., Du, X., Zhao, Q. et al. Efficient synthesis of Ala-Tyr by L-amino acid ligase coupled with ATP regeneration system. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 4336–4346 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04365-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04365-5