Abstract
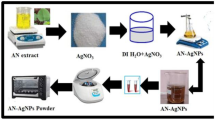
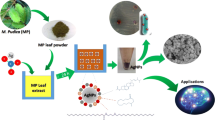
The green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) was considered to be efficacious over other approaches due to their eco-friendliness, cost-effectiveness, and high stability. The biosynthesis of AgNPs was achieved by the reduction of silver nitrate using the aqueous leaf extract of Solanum khasianum. The biosynthesized AgNPs were examined by a color change and UV–Vis spectroscopy with an absorption spectrum at 440 nm. The biomolecules existing in S. khasianum leaf extract accountable for bioreduction and capping of AgNPs were analyzed by FTIR analysis and confirmed the presence of alcohols, phenols, alkanes, carboxylic acid, nitro compounds, and amines. The crystalline nature of Sk-AgNPs with face-centered cubic lattice was confirmed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectrum. The average crystallite size of Sk-AgNPs was computed as 15.96 nm. The lattice constant, unit cell volume, and spacing values of Sk-AgNPs were parallel to the values indexed in the Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standard of silver (JCPDS-04–0783). Scanning electron microscope (SEM) imaging witnessed the spherical structure of synthesized AgNPs. Energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectrum acknowledged the AgNPs fabrication with strong signals of silver atoms at 3 keV energy. The biofabricated Sk-AgNPs showed a photoluminescence (PL) emission spectrum of 445 nm with an excitation at 330 nm. Sk-AgNPs showed considerable DPPH radical scavenging activity (87.98%) than BHT (86.14%) and also exhibited significant antidiabetic activity compared to acarbose. Sk-AgNPs revealed antibacterial potentiality against B. sphaericus, E. coli, S. aureus, and P. fluorescens. Moreover, Sk-AgNPs showed dose-dependent cytotoxicity against MCF-7 cell line. This method of green synthesis would support the eco-friendly fabrication of AgNPs from S. khasianum leaf extract with considerable therapeutic activities.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Ahmed, S., Ahmad, M., Lal Swami, B., & Ikram, S. (2016). A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. Journal of Advanced Research, 7, 17–28.
Krithiga, N., Rajalakshmi, A., & Jayachitra, A. (2015). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Clitoria ternatea and Solanum nigrum and study of its antibacterial effect against common nosocomial pathogens. Journal of Nanoscience, 2015, 1–8.
ValanArasu, M., Arokiyaraj, S., Viayaraghavan, A., SujinJeba Kumar, T., Duraipandiyan, V., Abdullah Al-Dhabi, N., & Kaviyarasu, K. (2019). One step green synthesis of larvicidal, and azo dye degrading antibacterial nanoparticles by response surface methodology. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology, B: Biology, 190, 154–162.
Kowshik, M., Ashtaputre, S., Kharrazi, S., Vogel, W., Urban, J., Kulkarni, S. K., & Paknikar, S. M. (2002). Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles by a silver-tolerant yeast strain MKY3. Nanotechnology, 14, 95–100.
Manivasagan, P., Venkatesan, J., Senthilkumar, K., Sivakumar, K., Kim, S. K. (2013). Biosynthesis, antimicrobial and cytotoxic effect of silver nanoparticles using a novel Nocardiopsis sp. MBRC-1. Bio Med Research International, 2013, 1–10.
Nahar, M. K., Zakaria, Z., Hashim, U., Bari, M. F. (2015). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Momordica charantia fruit extracts. Advanced Materials Research, 1109, 35–39. Trans Tech Publication Ltd.
Ahmed, S., & Ikram, S. (2015). Silver nanoparticles: One pot green synthesis using Terminalia arjuna extract for biological application. Journal of Nanomedicine & Nanotechnology, 6, 1–6.
Swamy, M. K., Akhtar, M. S., Mohanty, S. K., & Sinniah, U. R. (2015). Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using fruit extract of Momordica cymbalaria and assessment of their in vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxicity activities. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 15, 939–944.
Tarannum, N., Divya, & Gautam, Y. K. (2019). Facile green synthesis and applications of silver nanoparticles: A state of the art review. RSC Advances, 9, 34926–34948.
