Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a pivotal role in regulating a variety of biological processes and can be used as biomarkers for the early diagnosis of various diseases, such as psoriasis. Herein, we depict a simple and sensitive miRNA detection method based on dual signal recycles, which is developed on the basis of strand displacement amplification (SDA). The sensor is successfully applied to the detection of miRNA-21 with a wide linear range from 100 fM to 10 nM and a lower limit of detection (LOD) of 67 fM. Because of the simple operation yet improved detection capability, we thereby believe that the developed fluorescent biosensor can be potentially applied for early clinical diagnosis as well as biological researches.
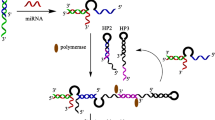
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Lee, P. J., & Papachristou, G. I. (2019). New insights into acute pancreatitis. Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 16, 479–496.
Mederos, M. A., Reber, H. A., & Girgis, M. D. (2021). Acute pancreatitis: A review. JAMA, 325, 382–390.
Yang, A. L., & McNabb-Baltar, J. (2020). Hypertriglyceridemia and acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology, 20, 795–800.
Wang, G. J., Gao, C. F., Wei, D., Wang, C., & Ding, S. Q. (2009). Acute pancreatitis: Etiology and common pathogenesis. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 15, 1427–1430.
Mandalia, A., Wamsteker, E. J. and DiMagno, M. J. (2018). Recent advances in understanding and managing acute pancreatitis. F1000Res, 7.
Xiang, H., Tao, X., Xia, S., Qu, J., Song, H., Liu, J., & Shang, D. (2017). Targeting microRNA function in acute pancreatitis. Frontiers in Physiology, 8, 726.
Wen, C., Sun, H., Pan, K., Sun, H., Zhang, Z., Cao, G. and Wang, M. (2019). Molecular mechanism exploration of pancreatitis based on miRNA expression profile. Clin Lab, 65.
Garcia-Rodriguez, S., Arias-Santiago, S., Blasco-Morente, G., Orgaz-Molina, J., Rosal-Vela, A., Navarro, P., Magro-Checa, C., Martinez-Lopez, A., Ruiz, J. C., Raya, E., Naranjo-Sintes, R., Sancho, J., & Zubiaur, M. (2017). Increased expression of microRNA-155 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from psoriasis patients is related to disease activity. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 31, 312–322.
Hawkes, J. E., Nguyen, G. H., Fujita, M., Florell, S. R., Callis Duffin, K., Krueger, G. G., & O’Connell, R. M. (2016). microRNAs in psoriasis. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 136, 365–371.
Sileno, S., Beji, S., D’Agostino, M., Carassiti, A., Melillo, G., & Magenta, A. (2021). microRNAs involved in psoriasis and cardiovascular diseases. Vasc Biol, 3, R49–R68.
Chen, C., Ridzon, D. A., Broomer, A. J., Zhou, Z., Lee, D. H., Nguyen, J. T., Barbisin, M., Xu, N. L., Mahuvakar, V. R., Andersen, M. R., Lao, K. Q., Livak, K. J., & Guegler, K. J. (2005). Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Research, 33, e179.
Forero, D. A., Gonzalez-Giraldo, Y., Castro-Vega, L. J., & Barreto, G. E. (2019). qPCR-based methods for expression analysis of miRNAs. BioTechniques, 67, 192–199.
Takei, F., Akiyama, M., Murata, A., Sugai, A., Nakatani, K., & Yamashita, I. (2020). RT-Hpro-PCR: A MicroRNA detection system using a primer with a DNA tag. ChemBioChem, 21, 477–480.
Reid, M. S., Le, X. C., & Zhang, H. (2018). Exponential isothermal amplification of nucleic acids and assays for proteins, cells, small molecules, and enzyme activities: An EXPAR example. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 57, 11856–11866.
Lobato, I. M., & O’Sullivan, C. K. (2018). Recombinase polymerase amplification: Basics, applications and recent advances. Trends Analyt Chem, 98, 19–35.
Kim, H. Y., Song, J., & Park, H. G. (2021). Ultrasensitive isothermal method to detect microRNA based on target-induced chain amplification reaction. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 178, 113048.
Wang, R., Zhao, X., Chen, X., Qiu, X., Qing, G., Zhang, H., Zhang, L., Hu, X., He, Z., Zhong, D., Wang, Y., & Luo, Y. (2020). Rolling circular amplification (RCA)-assisted CRISPR/Cas9 cleavage (RACE) for highly specific detection of multiple extracellular vesicle MicroRNAs. Analytical Chemistry, 92, 2176–2185.
Zhang, G. Z. L., Tong, J., Zhao, X., & Ren, J. (2020). CRISPR-Cas12a enhanced rolling circle amplification method for ultrasensitive miRNA detection. Microchemical Journal, 158, 105239.
Zhao, X., Zhang, L., Gao, W., Yu, X., Gu, W., Fu, W., & Luo, Y. (2020). Spatiotemporally controllable MicroRNA imaging in living cells via a near-infrared light-activated nanoprobe. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 12, 35958–35966.
Zhou, W., Hu, L., Ying, L., Zhao, Z., Chu, P. K., & Yu, X. F. (2018). A CRISPR-Cas9-triggered strand displacement amplification method for ultrasensitive DNA detection. Nature Communications, 9, 5012.
Gong, S., Zhang, S., Wang, X., Li, J., Pan, W., Li, N., & Tang, B. (2021). Strand displacement amplification assisted CRISPR-Cas12a strategy for colorimetric analysis of viral nucleic acid. Analytical Chemistry, 93, 15216–15223.
Zhang, X. L., Liu, Y. H., Du, S. M., Yin, Y., Kong, L. Q., Chang, Y. Y., Chai, Y. Q., Li, Z. H., & Yuan, R. (2021). Engineering a rolling-circle strand displacement amplification mediated label-free ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensing platform. Analytical Chemistry, 93, 9568–9574.
Xu, S. Y. (2015). Sequence-specific DNA nicking endonucleases. Biomol Concepts, 6, 253–267.
Bustin, S. A., & Mueller, R. (2005). Real-time reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) and its potential use in clinical diagnosis. Clinical Science (London, England), 109, 365–379.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the financial and equipment support from The Third Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.X. and Z.J. designed the strategy, completed the preparation of the research, and wrote the manuscript; Z.J. assisted data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Permission from the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee was received before making these experiments.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Zhao, X. Sensitive miRNA Detection for Early Diagnosis of Psoriasis Based on Dual Signal Recycles. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 125–134 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04114-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04114-0