Abstract
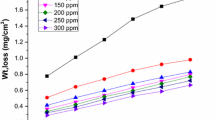
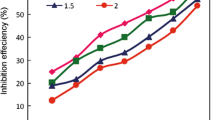
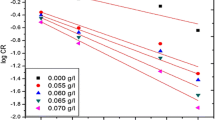
In this research investigation, conventional weight loss method, electrochemical measurements of potentiodynamic polarization and AC impedance spectroscopy were applied to inspect the Bombax ceiba leaves extract mitigation efficiency in 1.0 M H2SO4 medium at different temperatures. Behaviour of adsorption, parameters of thermodynamical and kinetic were intended in this study. Adsorption behaviour revealed that the phyto-organic constituents existing in the mitigator adsorbed on the metal exterior. The spectral studies then topographical experiments confirm the creation of insoluble film on mild steel in destructive medium. The contact angle method predicts the wettability character of the mild steel in the occurrence of mitigator. This research work exhibited that Bombax ceiba leaves extract act as a best low-cost, bio-friendly mitigator on mild steel in destructive medium.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during the current study are in this article.
References
Bhaskaran, R., Palaniswamy, N., Rengaswamy, N. S., & Jayachandran, M. (2005). A review of differing approaches used to estimate the cost of corrosion (and their relevance in the development of modern corrosion prevention and control strategies). Anti-Corrosion methods and Materials, 52, 29–41. https://doi.org/10.1108/00035590510574899
Bennett, L. H., Kruger, J., Parker, R. L., Passaglia, E., Reimann, C., Ruff, A. W., & Yakowitz, H. (1978a). Economic effects of metallic corrosion in the United States. NBS Special Publication pp. 511–1, SD Stock No. SN-003-003-01926-7.
Bennett, L. H., Kruger, J., Parker, R. L., Passaglia, E., Reimann, C., Ruff, A. W. & Yakowitz, H. (1978b). Appendix B, NBS Special Publication 511–2, SD Stock No. SN-003-003-01927-5.
Meltem, D., Yazici, B., & Erbil, M. (2004). The effect of indole on the corrosion behaviour of stainless steel. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 87(1), 138–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2004.05.043
Galal, A., Atta, N. F. & Al-Hassan, M. H. S. (2005). Effect of some thiophene derivatives on the electrochemical behavior of AISI 316 austenitic stainless steel in acidic solutions containing chloride ions: II. Effect of temperature and surface studies. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 89(1), 28–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2004.08.018
Fontana, M. J. (1988). Corrosion Engineering. Chapter11 (3rd ed.). London: McGraw-Hill.
Al-Otaibi, M. S., Al-Mayouf, A. M., Khan, M., Mousa, A. A., Al-Mazroa, S. A., & Alkhathlan, H. Z., (2014). Corrosion inhibitory action of some plant extracts on the corrosion of mild steel in acidic media. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 7(3), 340–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2012.01.015
Putilova, I. N., Balezin, S. A., & Barannik, O. P. (1960). Metallic CorrosionInhibitors. Translated from the Russian by Ryback. New York: Pergamon Press.
Sanyal, B. (1981). Organic compounds as corrosion inhibitors in different environments: A review. Progress in Organic Coatings, 9(2), 165–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/0033-0655(81)80009-X.
Singh, A., Ebenso, E. E., & Quraishi, M. A. (2012). Corrosion inhibition of carbon steel in HCl solution by some plant extracts. International Journal of Corrosion, 2012, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/897430
Lecante, A., Robert, F., Blandinières, P. A. & Roos, C. (2011). Anti-corrosive properties of S. tinctoria and G. ouregou alkaloid extracts on low carbon steel. Current Applied Physics, 11(3), 714–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2010.11.038
Bhandarkar, D., Dighe, V., & Datar, A. (2018). Development and validation of liquid chromatography-Tandem Mass spectrometric method for simultaneous quantitation of mangiferin and isoquercetin from died powder extract of Bombax ceiba Linn. International Journal of Science and Research, 7(1), 1562–1566. https://doi.org/10.21275/ART20179733
Karole, S., Gautam, G., & Gupta, S. (2017). Pharmacognostic and pharmacological profile of Bombax ceiba. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, 6(3), 16–27.
Ekpe, U. J., Ibok, U. J., Ita, B. I., Offiong, O. E., & Ebenso, E. E. (1995). Materials Chemistry and Physics, 40, 87–93.
