Abstract
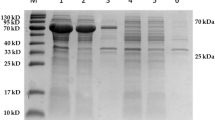
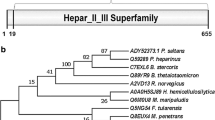
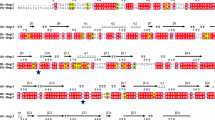
Heparin is a class of highly sulfated, acidic, linear, and complex polysaccharide that belongs to the heparin/heparan sulfate (HS) glycosaminoglycans family. Enzymatic depolymerization of heparin by heparinases is a promising strategy for the production of ultra-low molecular weight heparins (ULMWHs) as anticoagulants. In the present study, a novel heparinase-producing strain Raoultella NX-TZ-3–15 was isolated and identified from soil samples. Herein, the heparinase gene MBP-H1 was cloned to the pBENT vector to enable expression in Escherichia coli. The optimized conditions made the activity of recombinant heparinase reach the highest level (2140 U/L). The overexpressed MBP-H1 was purified by affinity chromatography and a purity of more than 90% was obtained. The condition for biocatalysis was also optimized and three metal ions Ca2+, Co2+, and Mg2+ were utilized to activate the reaction. In addition, the kinetics regarding the new fusion heparinase was also determined with a Vm value of 11.29 μmol/min and a Km value of 31.2 μmol/L. In short, due to excellent Km and Vmax, the recombinant enzyme has great potential to be used in the clinic in medicine and industrial production of low or ultra-low molecule weight heparin.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Shriver, Z., Capila, I., Venkataraman, G., & Sasisekharan, R. (2012). Heparin and heparan sulfate: Analyzing structure and microheterogeneity. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology: 159–76.
Capila, I., Hernáiz, M. A. J., Mo, Y. D., Mealy, T. R., Campos, B., Dedman, J. R., Linhardt, R. J., & Seaton, B. A. (2001). Annexin V–heparin oligosaccharide complex suggests heparan sulfate–mediated assembly on cell surfaces. Structure, 9, 57–64.
Satish, L., Santra, S., Tsurkan, M. V., Werner, C., Jana, M., & Sahoo, H. (2021). Conformational changes of GDNF-derived peptide induced by heparin, heparan sulfate, and sulfated hyaluronic acid – analysis by circular dichroism spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulation. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 182, 2144–2150.
Bergwik, J., Kristiansson, A., Larsson, J., Ekström, S., Åkerström, B., & Allhorn, M. (2021). Binding of the human antioxidation protein α1-microglobulin (A1M) to heparin and heparan sulfate. Mapping of binding site, molecular and functional characterization, and co-localization in vivo and in vitro. Redox Biology, 41, 101892.
Lin, J., Zheng, L., Liang, Q., Jiang, L., & Wei, Z. (2021). Preparation and characterization of partial de-O-sulfation of heparin oligosaccharide library. Carbohydrate Research, 499, 108226.
Singh, V., Haque, S., Kumari, V., El-Enshasy, H. A., Mishra, B. N., et al. (2019). Isolation, purification, and characterization of heparinase from Streptomyces variabilis MTCC 12266. Scientific Reports, 9, 6482.
Hovingh, P., & Linker, A. (1974). The disaccharide repeating-units of heparan sulfate. Carbohydrate Research, 37, 181–192.
Kumar, N., Bentolila, A., & Domb, A. J. (2005). Structure and biological activity of heparinoid. Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry, 5, 441–447.
Merilahti, P., Karelehto, E., & Susi, P. (2016). Role of heparan sulfate in cellular infection of integrin-binding coxsackievirus A9 and human parechovirus 1 isolates. PloS One, 11, e0147168.
Walenga, J. M., & Lyman, G. H. (2013). Evolution of heparin anticoagulants to ultra-low-molecular-weight heparins: A review of pharmacologic and clinical differences and applications in patients with cancer. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology, 88, 1–18.
Viskov, C., Just, M., Laux, V., Mourier, P., & Lorenz, M. (2009). Description of the chemical and pharmacological characteristics of a new hemisynthetic ultra-low-molecular-weight heparin, AVE5026. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 7, 1143–1151.
Ji, Y., Wang, Y., Zeng, W., Mei, X., Du, S., Yan, Y., Hao, J., Zhang, Z., Lu, Y., Zhang, C., Ge, J., & Xing, X.-H. (2020). A heparin derivatives library constructed by chemical modification and enzymatic depolymerization for exploitation of non-anticoagulant functions. Carbohydrate Polymers, 249, 116824.
