Abstract
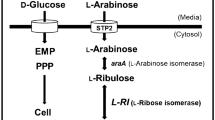
L-ribulose, a kind of high-value rare sugar, could be utilized to manufacture L-form sugars and antiviral drugs, generally produced from L-arabinose as a substrate. However, the production of L-ribulose from L-arabinose is limited by the equilibrium ratio of the catalytic reaction, hence, it is necessary to explore a new biological enzymatic method to produce L-ribulose. Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase (Rpi) is an enzyme that can catalyze the reversible isomerization between L-ribose and L-ribulose, which is of great significance for the preparation of L-ribulose. In order to obtain highly active ribose-5-phosphate isomerase to manufacture L-ribulose, ribose-5-phosphate isomerase A (OsRpiA) from Ochrobactrum sp. CSL1 was engineered based on structural and sequence analyses. Through a rational design strategy, a triple-mutant strain A10T/T32S/G101N with 160% activity was acquired. The enzymatic properties of the mutant were systematically investigated, and the optimum conditions were characterized to achieve the maximum yield of L-ribulose. Kinetic analysis clarified that the A10T/T32S/G101N mutant had a stronger affinity for the substrate and increased catalytic efficiency. Furthermore, molecular dynamics simulations indicated that the binding of the substrate to A10T/T32S/G101N was more stable than that of wild type. The shorter distance between the catalytic residues of A10T/T32S/G101N and L-ribose illuminated the increased activity. Overall, the present study provided a solid basis for demonstrating the complex functions of crucial residues in RpiAs as well as in rare sugar preparation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, W. L., Zhang, T., Jiang, B., & Mu, W. M. (2017). Enzymatic approaches to rare sugar production. Biotechnology Advances, 35, 267–274.
Chen, D., Chen, J., Liu, X., Guang, C., Zhang, W., & Mu, W. (2021). Biochemical identification of a hyperthermostable L-ribulose 3-epimerase from Labedella endophytica and its application for D-allulose bioconversion. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 189, 214–222.
Mahmood, S., Iqbal, M. W., Riaz, T., Zhang, W. L., & Mu, W. M. (2020). Characterization of recombinant L-ribose isomerase acquired from Cryobacterium sp. N21 with potential application in L-ribulose production. Process Biochemistry, 97, 1–10.
Hu, C., Li, L. Z., Zheng, Y. Y., Rui, L. L., & Hu, C. Y. (2011). Perspectives of biotechnological production of l-ribose and its purification. Appl Microbiol Biot, 92, 449–455.
Okano, K. (2009). Synthesis and pharmaceutical application of L-ribose. Tetrahedron, 65, 1937–1949.
Guo, Z. R., Long, L. K., & Ding, S. J. (2019). Characterization of a D-lyxose isomerase from Bacillus velezensis and its application for the production of D-mannose and L-ribose. Amb Express, 9, 149–160.
Helanto, M., Kiviharju, K., Leisola, M., & Nyyssola, A. (2007). Metabolic engineering of lactobacillus plantarum for production of L-ribulose. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 7083–7091.
Jiajun, C., Hao, W., Wenli, Z., & Wanmeng, M. (2020). Recent advances in properties, production, and applications of L-ribulose. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 104, 5663–5672.
Mahmood, S., Iqbal, M. W., Zhang, W. L., & Mu, W. M. (2021). A review on L-ribose isomerases for the biocatalytic production of L-ribose and L-ribulose. Food Research International, 145, 110409–110421.
Ahmed, Z., Shimonishi, T., Bhuiyan, S. H., Utamura, M., Takada, G., & Izumori, K. (1999). Biochemical preparation of L-ribose and L-arabinose from ribitol: A new approach. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 88, 444–448.
Helanto, M., Kiviharju, K., Granstrom, T., Leisola, M., & Nyyssola, A. (2009). Biotechnological production of L-ribose from L-arabinose. Appl Microbiol Biot, 83, 77–83.
Granstrom, T. B., Takata, G., Tokuda, M., & Izumori, K. (2004). Izumoring: A novel and complete strategy for bioproduction of rare sugars. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 97, 89–94.
Mahmood, S., Iqbal, M. W., Riaz, T., Hassanin, H. A. M., Zhu, Y. Y., Ni, D. W., & Mu, W. M. (2020). Characterization of a recombinant L-ribose isomerase from Mycetocola miduiensis and its application for the production of L-ribulose. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 135, 109510–109519.
Liu, X. X., Li, Z. J., Chen, Z., Wang, N., Gao, Y. H., Nakanishi, H., & Gao, X. D. (2019). Production of L-ribulose using an encapsulated L-arabinose isomerase in yeast spores. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 67, 4868–4875.
Yeom, S. J., Kim, N. H., Yoon, R. Y., Kwon, H. J., Park, C. S., & Oh, D. K. (2009). Characterization of a mannose-6-phosphate isomerase from Geobacillus thermodenitrificans that converts monosaccharides. Biotechnology Letters, 31, 1273–1278.
