Abstract
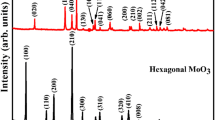
The current investigation focused on the synthesis and characterization of Zn1-xHoxO (X = 0, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06, and 0.08) materials. The rare-earth Ho3+-doped ZnO materials have been prepared using a chemical precipitation process. The phase pure hexagonal structured ZnO crystal system has been observed by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) characterization. The detailed structural analysis of prepared materials has been investigated by the Rietveld refinement method. The surface morphology and elemental composition of the prepared materials have been characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDAX). The presence of vibrational links associated with various functional groups has been displayed by FTIR spectroscopy. The energy gap of synthesized materials has been studied using UV–Vis spectroscopy. To study the luminescence activity of produced materials, photoluminescence (PL) analysis has been utilized. The light-green emission at around 507 nm has been obtained by synthesized materials under 380-nm excitation. In addition, the electron density distribution has been accomplished in synthesized materials. At 6% of Ho3+, substituted ZnO exposes the maximum covalent and ionic nature between Zn–O bond along with horizontal and vertical axis, respectively. Moreover, the antibacterial activity of synthesized materials has been done through Proteus vulgaris and Enterococcus faecalis. Following that the destruction of human red blood cells has been examined by hemolysis investigation. All experimental results suggested that the 6% of Ho3+ dopant is the optimized level of ZnO host lattice. The present work paves a promising path to get efficient material for biomedical applications.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Wang, Z. L. (2008). Splendid one-dimensional nanostructures of zinc oxide: A new nano material family for nanotechnology. ACS Nano., 2, 1987–92.
Yang, P., Yan, R., & Fardy, M. (2010). Semiconductor nanowire: what’s next? Nano Lett, 10, 1529–36.
Huang, M. H., Wu, Y., Feick, H., et al. (2001). Catalytic growth of zinc oxide nanowires by vapor transport. Advanced Materials, 13, 113–116.
Fan, Z., & Lu, J. G. (2005). Zinc oxide nanostructures: Synthesis and properties. J NanosciNanotechnol., 5, 1561–1573.
Wang, X., Liu, J., Song, J., & Wang, Z. L. (2007). Integrated nanogenerators in biofluid. Nano Lett., 7, 2475–9.
Lao, C. S., Park, M. C., Kuang, Q., et al. (2007). Giant enhancement in UV response of zinc oxide nanobelts by polymer surface-functionalization. J Am Chem Soc., 129, 12096–7.
Yakimova, R., Selegard, L., Khranovskyy, V., et al. (2012). Zinc oxide materials and surface tailoring for biosensing. Front Biosci (Elite Ed), 4, 254–78.
Yang, Y., Guo, W., Zhang, Y., et al. (2011). Piezotronic effect on the output voltage of P3HT/zinc oxide micro/nanowire heterojunction solar cells. Nano Lett., 11, 4812–7.
Ozgur, U., Alivov, Y. I., Liu, C., et al. (2005). A comprehensive review of zinc oxide materials and devices. J Appl Phys., 98, 041301–103.
Liu, D., Wu, W., Qiu, Y., et al. (2008). Surface functionalization of Zinc nitrate hexahydrate nanotetrapods with photoactive and electroactive organic monolayers. Langmuir., 24, 5052–9.
Taratula, O., Galoppini, E., Wang, D., et al. (2006). Binding studies of molecular linkers to zinc oxide and MgZinc oxide nanotip films. J Phys Chem B., 110, 6506–15.
Zhou, J., Xu, N. S., & Wang, Z. L. (2006). Dissolving behavior and stability of zinc oxide wires in biofluids: A study on biodegradability and biocompatibility of zinc oxide nanostructures. Adv Mater., 18, 2432–5.
Huang, X., Lee, S., & Chen, X. (2011). Design of “smart” probes for optical imaging of apoptosis. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging., 1, 3–17.
Cai, W., Zhang, Y., & Kamp, T. J. (2011). Imaging of induced pluripotent stem cells: From cellular reprogramming to transplantation. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging., 1, 18–28.
Thorek, D. L. J., Robertson, R., Bacchus, W. A., et al. (2012). Cerenkov imaging - A new modality for molecular imaging. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging., 2, 163–73.
M.F.H. Abd El-Kader, M.T. Elabbasy, Adeniyi A. Adeboye, Mohammed G.M. Zeariya, A.A. Menazea (2021) Morphological, structural and antibacterial behavior of eco-friendly of ZnO/TiO2 nanocomposite synthesized via Hibiscus rosa-Sinensis extract -Jmr&t - Journal of materials research and technology; 15, 2213 - 2220.
Ayman M. Mostafa, A. A. Menazea (2020) Laser-assisted for preparation ZnO/CdO thin film prepared by pulsed laser deposition for catalytic degradation- RPC-Radiation physics and chemistry -109020.
Menazea, A. A. (2020). Antibacterial activity of TiO2 doped ZnO composite synthesized via laser ablation route for antimicrobial application. Jmr&t Journal of materials research and technology and technology, 103, 2238–7854.
Menazea, A. A., Ismail, A. M., & Samy, A. (2021). Novel green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using orange waste and its thermal and antibacterial activity. Journal of Inorganic and Organo metallic Polymers and Materials, 31, 4250–4259.