Qiu, M., Huang, S., Luo, C., Wu, Z., Liang, B., Huang, H., Ci, Z., Zhang, D., Han, L., & Lin, J. (2021). Pharmacological and clinical application of heparin progress: An essential drug for modern medicine. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 139, 111561.
Fu, L., Suflita, M., & Linhardt, R. J. (2016). Bioengineered heparins and heparan sulfates. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 97, 237–249.
Zhang, Z., Zhao, Y., Luo, X., Feng, S., & Wu, L. (2022). Preparation of a heparin-like functionalized tannic acid-coated polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane for hemodialysis by a simple surface modification method. Applied Surface Science, 572, 151440.
Guo, J., Li, K., Ning, C., & Liu, X. (2020). Improved cellular bioactivity by heparin immobilization on polycarbonate film via an aminolysis modification for potential tendon repair. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 142, 835–845.
Jayaraman, S., Pérez, A., Miñambres, I., Sánchez-Quesada, J. L., & Gursky, O. (2022). Heparin binding triggers human VLDL remodeling by circulating lipoprotein lipase: Relevance to VLDL functionality in health and disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 1867, 159064.
Tripathi, C. K. M., Banga, J., & Mishra, V. (2012). Microbial heparin/heparan sulphate lyases: Potential and applications. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 94, 307–321.
Sepuru, K. M., & Rajarathnam, K. (2019). Structural basis of chemokine interactions with heparan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, and dermatan sulfate. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 294, 15650–15661.
Galliher, P. M., Cooney, C. L., Langer, R., & Linhardt, R. J. (1981). Heparinase production by Flavobacterium heparinum. Applied and environmental microbiology, 41, 360–365.
Galliher, P. M., Linhardt, R. J., Conway, L. J., Langer, R., & Cooney, C. L. (1982). Regulation of heparinase synthesis in Flavobacterium heparinum. European Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 15, 252–257.
Yang, V. C., Linhardt, R. J., Bernstein, H., Cooney, C. L., & Langer, R. (1985). Purification and characterization of heparinase from Flavobacterium heparinum. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 260, 1849–1857.
Yang, B.-C., Zhang, C., Wang, C., Zhou, H., Li, Z.-Y., Song, Y.-J., Zhang, T.-C., & Luo, X.-G. (2017). Soluble expression and purification of heparinase I in Escherichia coli using a hexahistidine-tagged small ubiquitin-like modifier as a fusion partner. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, 31, 1040–1045.
Ahn, M. Y., Shin, K. H., Kim, D. H., Jung, E. A., Toida, T., Linhardt, R. J., & Kim, Y. S. (1998). Characterization of a Bacteroides species from human intestine that degrades glycosaminoglycans. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 44, 423–429.
Kim, B. T., Kim, W. S., Kim, Y. S., Linhardt, R. J., & Kim, D. H. (2000). Purification and characterization of a novel heparinase from Bacteroides stercoris HJ-15. Journal of Biochemistry, 128, 323–328.
Yoshida, E., Sakai, K., Tokuyama, S., Miyazono, H., Maruyama, H., Morikawa, K., Yoshida, K., & Tahara, Y. (2002). Purification and characterization of heparinase that degrades both heparin and heparan sulfate from Bacillus circulans. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 66, 1181–1184.
Liu, C. Y., Su, W. B., Guo, L. B., & Zhang, Y. W. (2020). Cloning, expression, and characterization of a novel heparinase I from Bacteroides eggerthii. Preparative Biochemistry & Biotechnology, 50, 477–485.
Yapeng, C., Ningguo, G., Xiulan, C., Jing, Y., Shijun, Q., & Shuzheng, Z. (2003). Rapid purification, characterization and substrate specificity of heparinase from a novel species of Sphingobacterium. Journal of Biochemistry, 134, 365–371.
Banga, J., & Tripathi, C. K. (2009). Rapid purification and characterization of a novel heparin degrading enzyme from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. New Biotechnology, 26, 99–104.
Lénon, M., Ke, N., Ren, G., Meuser, M. E., Loll, P. J., Riggs, P., & Berkmen, M. (2021). A useful epitope tag derived from maltose binding protein. Protein Science, 30, 1235–1246.
Rosano, G. L., & Ceccarelli, E. A. (2014). Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: Advances and challenges. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5, 172.