Ju, X., Xu, X. Q., Shen, M., Mo, X. B., Fan, H., & Li, L. Z. (2020). Biochemical and structural insights into an Ochrobactrum sp. CSL1 ribose-5-phosphate isomerase A and its roles in isomerization of rare sugars. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 140, 109604–109613.
Chen, J. J., Wu, H., Zhang, W. L., & Mu, W. M. (2020). Ribose-5-phosphate isomerases: Characteristics, structural features, and applications. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 104, 6429–6441.
Essenberg, M. K., & Cooper, R. A. (1975). Two ribose-5-phosphate isomerases from Escherichia coli K12: Partial characterisation of the enzymes and consideration of their possible physiological roles. European journal of biochemistry, 55, 323–332.
Shen, M., Ju, X., Xu, X. Q., Yao, X. M., Li, L. Z., Chen, J. J., Hu, C. Y., Fu, J. L., & Yan, L. S. (2018). Characterization of Rihnse-5-Phosphate Isomerase B from newly isolated strain Ochrobactrum sp CSL1 producing L-rhamnulose from L-rhamnose. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 28, 1122–1132.
Wang, R., Xu, X. Q., Yao, X. M., Tang, H. T., Ju, X., & Li, L. Z. (2021). Enhanced isomerization of rare sugars by ribose-5-phosphate isomerase A from Ochrobactrum sp. CSL1. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 148, 109789–109797.
Sedmak, J. J., & Grossberg, S. E. J. A. B. (1977). A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using coomassie brilliant blue G250. Analytical Biochemistry, 79, 544–552.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Muniruzzaman, S., Tokunaga, H., & Izumori, K. (1994). Isolation of enterobacter agglomerans strain 221E from soil, a potent D-tagatose producer from galactitol. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 78, 145–148.
Jung, C. H., Hartman, F. C., Lu, T. Y. S., & Larimer, F. W. (2000). D-ribose-5-phosphate isomerase from spinach: Heterologous overexpression, purification, characterization, and site-directed mutagenesis of the recombinant enzyme. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 373, 409–417.
Ishikawa, K., Matsui, I., Payan, F., Cambillau, C., Ishida, H., Kawarabayasi, Y., Kikuchi, H., & Roussel, A. (2002). A hyperthermostable D-ribose-5-phosphate isomerase from Pyrococcus horikoshii characterization and three-dimensional structure. Structure, 10, 877–886.
Capriles, P., Baprista, L. P. R., Guedes, I. A., Guimaraes, A. C. R., Custodio, F. L., Alves-Ferreira, M., & Dardenne, L. E. (2015). Structural modeling and docking studies of ribose 5-phosphate isomerase from Leishmania major and Homo sapiens: A comparative analysis for Leishmaniasis treatment. Journal of Molecular Graphics & Modelling, 55, 134–147.
Zhang, X. F., Xu, X. Q., Yao, X. M., Wang, R., Tang, H. T., Ju, X., & Li, L. Z. (2020). Exploring multifunctional residues of ribose-5-phosphate isomerase B from Ochrobactrum sp. CSL1 enhancing isomerization of D-Allose. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 68, 3539–3547.
Kaur, P. K., Tripathi, N., Desale, J., Neelagiri, S., Yadav, S., Bharatam, P. V., & Singh, S. (2016). Mutational and structural analysis of conserved residues in ribose-5-phosphate isomerase B from Leishmania donovani: Role in substrate recognition and conformational stability. Plos One, 11, 0150764–0150784.
Ziwei, C., Wei, X., Wenli, Z., Tao, Z., Bo, J., & Wanmeng, M. (2018). Characterization of a thermostable recombinant L-rhamnose isomerase from Caldicellulosiruptor obsidiansis OB47 and its application for the production of L-fructose and L-rhamnulose. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 98, 2184–2193.
Wen, L. Q., Zang, L. L., Huang, K., Li, S. S., Wang, R. L., & Wang, P. G. (2016). Efficient enzymatic synthesis of L-rhamnulose and L-fuculose. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 26, 969–972.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21676173 and 32001634).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qian Zheng: Writing (original draft) and investigation. Rong Wang: Methodology and investigation. Xin Ju: Conceptualization, methodology, and writing—original draft. Xujing Gu: Investigation. Xinqi Xu: Investigation and writing—original draft. Zhi Chen: Investigation. Liangzhi Li: Project administration, supervision, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
No related ethical issues.
Consent to Participate
The authors promise that the work described has not been published previously, that it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere, and that its publication is approved by all authors and tacitly or explicitly by the responsible authorities where the work was carried out.
Consent for Publication
The authors promise that if the manuscript is accepted, it will not be published elsewhere in the same form, in English, or in any other language, without the written consent of the publisher.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Q., Wang, R., Ju, X. et al. Enhancement of L-ribulose Production from L-ribose Through Modification of Ochrobactrum sp. CSL1 Ribose-5-phosphate Isomerase A. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194, 4852–4866 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04015-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04015-2