Bindhu, M. R., Umadevi, M., Esmail, G. A., Al-Dhabi, N. A., & Arasu, M. V. (2020). Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Moringa oleifera flower and assessment of antimicrobial and sensing properties. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology, B: Biology, 205, 111836.
Devanesan, S., AlSalhi, M. S., Vishnu Balaji, R., Ranjitsingh, A. J. A., Ahamed, A., Alfuraydi, A. A., AlQahtani, F. Y., Aleanizy, F. S., & Othman, A. H. (2018). Antimicrobial and cytotoxicity effects of synthesized silver nanoparticles from Punica granatum peel extract. Nanoscale Research Letters, 13, 2–10.
Gardea-Torresdey, J. L., Parsons, J. G., Gomez, E., Peralta-Videa, J., Troiani, H. E., Santiago, P., & Yacaman, M. J. (2002). Formation and growth of Au nanoparticles inside live alfalfa plants. Nano Letters, 2, 397–401.
Prasad, K. S., Pathak, D., Patel, A., Dalwadi, P., Prasad, R., Patel, P., & Selvaraj, K. (2011). Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Nicotiana tobaccum leaf extract and study of their antibacterial effect. African Journal of Biotechnology, 10, 8122–8130.
Vanaja, M., Paulkumar, K., Gnanajobitha, G., Rajeshkumar, S., Malarkodi, C., Annadurai, S. (2014). Herbal plant synthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles by Solanum trilobatum and its characterization. International Journal of Metals, 2014, 1–9.
Lashin, I., Fouda, A., Gobouri, A. A., Azab, E., Mohammedsaleh, Z. M., & Makharita, R. R. (2021). Antimicrobial and in vitro cytotoxic efficacy of biogenic silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) fabricated by callus extract of Solanum incanum L. Biomolecules, 11, 1–22.
Pilaquinga, F., Morejon, B., Ganchala, D., Morey, J., Pina, N., Debut, A., & Neira, M. (2019). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Solanum mammosum L. (Solanaceae) fruit extract and their larvicidal activity against Aedes aegypti L.(Diptera: Culicidae). Plos one, 14, e0224109.
Kaunda, J. S., & Zhang, Y. J. (2019). The genus solanum: An ethnopharmacological, phytochemical and biological properties review. Natural Products and Bioprospecting, 9, 77–137.
Chirumamilla, P., Gopu, C., Jogam, P., & Taduri, S. (2021). Highly efficient rapid micropropagation and assessment of genetic fidelity of regenerants by ISSR and SCoT markers of Solanum khasianum Clarke. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 144, 397–407.
Chirumamilla, P., Dharavath, S. B., & Taduri, S. (2022). GC–MS profiling and antibacterial activity of Solanum khasianum leaf and root extracts. Bulletin of the National Research Centre, 46, 1–10.
Govindappa, M., Hemashekhar, B., Arthikala, M. K., Rai, V. R., & Ramachandra, Y. L. (2018). Characterization, antibacterial, antioxidant, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory and antityrosinase activity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Calophyllum tomentosum leaves extract. Results in Physics, 9, 400–408.
Ruch, R. J., Cheng, S. J., & Klaunig, J. E. (1989). Prevention of cytotoxicity and inhibition of intercellular communication by antioxidant catechins isolated from Chinese green tea. Carcinogenesis, 10, 1003–1008.
Oyaizu, M. (1986). Studies on products of browning reaction antioxidative activities of products of browning reaction prepared from glucosamine. The Japanese Journal of Nutrition and Dietetics, 44, 307–315.
Pavithra, K., & Vadivukkarasi, S. (2015). Evaluation of free radical scavenging activity of various extracts of leaves from Kedrostis foetidissima (Jacq.) Cogn. Food Science and Human Wellness, 4, 42–46.
Elya, B., Handayani, R., Sauriasari, R., Hasyyati, U. S., Permana, I. T., & Permatasari, Y. I. (2015). Antidiabetic activity and phytochemical screening of extracts from Indonesian plants by inhibition of alpha amylase, alpha glucosidase and dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 18, 279–278.
