Abstract
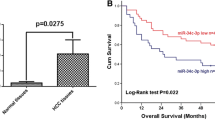
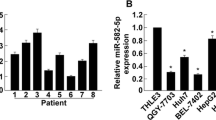
In cell biological functions and viability, cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) takes an essential part. miR-195-5p is pivotal in pathogenesis and development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). But in HCC, whether there is a connection between CDK1 and miR-195-5p remains an unanswered question. In view of this, this study focuses on exploring the mechanism of miR-195-5p/CDK1 in the progression of HCC. The bioinformatics method was applied to predict target mRNA and upstream miRNAs, and further analyzes the signal enrichment pathway of target mRNA. We utilized qRT-PCR and Western blot for detecting expression of genes, as well as their corresponding protein levels. Cell cycle was assayed through flow cytometry. As for the examination of DNA replication, the EDU staining was employed. Cell proliferation was determined via plate colony formation assay. The combined application of bioinformatics analysis and dual-luciferase gene assay assisted in figuring out the binding relationship between miR-195-5p and CDK1. DNA damage was marked by immunofluorescence staining. CDK1 was overexpressed in HCC cells, and enriched in cell cycle and DNA replication pathway. Silencing CDK1 modulated cell cycle of HCC cells and inhibited DNA replication and proliferation. In HCC cells, miR-195-5p targeted and reduced CDK1 expression, inhibited the G1 phase-to-S phase transition, induced DNA damage response, and inhibited DNA replication and proliferation. miR-195-5p targeted CDK1 and repressed synthesis of new DNA in HCC cells, thus restraining HCC cell proliferation.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Pinero, F., Dirchwolf, M., & Pessoa, M. G. (2020). Biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma: Diagnosis, prognosis and treatment response assessment. Cells, 9, 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061370
Sim, H. W., & Knox, J. (2018). Hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of immunotherapy. Current Problems in Cancer, 42, 40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2017.10.007
Santamaria, D., et al. (2007). Cdk1 is sufficient to drive the mammalian cell cycle. Nature, 448, 811–815. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06046
Garnier, D., Loyer, P., Ribault, C., Guguen-Guillouzo, C., & Corlu, A. (2009). Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 plays a critical role in DNA replication control during rat liver regeneration. Hepatology, 50, 1946–1956. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23225
Johnson, N., et al. (2009). Cdk1 participates in BRCA1-dependent S phase checkpoint control in response to DNA damage. Molecular Cell, 35, 327–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2009.06.036
Chow, J. P., Poon, R. Y., & Ma, H. T. (2011). Inhibitory phosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinase 1 as a compensatory mechanism for mitosis exit. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 31, 1478–1491. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00891-10
Sung, W. W., et al. (2014). High nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio of Cdk1 expression predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. BMC Cancer, 14, 951. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-14-951
Willder, J. M., et al. (2013). Androgen receptor phosphorylation at serine 515 by Cdk1 predicts biochemical relapse in prostate cancer patients. British Journal of Cancer, 108, 139–148. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2012.480
Danhier, F., Ucakar, B., Magotteaux, N., Brewster, M. E., & Preat, V. (2010). Active and passive tumor targeting of a novel poorly soluble cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor, JNJ-7706621. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 392, 20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.03.018
Jin, J., et al. (2020). LINC00346 Acts as a competing endogenous Rna regulating development of hepatocellular carcinoma via modulating CDK1/CCNB1 AXIS. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 8, 54. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00054
Xu, T., et al. (2009). MicroRNA-195 suppresses tumorigenicity and regulates G1/S transition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology, 50, 113–121. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.22919
Ozata, D. M., et al. (2011). The role of microRNA deregulation in the pathogenesis of adrenocortical carcinoma. Endocrine-Related Cancer, 18, 643–655. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-11-0082
Zhang, Q. Q., et al. (2012). MicroRNA-195 plays a tumor-suppressor role in human glioblastoma cells by targeting signaling pathways involved in cellular proliferation and invasion. Neuro-Oncology, 14, 278–287. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nor216
Li, D., et al. (2011). Analysis of MiR-195 and MiR-497 expression, regulation and role in breast cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 17, 1722–1730. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1800
Huang, D. P., et al. (2021). Bioinformatics analyses of potential miRNA-mRNA regulatory axis in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. International Journal of Medical Sciences, 18, 335–346. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.50126
Yang, W., et al. (2016). Accumulation of cytoplasmic Cdk1 is associated with cancer growth and survival rate in epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncotarget, 7, 49481–49497. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10373
Piao, J., et al. (2019). High expression of CDK1 and BUB1 predicts poor prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gene, 701, 15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.081
Wu, C. X., et al. (2018). Blocking CDK1/PDK1/beta-catenin signaling by CDK1 inhibitor RO3306 increased the efficacy of sorafenib treatment by targeting cancer stem cells in a preclinical model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics, 8, 3737–3750. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.25487
Xu, H., et al. (2015). MicroRNA-195-5p acts as an anti-oncogene by targeting PHF19 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology Reports, 34, 175–182. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.3957
Johnson, N., et al. (2011). Compromised CDK1 activity sensitizes BRCA-proficient cancers to PARP inhibition. Nature Medicine, 17, 875–882. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2377
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chunhui Zhou: conceptualization, methodology, software, data curation, writing- original draft preparation.
Sujuan Zhu: visualization, investigation, supervision, validation.
Haiping Li: writing- reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
All authors approved to participate in this research.
Consent for publication
All authors approved the final manuscript and submitted it to this journal.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, C., Zhu, S. & Li, H. miR-195-5p Targets CDK1 To Regulate New DNA Synthesis and Inhibit the Proliferation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 3477–3490 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04279-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04279-8