Abstract
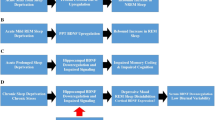
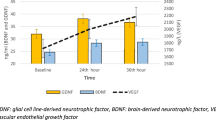
The purpose of this article was to investigate the level of serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its relationship with suicidal symptoms and severity in mentally ill suicide attempt patients, and to explore the possible role of serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the occurrence of psychotic suicidal behavior. A retrospective analysis was performed on patients with depression in the neurology department of a hospital. General physical examination, neurological specialist examination, and cranial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examination were performed on any selected group. We applied the 24-item Hamilton Depression Scale, Hamilton Anxiety Scale, and Mini-Intelligence Mental State Scale, and performed polysomnography and electroencephalography (EEG) monitoring to conduct statistical analysis on sleep indicators. The amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) values of the right frontal gyrus, left posterior cerebellar lobe, right anterior cerebellar lobe, and right occipital lingual gyrus of the patient group were significantly lower than those of the control group. The ReHo values of the right superior parietal lobule, the left precuneus, and the right occipital lingual gyrus were significantly higher than those of the control group. The genotype and allele frequency distribution of FKBP5, AVPR1B, and CRHR2 gene SNPs had no significant difference between the case group and the control group (P > 0.05). The ReHo value of the precuneus is significantly correlated with the proportion of N3 sleep, and the dysfunction of the precuneus or default network may be related to the altered sleep structure in patients with depression. The GT and TT genotypes at rs9324924 of the NR3C1 gene are associated with suicide attempts.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Kang, S. G., Mariani, S., Marvin, S. A., Ko, K. P., Redline, S., & Winkelman, J. W. (2018). Sleep EEG spectral power is correlated with subjective-objective discrepancy of sleep onset latency in major depressive disorder. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 85, 122–127.
Kwan, Y., Baek, C., Chung, S., Kim, T. H., & Choi, S. (2018). Resting-state quantitative EEG characteristics of insomniac patients with depression. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 124, 26–32.
Zangani, C., Casetta, C., Saunders, A. S., Donati, F., Maggioni, E., & D’Agostino, A. (2020). Sleep abnormalities across different clinical stages of Bipolar Disorder: A review of EEG studies. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 118, 247–257.
Plante, D. T. (2021). The evolving nexus of sleep and depression. American Journal of Psychiatry, 178(10), 896–902.
Jahrami, H., Alekri, E., BaHammam, A. S., Alsalman, A., Bragazzi, N. L., Alhaj, O., & Saif, Z. (2021). The association between micronutrient status and sleep quality in patients with depression: A case-control study. Sleep Breath, 25(3), 1571–1579.
Lima Giacobbo, B., Doorduin, J., Klein, H. C., Dierckx, R. A., Bromberg, E., & de Vries, E. F. (2019). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in brain disorders: Focus on neuroinflammation. Molecular Neurobiology, 56(5), 3295–3312.
Gawęda, Ł, Pionke, R., Krężołek, M., Frydecka, D., Nelson, B., & Cechnicki, A. (2020). The interplay between childhood trauma, cognitive biases, psychotic-like experiences and depression and their additive impact on predicting lifetime suicidal behavior in young adults. Psychological Medicine, 50(1), 116–124.
Dombrovski, A. Y., Hallquist, M. N., Brown, V. M., Wilson, J., & Szanto, K. (2019). Value-based choice, contingency learning, and suicidal behavior in mid-and late-life depression. Biological Psychiatry, 85(6), 506–516.
Rahmani, M., Rahmani, F., & Rezaei, N. (2020). The brain-derived neurotrophic factor: Missing link between sleep deprivation, insomnia, and depression. Neurochemical Research, 45(2), 221–231.
Cai, H., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., & Hu, B. (2018). A case-based reasoning model for depression based on three-electrode EEG data. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 11(3), 383–392.
Gerstenberg, M., Furrer, M., Tesler, N., Franscini, M., Walitza, S., & Huber, R. (2020). Reduced sleep spindle density in adolescent patients with early-onset schizophrenia compared to major depressive disorder and healthy controls. Schizophrenia Research, 221, 20–28.
Fischer, S., Gardini, E. S., Haas, F., & Cleare, A. J. (2019). Polymorphisms in genes related to the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and antidepressant response–systematic review. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 96, 182–196.
Jablochkova, A., Bäckryd, E., Kosek, E., Mannerkorpi, K., Ernberg, M., Gerdle, B., & Ghafouri, B. (2019). Unaltered low nerve growth factor and high brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in plasma from patients with fibromyalgia after a 15-week progressive resistance exercise. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 51(10), 779–787.
Tang, L., Chen, Y., Xiang, Q., Xiang, J., Tang, Y., & Li, J. (2020). The GCAG haplotype of the CRHBP gene may decrease the risk for robbery behavior among the Han Chinese. Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers, 24(7), 436–442.
Haghighat, N., Rajabi, S., & Mohammadshahi, M. (2021). Effect of synbiotic and probiotic supplementation on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor level, depression and anxiety symptoms in hemodialysis patients: A randomized, double-blinded, clinical trial. Nutritional Neuroscience, 24(6), 490–499.
Fonseka, T. M., Bhat, V., & Kennedy, S. H. (2019). The utility of artificial intelligence in suicide risk prediction and the management of suicidal behaviors. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 53(10), 954–964.
Kim, J. H., & Kim, D. Y. (2018). Aquarobic exercises improve the serum blood irisin and brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in elderly women. Experimental Gerontology, 104, 60–65.
Calandre, E. P., Rico-Villademoros, F., & Slim, M. (2018). Suicidal behaviors in patients with rheumatic diseases: A narrative review. Rheumatology International, 38(4), 537–548.
Pawełczyk, T., Grancow-Grabka, M., Trafalska, E., Szemraj, J., Żurner, N., & Pawełczyk, A. (2019). An increase in plasma brain derived neurotrophic factor levels is related to n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid efficacy in first episode schizophrenia: Secondary outcome analysis of the OFFER randomized clinical trial. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 236(9), 2811–2822.
Uzel, M. M., Elgin, U., Boral, B., Çiçek, M., Şen, E., Şener, B., & Yılmazbaş, P. (2018). The effect of trabeculectomy on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in primary open-angle glaucoma. Graefes Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology, 256(6), 1173–1178.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the higher authorities for the facilities provided. We would like to thank Professor Wu Shouling for his guidance during the course of this project. The authors also thank all the members of the Kailuan Mental Health Center for their contribution and the participants who contributed their data. The author declares that no conflict of interest is associated with this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This study was done by the authors named in this article, and the authors accept all liabilities resulting from claims which relate to this article and its contents.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Li, N., Wang, J. et al. Correlation Between Sleep Electroencephalogram, Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, AVPR1B Gene Polymorphism, and Suicidal Behavior in Patients with Depression. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 2767–2785 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04197-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04197-9