Abstract
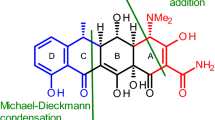
The accurate and early diagnosis of infection is an important feature in the biomedical sciences for better treatment and to decrease the rate of morbidity associated with diseases. Doxycycline (DC) is a semisynthetic antibiotic that belongs to tetracycline family and usually prescribed to treat a variety of infections. The objective of the present research work was to develop a new radiopharmaceutical 99mTc-Doxycycline (99mTc-DC), by using SnCl2·2H2O as a reducing agent for diagnostic applications. It was confirmed through this study that 99mTc-DC possessed high radiolabeling yield (95%). In vitro studies were performed by incubating 99mTc-DC in human serum at 37 °C. The in vitro binding interaction of the labeled antibiotic was analyzed with bacterial strain (live Staphylococcus aureus cells), and its stability was further determined. Moreover, for in vivo infection imaging study, the infection was induced with S. aureus (gram positive) cells intramuscularly injected in mice models followed by biodistribution studies for 99mTc-DC that were performed. Biodistribution studies of 99mTc-DC showed that the radiotracer was significantly accumulated at the site of infection and indicated the renal route of excretion. Scintigraphic images obtained as a result of in vivo study showed good uptake of prepared radiotracer (99mTc-DC) in the infectious lesions at 1-, 4-, and 24-h post-injection. Target-to-non-target ratios for 99mTc-DC were significantly different for the infectious lesions and non-infected tissues and remained 2.13 ± 0.3 up to 24-h post-injection of 99mTc-DC. 99mTc-DC showed preferential binding to living bacterial infected sites as compared to other parts of the body, and thus it can be inferred that 99mTc-DC might be a potential candidate to diagnose the infection.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data are available in supplementary information file (PDF).
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Ferreira, S. M., Domingos, G. P., Ferreira Ddos, S., Rocha, T. G., Serakides, R., de Faria Rezende, C. M., Cardoso, V. N., Fernandes, S. O., & Oliveira, M. C. (2012). Technetium-99m-labeled ceftizoxime loaded long-circulating and pH-sensitive liposomes used to identify osteomyelitis. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 22, 4605–4608.
Eckelman, W.C. (2009). Unparalleled contribution of technetium-99m to medicine over 5 decades. JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging, 2, 364–368.
van der Laken, C. J., Boerman, O. C., Oyen, W. J., van de Ven, M. T., Edwards, D. S., Barrett, J. A., van der Meer, J. W., & Corstens, F. H. (1997). Technetium-99m-labeled chemotactic peptides in acute infection and sterile inflammation. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 38, 1310–1315.
Calame, W., Welling, M., Feitsma, H. I., Ensing, G. J., & Pauwels, E. K. (1993). Improved detection of a staphylococcal infection by monomeric and protein A-purified polyclonal human immunoglobulin. European journal of nuclear medicine, 20, 490–494.
Welling, M., Feitsma, H. I., Calame, W., & Pauwels, E. K. (1997). Detection of experimental infections with 99mTc-labeled monoclonal antibodies against TNF-alpha and interleukin-8. Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 24, 649–655.
Follacchio, G. A., Pala, A., Scaccianoce, S., Monteleone, F., Colletti, P. M., Rubello, D., & Liberatore, M. (2019). In vivo microbial targeting of 99mTc-labeled human β-defensin-3 in a rat model of infection. Clinical Nuclear Medicine, 44, 602–606.
Kniess, T., Laube, M., Wüst, F., & Pietzsch, J. (2017). Technetium-99m based small molecule radiopharmaceuticals and radiotracers targeting inflammation and infection. Dalton Transactions, 46, 14435–14451.
Vinjamuri, S., Solanki, K. K., Bomanji, J., Siraj, Q., Britton, K. E., Hall, A. V., O’Shaughnessy, E., & Das, S. S. (1996). Comparison of 99mTc infecton imaging with radiolabelled white-cell imaging in the evaluation of bacterial infection. The Lancet, 347, 233–235.
Boerman, O. C., Rennen, H., Oyen, W. J. G., & Corstens, F. H. M. (2001). Radiopharmaceuticals to image infection and inflammation. Seminars in Nuclear Medicine, 31, 286–295.
Ahmed, N., Fatima, S., Saeed, M. A., Zia, M., & Irfan Ullah, J. (2019). (99m) Tc-Ceftizoxime: Synthesis, characterization and its use in diagnosis of diabetic foot osteomyelitis. Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology, 63, 61–68.
Chattopadhyay, S., Ghosh, M., Sett, S., Das, M. K., Chandra, S., De, K., Mishra, M., Sinha, S., Ranjan Sarkar, B., & Ganguly, S. (2012). Preparation and evaluation of 99mTc-cefuroxime, a potential infection specific imaging agent: A reliable thin layer chromatographic system to delineate impurities from the 99mTc-antibiotic. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 70, 2384–2387.
Qaiser, S. S., Khan, A. U., & Khan, M. R. (2010). Synthesis, biodistribution and evaluation of 99mTc-sitafloxacin kit: A novel infection imaging agent. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 284, 189–193.
Dutta, P., Bhansali, A., Mittal, B. R., Singh, B., & Masoodi, S. R. (2006). Instant 99mTc-ciprofloxacin scintigraphy for the diagnosis of osteomyelitis in the diabetic foot. Foot & Ankle International, 27, 716–722.