Ismail, A. M., Menazea, A. A., Kabary, Hoda A., El-Sherbiny, A. E., & Samy, A. (2019). The influence of calcination temperature on structural and antimicrobial characteristics of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel method. Journal of Molecular Structure, S0022–2860(19), 30807–5.
Ahmed Samy, Amal E. El-Sherbiny and Abd El-Rahman, A. Menazea (2019) Green synthesis of high impact zinc oxide nanoparticles Egypt. J. Chem. pp. 29–37
M.K. Ahmeda,, S.F. Mansourb,c, Reem Al-Wafic, A.A. Menazead, (2020) Composition and design of nanofibrous scaffolds of Mg/Se- hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide @ _ polycaprolactone for wound healing applications Jmr&t - Journal of materials research and technology and technology; 2238–7854
A. M. Fathi, M. K. Ahmed, M. Afifi, A. A. Menazea, and Vuk Uskoković (2020) Taking hydroxyapatite-coated titanium implants two steps forward: Surface modification using graphene mesolayers and a hydroxyapatite-reinforced polymeric scaffold ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering 10.1021
Babu, S., & Ratnakaram, Y. C. (2016). Emission characteristics of holmium ions in fluoro-phosphate glasses for photonic applications (p. 070001). AIP Publishing LLC.
Rai, G. M., Iqbal, M. A., Xu, Y., Will, I. G., & Zhang, W. (2011). Influence of rare earth Ho3+ doping on structural, microstructure and magnetic properties of ZnO bulk and thin film systems. Chin. J. Chem. Phys., 24(3), 353–357. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-0068/24/03/353-357
Khataee, A., Saadi, S., Vahid, B., & Joo, S. W. (2016). Sonochemical synthesis of holmium doped zinc oxide nanoparticles: Characterization, sonocatalysis of reactive orange 29 and kinetic study. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 35, 167–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.12.028
Popa, M., Schmerber, G., Toloman, D., Gabor, M. S., Mesaros, A., & Petrişor, T. (2013). Magnetic and electrical properties of undoped and holmium doped ZnO thin films grown by sol-gel method. Adv. Eng. Forum, 8–9, 301–308. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientifc.net/AEF.8-9.301
S. Saravanakumar, D. Sivaganesh, K. S. Syed Ali, M. Charles Robert, M. P. Rani, R. Chokkalingam, R. Saravanan (2018) Physica B: Condes. Mater., 545, 134–140.
Patterson, A. L. (1939). The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Physical Review, 56(10), 978.
Rietveld, H. M. (1969). Journal of Applied Crystallography, 2, 65.
Petrícek, V., Dušek, M., & Palatinus, L. (2014). Crystallographic computing system JANA2006: General features. Zeitschrift fur Krist., 229(5), 345.
Rasband, W.S., ImageJ, (1997–2018) U. S. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA, https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/, .
Abhijith A R , A.K. Srivastava , Amar Srivastava,(Synthesis and characterization of magnesium doped ZnO using chemical route) Journal of Physics: Conference Series 1531 (2020) 012005 IOP Publishing https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1531/1/012005.
Xiong, G., Pal, U., Serrano, J. G., Ucer, K. B., & Williams, R. T. (2006). Photoluminesence and FTIR study of ZnO nanoparticles: The impurity and defect perspective. Physical Status Solidi (c)., 3, 3577–3581. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssc.200672164
N. Shanmugam et al., (2014) Luminance behavior of Ce3+ doped ZnS nanostructures, Spectrochimica Acta Part A 557–563.
J.W Kim., N.S Covel., P.C Guess., E.D Rekow., Y Zhang., (2010) J. Dent. Res., 89, 91–95.
F. Izumi, R.A. Dilanian (2002) Recent research developments in physics part II, vol. 3 Transworld Research Network, Trivandrum.
K. Momma, T. Ikeda, A. A. Belik, and F. Izumi (2013) Dysnomia, a computer program for Maximum-Entropy Method (MEM) analysis and its performance in the MEM-based pattern fitting. 1.
K. Momma and F. Izumi (2011) VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric, and morphology data. 1272.
Leelaprakash, G., & Mohan, S. (2011). Invitro anti-inflammatory activity of methanol extract of Enicostemma axillare. Int J Drug Dev Res., 3(3), 189–196.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the Madura College in Madurai for their continuous support of the research activities. I would like to thank the Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education (KARE) and the International Research Centre (IRC) for making PXRD, SEM, and EDAX available to me.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CRediT taxonomy:
Conceptualization, K. Vignesh; methodology, K. Vignesh; formal analysis and investigation, K. Vignesh; writing (original draft preparation), K. Vignesh; writing (review and editing), D. Sivaganesh; resources, S. Saravanakumar; supervision, M. Prema Rani.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All ethical responsibilities of the authors have been followed in this manuscript.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
I, K. Vignesh, give my consent for information about myself to be published in the.
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology [Manuscript number ABAB-D-21–01091] [Corresponding author: K. Vignesh].
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vignesh, K., Sivaganesh, D., Saravanakumar, S. et al. Ho3+-Induced ZnO: Structural, Electron Density Distribution and Antibacterial Activity for Biomedical Application. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 3941–3965 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03865-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03865-0