Dasari, R., Chirumamilla, P., & Taduri, S. (2021). Cytotoxicity, DNA cleavage and antimicrobial activity of Citrullus Colocynthis plant extracts. American Journal of Ethnomedicine, 8, 1–5.
Jini, D., & Sharmila, S. (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Allium cepa and its in vitro antidiabetic activity. Materials Today: Proceedings, 22, 432–438.
Pavani, C., & Shasthree, T. (2021). Biological activity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles and different plant extracts of Solanum khasianum Clarke. International Research Journal on Advanced Science Hub, 3, 12–17.
Gomathi, M., Rajkumar, P. V., Prakasam, A., & Ravichandran, M. (2017). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Datura stramonium leaf extract and assessment of their antibacterial activity. Resource-Efficient Technologies, 3, 280–284.
Renuka, R., Devi, K. R., Sivakami, M., Thilagavathi, T., Uthrakumar, R., & Kaviyarasu, K. (2020). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Phyllanthus emblica fruit extract for antimicrobial application. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 24, 101567.
Jana, S., & Pal, T. (2007). Synthesis, characterization and catalytic application of silver nanoshell coated functionalized polystyrene beads. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 7, 2151–2156.
Muthukrishnan, S., Bhakya, S., & Kumar, T. S. (2015). Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial effect of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using Ceropegia thwaitesii-an endemic species. Industrial Crops and Products, 63, 119–124.
Yousaf, H., Mehmood, A., Ahmad, K. S., & Raffi, M. (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications as an alternative antibacterial and antioxidant agents. Materials Science and Engineering C, 112, 110901.
Prabakar, K., Sivalingam, P., Rabeek, S. I., Muthuselvam, M., Devarajan, N., Arjunan, A., Karthick, R., Suresh, M. M., & Wembonyama, J. P. (2013). Evaluation of antibacterial efficacy of phyto fabricated silver nanoparticles using Mukia scabrella (Musumusukkai) against drug resistance nosocomial gram negative bacterial pathogens. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 104, 282–288.
Jain, S., & Mehata, M. S. (2017). Medicinal plant leaf extract and pure flavonoid mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their enhanced antibacterial property. Science and Reports, 7, 1–3.
Kanmani, P., & Lim, S. T. (2013). Synthesis and characterization of pullulan-mediated silver nanoparticles and its antimicrobial activities. Carbohydrate Polymers, 97, 421–428.
Devaraj, P., Kumari, P., Aarti, C., & Renganathan, A. (2013). Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using cannonball leaves and their cytotoxic activity against MCF-7 cell line. Journal of Nanotechnology, 13, 1–6.
Jemal, K., Sandeep, B. V., Pola, S. (2017). Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of the antibacterial activity of Allophylus serratus leaf and leaf derived callus extracts mediated silver nanoparticles. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2017, 1–12.
Botcha, S., & Prattipati, S. D. (2020). Callus extract mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles, their characterization and cytotoxicity evaluation against MDA-MB-231 and PC-3 Cells. Bio Nano Science, 15, 1–2.
Kalpana, D., Han, J. H., Park, W. S., Lee, S. M., Wahab, R., & Lee, Y. S. (2019). Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Torreya nucifera and their antibacterial activity. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 12, 1722–1732.
Anandalakshmi, K., Venugobal, J., & Ramasamy, V. (2016). Characterization of silver nanoparticles by green synthesis method using Pedalium murex leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Applied Nanoscience, 6, 399–408.
Chung, I. M., Park, I., Seung-Hyun, K., Thiruvengadam, M., & Rajakumar, G. (2016). Plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Their characteristic properties and therapeutic applications. Nanoscale Research Letters, 11, 1–4.
Lanje, A. S., Sharma, S. J., & Pode, R. B. (2010). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: A safer alternative to conventional antimicrobial and antibacterial agents. Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2, 478–483.
Bykkam, S., Ahmadipour, M., Narisngam, S., Kalagadda, V. R., & Chidurala, S. C. (2015). Extensive studies on X-ray diffraction of green synthesized silver nanoparticles. Advances in Nanoparticles, 4, 1–10.