Vasudha, V. G., & Saratha, R. (2011). Studies on inhibition on acid corrosion of mild steel by Terminalia catappa (Tropical almond) leaves. Oriental Journal of Chemistry, 27(3), 1165–1171. http://www.orientjchem.org/?p=24590
Ekpe, U. J., Ibok, U. J., Ita, B. I., Offiong, O. E., & Ebenso, E. E. (1995). Inhibitory action of methyl and phenyl thiosemicarbazone derivatives on the corrosion of mild steel in hydrochloric acid. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 40(2), 87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/0254-0584(94)01464-R
Abboud, Y., Abourriche, A., Saffaj, T., Berrada, M., Charrouf, M., Bennamara, A., & Hannache H. (2009). A novel azo dye, 8-quinolinol-5-azoantipyrine as corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic media. Desalination, 237(1–3), 175–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.12.031
Farooqi, I. H., Hussain, A., Quraishi, M. A., & Saini, P. A. (1999). Study of low costeco‐friendly compounds as corrosion inhibitors for cooling systems. Anti-Corrosion Methods and Materials, 46(5), 328–335. https://doi.org/10.1108/00035599910295508
El Azhar, M., Mernari, B., Traisnel, M., & Fouad bentiss. (2001). Corrosion inhibition of mild steel by the new class of inhibitors [2,5-bis(n-pyridyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazoles] in acidic media. Corrosion Science, 43(12), 2229–2238. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(01)00034-8
Schulthess, C. P., & Dey. D. K. (1996). Estimation of Langmuir constants using linear and nonlinear least squares regression analyses. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 60, 433–442. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1996.03615995006000020014x
Langmuir, I. (1917). The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. II. Liquids. Journal of American Chemical Society, 183(1), 102–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-0032(17)90938-X
Temkin, M. J., & Pyzhev, V. (1940). Recent modifications to Langmuir isotherms. Acta Physiochim USSR, 12, 217–222.
Ramananda Singh, M., Bhrara, K., & Singh, G. (2008). The inhibitory effect of Diethanolamine on corrosion of mild steel in 0.5 M sulphuric acid medium. Portugaliae Electrochemica Acta, 26(6), 479–492. https://doi.org/10.4152/pea.200806479
Khamis, E. (1990). The effect of temperature on the acidic dissolution of steel in the presence of inhibitors. Corrosion, 46(6), 476–484. https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3585135
El-Awady, Y. A., & Ahmed, A. I. (1985). Effect of temperature and inhibitors on the corrosion of aluminium in 2N HCl solutions: A kinetic study. Indian Journal of Chemistry, 24A, 601–606.
El-Awady, A. A., Abd-El-Nabey, B. A., & Aziz, S. G. (1992). Kinetic thermodynamic and adsorption isotherms analyses for the inhibition of the acid corrosion of steel by cyclic and open- chain amines. Journal of Electrochemical Society, 139(8), 2149–2154. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2221193
Abd El Rehim, S. S., Magdy, Ibrahim, A. M., & Khalid, E. F. (2001). The inhibition of 4-(2′-amino-5′-methylphenylazo) antipyrine on corrosion of mild steel in HCl solution, Materials Chemistry and Physics, 70(3), 268–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(00)00462-4
Umoren, S. A., Ebenso, E. E., Okafor, P. C., & Ogbobe, O. (2006). Water soluble polymers as corrosion inhibitors of mild steel in acidic medium. Pigment and Resin Technology, 35(6), 346–352. https://doi.org/10.1108/03699420610711353
Sudhish K. Shukla, & Ebenso, Eno E. (2011). Corrosion inhibition, adsorption behaviour and thermodynamic properties of streptomycin on mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 6, 3277–3291.