Britton, K. E., Wareham, D. W., Das, S. S., Solanki, K. K., Amaral, H., Bhatnagar, A., Katamihardja, A. H. S., Malamitsi, J., Moustafa, H. M., Soroa, V. E., Sundram, F. X., & Padhy, A. K. (2002). Imaging bacterial infection with (99m)Tc-ciprofloxacin (Infecton). Journal of clinical pathology, 55, 817–823.
Rizvi, S. F. A., Tariq, S., Mehdi, M., & Hassan, A. J. (2019). Synthesis of 99mTc-roxithromycin: A novel diagnostic agent to discriminate between septic and aseptic inflammation. Chemical Biology & Drug Design, 93, 1166–1174.
Motaleb, M. A. (2007). Preparation and biodistribution of 99mTc-lomefloxacin and 99mTc-ofloxacin complexes. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 272, 95–99.
Hina, S., Rajoka, M. I., Roohi, S., Haque, A., & Qasim, M. (2014). Preparation, biodistribution, and scintigraphic evaluation of 99mTc-clindamycin: An infection imaging agent. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 174, 1420–1433.
Erfani, M., Doroudi, A., Hadisi, L., Andishmand, A., Mirshojaei, S. F., & Shafiei, M. (2013). (99m) Tc-tricabonyl labeling of ofloxacin and its biological evaluation in Staphylococcus aureus as an infection imaging agent. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm, 56, 627–631.
Ordonez, A. A., & Jain, S. K. (2018). Pathogen-specific bacterial imaging in nuclear medicine. Seminars in nuclear medicine, 48, 182–194.
Bunschoten, A., Welling, M. M., Termaat, M. F., Sathekge, M., & van Leeuwen, F. W. B. (2013). Development and prospects of dedicated tracers for the molecular imaging of bacterial infections. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 24, 1971–1989.
Ïlem-Özdemir, D., Asikoglu, M., Ozkilic, H., Yilmaz, F., Hosgor-Limoncu, M., & Ayhan, S. (2014). (99m) Tc-Doxycycline hyclate: A new radiolabeled antibiotic for bacterial infection imaging. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm, 57, 36–41.
Bartlett John, G., Bustetter Larry, A., Gorbach Sherwood, L., & Onderdonk Andrew, B. (1975). Comparative effect of tetracycline and doxycycline on the occurrence of resistant Escherichia coli in the fecal flora. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 7, 55–57.
Sanad, M. H., & Ibrahim, A. A. (2018). Preparation and biological evaluation of 99mTc N-histamine as a model for brain imaging: In silico study and preclinical evaluation. Radiochimica Acta, 106, 229–238.
Auletta, S., Galli, F., Lauri, C., Martinelli, D., Santino, I., & Signore, A. (2016). Imaging bacteria with radiolabelled quinolones, cephalosporins and siderophores for imaging infection: A systematic review. Clinical and Translational Imaging, 4, 229–252.
Ercan, M. T., Aras, T., & Unsal, I. S. (1992). Evaluation of 99mTc-erythromycin and 99mTc-streptomycin sulphate for the visualization of inflammatory lesions. International Journal of Radiation Applications and Instrumentation. Part B, 19, 803–806.
Fazli, A., Salouti, M., & Mazidi, M. (2013). 99mTc-ceftriaxone, as a targeting radiopharmaceutical for scintigraphic imaging of infectious foci due to Staphylococcus aureus in mouse model. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 298, 1227–1233.
Siaens, R. H., Rennen, H. J., Boerman, O. C., Dierckx, R., & Slegers, G. (2004). Synthesis and comparison of 99mTc-enrofloxacin and 99mTc-ciprofloxacin. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 45, 2088–2094.
Shah, S. Q., & Khan, M. R. (2011). Radiolabeling of gemifloxacin with technetium-99m and biological evaluation in artificially Streptococcus pneumoniae infected rats. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 288, 307–312.
Motaleb, M. A., El-Kolaly, M. T., Ibrahim, A. B., & Abd El-Bary, A. (2011). Study on the preparation and biological evaluation of 99mTc–gatifloxacin and 99mTc–cefepime complexes. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 289, 57–65.
Sharma, D., Misba, L., & Khan, A. U. (2019). Antibiotics versus biofilm: An emerging battleground in microbial communities. Antimicrobial Resistance & Infection Control, 8, 76–86.
Pang, Z., Raudonis, R., Glick, B. R., Lin, T. J., & Cheng, Z. (2019). Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Biotechnology Advances, 37, 177–192.
Roohi, S., Mushtaq, A., Jehangir, M., & Malik, S. A. (2006). Synthesis, quality control and biodistribution of 99mTc-Kanamycin. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 267, 561–566.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Syed Faheem Askari Rizvi: Conceptualization, methodology, validation, investigation, and writing—original draft. Tania Jabbar: Resources and methodology. Wajeehah Shahid: Resources and project administration. Mahmoud Hamdi Sanad: Formal analysis and visualization. Haixia Zhang: Validation, resources, writing (review and editing), and supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All applicable national, international, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. Animal studies were approved by the Institutional Ethical Review Committee for Care and Use of Animals (IERCCUA), Institute of Microbiology and Biochemistry (IMBB), The University of Lahore (UOL), Lahore, Pakistan, and performed in compliance with guidelines from the National Institute of Health, Islamabad, Pakistan. This article does not contain any human studies performed by any of the authors.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
The consent was taken from all co-authors.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rizvi, S.F.A., Jabbar, T., Shahid, W. et al. Facile One-Pot Strategy for Radiosynthesis of 99mTc-Doxycycline to Diagnose Staphylococcus aureus in Infectious Animal Models. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194, 2672–2683 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03856-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03856-1