Joy, J., Gurumurthy, M. S., Thomas, R., & Balachandran, M. (2021). Biosynthesized Ag Nanoparticles: A promising pathway for bandgap tailoring. Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry, 11, 8875–8883.
Gnanajobitha, G., Rajeshkumar, S., Kannan, C., & Annadurai, G. (2013). Preparation and characterization of fruit-mediated silver nanoparticles using pomegranate extract and assessment of its antimicrobial activity. Journal of Environmental Nanotechnology, 2, 4–10.
Nindawat, S., & Agrawal, V. (2019). Fabrication of silver nanoparticles using Arnebiahispidissima (Lehm.) A. DC. root extract and unravelling their potential biomedical applications. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, 47, 166–180.
Pirtarighat, S., Ghannadnia, M., & Baghshahi, S. (2019). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the plant extract of Salvia spinosa grown in vitro and their antibacterial activity assessment. Journal of Nanostructure in Chemistry, 9, 1–9.
Oves, M., Aslam, M., Rauf, M. A., Qayyum, S., Qari, H. A., Khan, M. S., Alam, M. Z., Tabrez, S., Pugazhendhi, A., & Ismail, I. M. (2018). Antimicrobial and anticancer activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from the root hair extract of Phoenix dactylifera. Materials Science and Engineering C, 89, 429–443.
Kagithoju, K., Godishala, V., & Nanna, R. S. (2015). Eco-friendly and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Strychnos potatorum Linn. F. and their bactericidal activities. 3 Biotech, 5, 709–714.
Chitra, G., Balasubramani, G., Ramkumar, R., Sowmiya, R., & Perumal, P. (2015). Mukiamaderaspatana (Cucurbitaceae) extract-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles to control Culexquinquefasciatus and Aedesaegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasitology Research, 114, 1407–1415.
Vorobyova, V., Vasyliev, G., & Skiba, M. (2020). Eco-friendly “green” synthesis of silver nanoparticles with the black currant pomace extract and its antibacterial, electrochemical, and antioxidant activity. Applied Nanoscience, 10, 4523–4534.
Keshari, A. K., Srivastava, R., Singh, P., Yadav, V. B., & Nath, G. (2020). Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized by Cestrum nocturnum. Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine, 11, 37–44.
Xu, J., Han, X., Liu, H., & Hu, Y. (2006). Synthesis and optical properties of silver nanoparticles stabilized by gemini surfactant. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 273, 179–183.
Fayaz, M., Tiwary, C. S., Kalaichelvan, P. T., & Venkatesan, R. (2010). Blue orange light emission from biogenic synthesized silver nanoparticles using Trichoderma viride. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 75, 175–178.
Annamalai, J., & Nallamuthu, T. (2016). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Characterization and determination of antibacterial potency. Applied Nanoscience, 6, 259–265.
Alomar, T. S., AlMasoud, N., Awad, M. A., El-Tohamy, M. F., & Soliman, D. A. (2020). An eco-friendly plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Characterization, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 249, 123007.
Kanipandian, N., Kannan, S., Ramesh, R., Subramanian, P., & Thirumurugan, R. (2014). Characterization, antioxidant and cytotoxicity evaluation of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Cleistanthus collinus extract as surface modifier. Materials Research Bulletin, 49, 494–502.
Das, G., Patra, J. K., Debnath, T., Ansari, A., & Shin, H. S. (2019). Investigation of antioxidant, antibacterial, antidiabetic, and cytotoxicity potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized using the outer peel extract of Anana scomosus (L.). PloS one, 14, e0220950.
Meir, S., Kanner, J., Akiri, B., & Philosoph-Hadas, S. (1995). Determination and involvement of aqueous reducing compounds in oxidative defense systems of various senescing leaves. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 43, 1813–1819.
Kumar, O., Singh, S., Srivastava, B., Bhadouria, R., & Singh, R. (2019). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Holoptelea integrifolia and preliminary investigation of its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic and antibacterial activities. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7, 1–7.
Jalilian, F., Chahardoli, A., Sadrjavadi, K., Fattahi, A., & Shokoohinia, Y. (2020). Green synthesized silver nanoparticle from Allium ampeloprasum aqueous extract: Characterization, antioxidant activities, antibacterial and cytotoxicity effects. Advanced Powder Technology, 31, 1323–1332.