Heyde, S. A. H., & Nørholm, M. H. H. (2021). Tailoring the evolution of BL21(DE3) uncovers a key role for RNA stability in gene expression toxicity. Communications Biology, 4, 963.
Austin, B. P., Nallamsetty, S., & Waugh, D. S. (2009). Hexahistidine-tagged maltose-binding protein as a fusion partner for the production of soluble recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.), 498, 157–72.
Dilworth, M. V., Piel, M. S., Bettaney, K. E., Ma, P., Luo, J., Sharples, D., Poyner, D. R., Gross, S. R., Moncoq, K., Henderson, P. J. F., Miroux, B., & Bill, R. M. (2018). Microbial expression systems for membrane proteins. Methods, 147, 3–39.
Hang, B., Pan, J., Ni, D., Zheng, Q., Zhang, X., Cai, J., Huang, L., Wei, P., & Xu, Z. (2016). High-level production of aquaporin Z in Escherichia coli using maltose-binding protein/polyhistidine dual-affinity tag fusion system. Process Biochemistry, 51, 599–606.
Nekhili, H., Bouras, N., Jiang, Y., Toumatia, O., Lamari, L., Zitouni, A., & Jiang, Cl. (2021). Thermo-halotolerant mycelial bacteria from Algerian soils: Isolation, taxonomy and antagonistic properties. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 33, 101972.
Zimmermann, J. J., Langer, R., & Cooney, C. L. (1990). Specific plate assay for bacterial heparinase. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 56, 3593–3594.
Maurer, J., Haselbach, S., Klein, O., Baykut, D., Vogel, V., & Mäntele, W. (2011). Analysis of the complex formation of heparin with protamine by light scattering and analytical ultracentrifugation: Implications for blood coagulation management. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 133, 1134–1140.
Lai, T. E., Pullammanappallil, P. C., & Clarke, W. P. (2006). Quantification of cellulase activity using cellulose-azure. Talanta, 69, 68–72.
Yu, V. C., Yu, P. H., Ho, K. C., & Lee, F. W. (2011). Isolation and identification of a new tetrodotoxin-producing bacterial species, Raoultella terrigena, from Hong Kong marine puffer fish Takifugu niphobles. Marine Drugs, 9, 2384–2396.
Costa, S., Almeida, A., Castro, A., & Domingues, L. (2014). Fusion tags for protein solubility, purification and immunogenicity in Escherichia coli: The novel Fh8 system. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5, 63.
Huang, J., Cao, L., Guo, W., Yuan, R., Jia, Z., & Huang, K. (2012). Enhanced soluble expression of recombinant Flavobacterium heparinum heparinase I in Escherichia coli by fusing it with various soluble partners. Protein Expression and Purification, 83, 169–176.
Gao, L.-W., Zhu, H.-T., Liu, C.-Y., Lv, Z.-X., Fan, X.-M., & Zhang, Y.-W. (2020). A highly active heparinase I from Bacteroides cellulosilyticus: Cloning, high level expression, and molecular characterization. PloS One, 15, e0240920.
Zhou, L. J., Guo, L. B., Wei, W., Lv, Z. X., & Zhang, Y. W. (2021). A novel chondroitin AC lyase with broad substrate specificity from Pedobacter rhizosphaerae: Cloning, expression, and characterization. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 9, 808872.
Luo, Y., Huang, X., & McKeehan, W. L. (2007). High yield, purity and activity of soluble recombinant Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron GST-heparinase I from Escherichia coli. Archive of Biochemistry and Biophysic, 460, 17–24.
Xu, S., Qiu, M., Zhang, X., & Chen, J. (2017). Expression and characterization of an enhanced recombinant heparinase I with chitin binding domain. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 105, 1250–1258.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFA0910800), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2022A1515012043), and the Special Funds for Development of Strategic Emerging Industries in Shenzhen (JCYJ20190808145613154, KQJSCX20180328100801771), and Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (ZDSYS20210623100800001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y. Lin: conceptualization, methodology, software; Y. Lin: conceptualization, methodology, software; Y. Jiang: visualization, investigation; H. M. Mehwish: data curation, writing-original draft preparation; M. S. R. Rajoka: software, validation, writing-original draft preparation. Liqing Zhao: supervision, funding, validation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Yes. All authors agreed to participate in this research.
Consent for Publication
Yes. All authors have approved the last version of the manuscript for its submission.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Lin, Y., Jiang, Y. et al. Cloning and Expression of Heparinase Gene from a Novel Strain Raoultella NX-TZ-3–15. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194, 4971–4984 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03917-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03917-5