Abstract
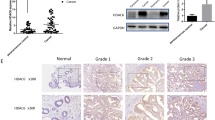
Endometrial cancer (EC) ranks fourth among the most common gynecologic malignancies. Despite advances in medical technology, the pathogenesis is still unclear. Numerous reports have identified the involvement of lncRNA in the malignant progression of endometrial cancer. The aim of the study was to investigate the expression level of lncRNA ENST00000585827 (lncRNA E27) in endometrial cancer and the molecular mechanism that regulates the development of endometrial cancer. Combined with the results of the previous study, PCR analysis confirmed that lncRNA E27 was significantly upregulated in endometrial cancer cell lines. The results of CCK-8, wound healing assay, and transwell experiments showed that lncRNA E27 could significantly inhibit cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Flow cytometry results confirmed that lncRNA E27 could promote apoptosis. Furthermore, based on bioinformatics predictions, dual-luciferase assay and RT-qPCR analysis confirmed that miR-424, as its downstream molecule, competitively regulates the expression of E2F6/E2F7. Rescue experiments further supported that lncRNA E27 inhibited proliferation, migration, invasion, and promoted apoptosis of endometrial cancer through miR-424/E2F6/E2F7 signaling axis. Conclusively, our findings revealed the role of lncRNA E27 in regulating the miR-424/E2F6/E2F7 signaling axis during EC progression, opening up new strategies for the treatment of endometrial cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data in the article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
References
Piulats, J., et al. (2017). Molecular approaches for classifying endometrial carcinoma. Gynecologic oncology, 145(1), 200–207.
Yeramian, A., et al. (2013). Endometrial carcinoma: Molecular alterations involved in tumor development and progression. Oncogene, 32(4), 403–413.
Garg, K., & Soslow, R. (2014). Endometrial carcinoma in women aged 40 years and younger. Archives of pathology & laboratory medicine, 138(3), 335–342.
Yu, W., et al. (2010). Dietary vitamin D exposure prevents obesity-induced increase in endometrial cancer in Pten+/- mice. Cancer Prevention Research (Philadelphia, Pa.), 3(10), 1246–58.
Takenaka, K., et al. (2016). The emerging role of long non-coding RNAs in endometrial cancer. Cancer genetics, 209(10), 445–455.
Li, Q., et al. (2021). LINC00958/miR-3174/PHF6 axis is responsible for triggering proliferation, migration and invasion of endometrial cancer. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences, 25(22), 6853–6861.
Zhang, Q., et al. (2020). lncRNA NR2F1-AS1 promotes breast cancer angiogenesis through activating IGF-1/IGF-1R/ERK pathway. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine, 24(14), 8236–8247.
Zhang, L., et al. (2021). Long noncoding RNA ROR1-AS1 enhances STC2-mediated cell growth and autophagy in cervical cancer through miR-670-3p. Journal of receptor and signal transduction research, 41(6), 582–592.
Zheng, Y., Tan, K., & Huang, H. (2019). Long noncoding RNA HAGLROS regulates apoptosis and autophagy in colorectal cancer cells via sponging miR-100 to target ATG5 expression. Journal of cellular biochemistry, 120(3), 3922–3933.
Guo, Q., et al. (2020). Long noncoding RNA PITPNA-AS1 promotes cervical cancer progression through regulating the cell cycle and apoptosis by targeting the miR-876-5p/c-MET axis. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy= Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie, 128, 110072.
Zuo, X., et al. (2021). Long non‑coding RNA LINC01224 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by regulating AKT3 expression via targeting miR‑485‑5p in endometrial carcinoma. Oncology reports, 46(3), 186.
Lv, C., et al. (2022). Long noncoding RNA EIF1AX-AS1 promotes endometrial cancer cell apoptosis by affecting EIF1AX mRNA stabilization. Cancer science, 113(4), 1277–1291.
Mei, J., et al. (2022). Long noncoding RNA TINCR facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression and dampens chemosensitivity to oxaliplatin by regulating the miR-195-3p/ST6GAL1/NF-κB pathway. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research : CR, 41(1), 5.
Cheng, Z., et al. (2022). Long noncoding RNA LHFPL3-AS2 suppresses metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by interacting with SFPQ to regulate TXNIP expression. Cancer letters, 531, 1–13.
Smolle, M., et al. (2015). Long non-coding RNAs in endometrial carcinoma. International journal of molecular sciences, 16(11), 26463–26472.
Du, Y., et al. (2018). lncRNA DLEU1 contributes to tumorigenesis and development of endometrial carcinoma by targeting mTOR. Molecular carcinogenesis, 57(9), 1191–1200.
Cui, Z., et al. (2018). LncRNA MIR22HG negatively regulates miR-141–3p to enhance DAPK1 expression and inhibits endometrial carcinoma cells proliferation. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy= Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie, 104, 223–228.
Niu, Z., et al. (2020). Role of long noncoding RNA-mediated competing endogenous RNA regulatory network in hepatocellular carcinoma. World journal of gastroenterology, 26(29), 4240–4260.
Chen, B., et al. (2018). Long non-coding RNA NNT-AS1 sponges miR-424/E2F1 to promote the tumorigenesis and cell cycle progression of gastric cancer. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine, 22(10), 4751–4759.
Gao, Y., et al. (2017). Long noncoding RNA PVT1 facilitates cervical cancer progression via negative regulating of miR-424. Oncology research, 25(8), 1391–1398.
Li, Q., et al. (2015). MicroRNA-424 may function as a tumor suppressor in endometrial carcinoma cells by targeting E2F7. Oncology reports, 33(5), 2354–2360.
Zhan, L., et al. (2014). Promising roles of mammalian E2Fs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cellular signalling, 26(5), 1075–1081.
Zhang, Z., et al. (2022). SAPCD2 promotes neuroblastoma progression by altering the subcellular distribution of E2F7. Cell death & disease, 13(2), 174.
Zhou, H., Guo, R., & Wang, C. (2019). Retracted article: Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 accelerates cell progression in cervical cancer by regulating the miR-889-3p/E2F7 axis through the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. RSC advances, 9(59), 34627–34635.
Liu, J., et al. (2018). A miR-26a/E2F7 feedback loop contributes to tamoxifen resistance in ER-positive breast cancer. International journal of oncology, 53(4), 1601–1612.
Zhao, Y., et al. (2020). MiR-424-5p regulates cell cycle and inhibits proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting E2F7. PLoS ONE, 15(11), e0242179.
Cheng, C., et al. (2020). Up-regulation of miR-26a-5p inhibits E2F7 to regulate the progression of renal carcinoma cells. Cancer management and research, 12, 11723–11733.
Ma, Y., et al. (2021). LINC00174 facilitates proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells via MiR-3127-5p/ E2F7 axis. Journal of microbiology and biotechnology, 31(8), 1098–1108.
Funding
This project is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81860495).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D. F.: writing, conceptualization, methodology, software.
Q. Z.: data curation, writing, original draft preparation.
M. M.: visualization, investigation.
Q. D.: supervision, methodology.
Y. W.: software, validation, data curation.
Q. L.: reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
The animal experiments in the study were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, D., Zhang, Q., Mu, M. et al. lncRNA ENST00000585827 Contributes to the Progression of Endometrial Carcinoma via Regulating miR-424/E2F6/E2F7 Axis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 3096–3108 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04267-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04267-y