Avwioroko, O. J., Oyetunde, T. T., Atanu, F. O., Otuechere, C. A., Anigboro, A. A., Dairo, O. F., Ejoh, A. S., Ajibade, S. O., & Omorogie, M. O. (2020). Exploring the binding interactions of structurally diverse dichalcogenoimidodiphosphinate ligands with α-amylase: Spectroscopic approach coupled with molecular docking. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 24, 1–12.
Goodman, G., Hardman, J., Limbird, L., & Goodman, G. A. (2006). Insulin, oral hypoglycaemic agents and the pharmacology of endocrine pancreas. Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 60, 1686–1710.
Vijayakumar, S., Divya, M., Vaseeharan, B., Chen, J., Biruntha, M., Silva, L. P., … & Dasgupta, N. (2021). Biological compound capping of silver nanoparticle with the seed extracts of blackcumin (Nigella sativa): A potential antibacterial, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant.Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 31,624635.
Saratale, R. G., Shin, H. S., Kumar, G., Benelli, G., Kim, D. S., & Saratale, G. D. (2018). Exploiting antidiabetic activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Punica granatum leaves and anticancer potential against human liver cancer cells (HepG2). Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, 46, 211–222.
Saratale, G. D., Saratale, R. G., Kim, D. S., Kim, D. Y., & Shin, H. S. (2020). Exploiting fruit waste grape pomace for silver nanoparticles synthesis, assessing their antioxidant, antidiabetic potential and antibacterial activity against human pathogens: A novel approach. Nanomaterials, 10, 1–18.
Chirumamilla, P., Vankudoth, S., Dharavath, S. B., Dasari, R., & Taduri, S. (2022). In vitro anti-inflammatory activity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles and leaf methanolic extract of Solanum khasianum Clarke. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India Section B: Biological Sciences, 10, 1–7.
Xu, H., Qu, F., Lai, W., Wang, Y. A., Aguilar, Z. P., & Wei, H. (2012). Role of reactive oxygen species in the antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli O157:H7. BioMetals, 25, 45–53.
Gopu, C., Chirumamilla, P., Kagithoju, S., Taduri, S. (2022). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Momordica cymbalaria aqueous leaf extracts and screening of their antimicrobial activity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India Section B: Biological Sciences, 27, 1–12.
Dos Santos, C. A., Seckler, M. M., Ingle, A. P., Gupta, I., Galdiero, S., Galdiero, M., … & Rai, M. (2014). Silver nanoparticles: Therapeutical uses, toxicity, and safety issues.Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 103, 1931–1944.
Das, S., & Chakraborty, T. (2018). A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticle and zinc oxide nanoparticle from different plants extract and their antibacterial activity against multi-drug resistant bacteria. Journal of Innovations in Pharmaceutical and Biological Sciences, 5, 63–73.
Zhang, X. F., Shen, W., & Gurunathan, S. (2016). Silver nanoparticle-mediated cellular responses in various cell lines: An in vitro model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17, 1–26.
Liao, C., Li, Y., & Tjong, S. C. (2019). Bactericidal and cytotoxic properties of silver nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20, 1–47.
Ferdous, Z., & Nemmar, A. (2020). Health impact of silver nanoparticles: A review of the biodistribution and toxicity following various routes of exposure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21, 1–31.
Jaswal, T., & Gupta, J. (2021). A review on the toxicity of silver nanoparticles on human health. Materials Today: Proceedings, 222, 1–9.
Antony, J. J., Sivalingam, P., & Chen, B. (2015). Toxicological effects of silver nanoparticles. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 40, 729–732.
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank the Department of Biotechnology, Kakatiya University, for providing all the facilities for the conduction of the experiments. The authors also thank Dr. J. Srinivas, Department of Statistics, Kakatiya University, Warangal, for his guidance and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PC, SD, and TS designed the experiment, analyzed data, wrote the manuscript, and contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chirumamilla, P., Dharavath, S.B. & Taduri, S. Eco-friendly Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Leaf Extract of Solanum khasianum: Optical Properties and Biological Applications. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 353–368 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04156-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04156-4