Ahamad, I., Prasad, R., & Quraishi, M.A. (2010). Adsorption and inhibitive properties of some new Mannich bases of Isatin derivatives on corrosion of mild steel in acidic media. Corrosion Science, 52, 1472–1481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2010.01.015
Quraishi, M. A., Ambrish Singh, Vinod Kumar Singh, Dileep Kumar Yadav, & Ashish Kumar Singh. (2010). Green approach to corrosion inhibition of mild steel in hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid solutions by the extract of Murraya koenigii leaves. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 122(1), 114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.02.066
Gallego, S. M., Benavides, M. P., & Tomaro, M. L. (1996). Effect of heavy metal ion excess on sunflower leaves: evidence for involvement of oxidative stress. Plant Science, 121(2), 151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(96)04528-1
Safak, Serpil., Berrin Duran, Aysel Yurt, & Gülşen Türkoğlu. (2012). Schiff bases as corrosion inhibitor for aluminium in HCl solution, Corrosion Science, 54, 251–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2011.09.026
Violet Dhayabaran, Johnson Princy Merlin, Sharmila Lydia, I., & Shanthi, R. (2005). Inhibition of corrosion of aluminium in presence of fluorescein in basic medium. Ionics, 10(3), 288–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02382831
Mansfeld, F., Kending, M .W., & Tsai, S. (1981). Recording and analysis of AC Impedance data for corrosion studies. Corrosion, 37(5), 301–307. https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3621688
Sribharathy, V., Susai Rajendran, Rengan, P., & Nagalakshmi, R. (2013). Corrosion inhibition by an aqueous extract of Aloe vera (L.) Burm F. (Liliaceae). European Chemical Bulletin, 2(7), 471–476. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260336601
Syed Abuthahir, S. S., Jamal Abdul Nasser, A., & Rajendran, S. (2013). Electrochemical and surface analysis studies on corrosion inhibition of mild steel by 1-(8-hydroxyquinolin-2-ylmethyl)thiourea. European chemical bulletin, 2(11), 932–935. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283068441
Cornell, R. M., & Schwertmann, U. (1996). The iron–oxides – structure, properties, reactions, occurences and uses. Berlin: Springer pp. 573. https://doi.org/10.1002/3527602097
Jasinski, R., & Lob, A. (1988). FT-IR measurements of iron oxides on low alloy steel. Journal of Electrochemical Society, 135(3), 551. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1149/1.2095656
Leelavathi, S., & Rajalakshmi, R. (2013). Dodonaea viscosa (L.) leaves extract as acid corrosion inhibitor for mild Steel – A Green approach. Journal of Material and Environmental Science, 4(5), 625–638. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279594808
Mathina, A., & Rajalakshmi, R. (2016). Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in acid medium using Canna indica as green corrosion inhibitor. Rasayan Journal of chemistry, 9(1), 56–66. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/306225500
Ganesha, A., ArthobaNaik, Y., Vijay Kumar, S., Venkatesha, T. V., & Sherigara, B. S. (2008). An electroactive co-polymer as corrosion inhibitor for steel in sulphuric acid medium. Applied Surface Science, 254, 5569–5573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.02.103
Bothi Raja, P., & Sethuraman, M. G. (2010). Studies on the inhibition of mild steel corrosion by Rauvolfia serpentina in acid media. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 19, 761–766. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-009-9541-4
Rajiv Prakash., GopalJi., Sudhish Kumar Shukla., Priyanka Dwivedi., Shanthi Sundaram., & Ebenso, E. E. (2012). Partheniumhysterophorusplant extract as an efficient green corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environment. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 7(10), 9933–9945. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267856332
Niketan Patel., Anamika Rawat., Smita Jauhari., & Girish Mehta. (2010). Inhibitive action of Brideliaretusa leaves extract on corrosion of mild steel in acidic media. European Journal Chemistry, 1(2), 129–133. https://doi.org/10.5155/eurjchem.1.2.129-133.52
Chandan M. Reddy, Bhargav D. Sanketi & Narendra Kumar, S. (2016). Corrosion inhibition of mild steel by Capsicum annum fruit paste. Science Direct, 8, 603–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pisc.2016.06.033
Wang, B., Du, M., Zhang, J., & Gao, C. J. (2011). Electrochemical and surface analysis studies on corrosion inhibition of Q235 steel by imidazoline derivative against CO2 corrosion. Corrosion Science, 53(1), 353–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2010.09.042
Prajitno, D. H., Maulana, A., & Syarif, D. G. (2016). Effect of surface roughness on contact angle measurement of nanofluid on surface of stainless steel 304 by sessile drop. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 739, 1–5. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/739/1/012029
Zakvi, & Mehta. (1988). Inhibition of corrosion of mild steel in acid extracts of mahasudharsana Churna. Journal of Electrochemical Society of India, 37(3), 237–239.
Arifa Farzana, B. Mushira banu, A. & Riaz Ahamed, K. (2021). Andrographis echioides leaves extract as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acid medium. Materials Today Proceedings, 47, 2080–2090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.04.478
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author and co-authors are obliged to their organization and the instrumentation facilities funded by DBT-STAR College Scheme to complete their research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mushira Banu Ahmed Meeran: conceptualization, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, visualization, writing—original draft.
Arifa Farzana Bijili: resources, writing, validation.
Riaz Ahamed Abdul Khader: review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meeran, M.B.A., Bijili, A.F. & Khader, R.A.A. Evaluation of Corrosion Mitigation Behaviour of Bombax ceiba Leaves Extract. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 3787–3806 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03925-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03925-5