Abstract
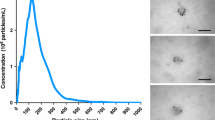
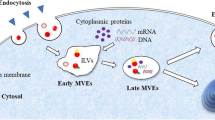
Most small molecule anticancer drugs have high lipophilicity and low water solubility, which is often regarded as a key obstacle to their development and clinical applications. A variety of nano-size drug carriers, like liposomes, has been developed for solubilizing these drugs. Naturally secreted by cells, exosomes have good biocompatibility and are considered as “natural liposomes.” Exosomes released by mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) not only have the properties like the ones generated by other cells but may also possess many therapeutic bioactive factors uniquely secreted by stem cells. In the present study, exosomes secreted by murine adipose stem cells (mASCs) were isolated, identified, and characterized. Its potential as drug delivery carrier and its biological effects on hepatoma cells and normal liver cell lines were explored in vitro. The data indicated that mASC exosomes separated by our improved sequential filtration method have particle size distribution in 30–150 nm, positively expresses TSG101, CD63, CD9, GADPH, and negatively expresses calnexin. The exosomes of mASCs obtained by this method could be taken up by cells and inhibit the cell activity of hepatoma cells HepG2, while enhance the normal cell activity of THLE-2. The results suggest that ASC exosomes are ideal potential drug delivery carriers and have the prospect of applications in carcinoma treatments.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Narvekar, M., Xue, H. Y., Eoh, J. Y., & Wong, H. L. (2014). An Official Journal of the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists, 15, 822–833.
Gelderblom, H., Verweij, J., Nooter, K., & Sparreboom, A. (2001). European journal of cancer, 37, 1590–1598.
Savjani, K. T., Gajjar, A. K., & Savjani, J. K. (2012). ISRN pharmaceutics, 2012, 1–10.
D B, Chen, T Z, Yang, & W H, Lu. (2001). Chemical & pharmaceutical bulletin, 49, 1444–1447.
Wang, H.X., Wu, J.P., X, L., Xie, K., Chen, C., & Dong.Y. H. (2017). Chemical communications, 53, 2618–2621.
Wang, H., Lu, Z., Wang, L., Guo, T., & Zheng, S. (2017). Cancer research, 77, 6963–6974.
Qiang, P. A., Shu, Z. A., Qin, Y. B., Tz, B., Xqw, A., & Li, J. A. (2013). Biomaterials, 34, 8521–8530.
Yta, B., Sl, A., Jian, S. C., Tj, A., Mz, A., & Gja, D. (2014). Biomaterials, 35(7), 2383–2390.
Gulei, D., Irimie, A. I., & Cojocneanu-Petric, R. (2018). Schultze, Joachim L, & I Berindan-Neagoe. Bioconjugate chemistry, 29, 635–648.
Szabo, G., & Momen-Heravi, F. (2017). Nature reviews gastroenterology and hepatology, 14, 455–466.
Kim, M. S., Haney, M. J., Zhao, Y., Mahajan, V., & Deygend, I. (2016). Nanomedicine, 12, 655–664.
Kim, M. S., Haney, M. J., Zhao, Y. L., Yuan, D. F., Deygen, I., Klyachko, N. L., Kabanov, A. V., & Batrakova, E. V. (2017). Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, biology, and medicine, 14, 195–204.
Long, K. B., & Beatty, G. L. (2013). Oncolmmunology, 2(12), e26860.
Kaur, S., Singh, S. P., Elkahloun, A. G., Wu, W., Abu-Asab, M. S., & Roberts, D. D. (2014). Matrix biology, 37, 49–59.
Puthanveettil, S., & Kandel, E. (2011). Two faces of evil: Cancer and neurodegeneration, 143–160.
Pittenger, M. F., & Phinney, D. G. (2017). Stem cells, 35, 851–858.
Ferguson, S. W., Wang, J. L., Lee, C. J., Liu, M., Neelamegham, S., Canty, J. M., & Nguyen, J. (2018). Scientific reports, 8, 1419–1430.
Zuk, P. A., Zhu, M., Mizuno, H., Huang, J., Futrell, J. W., & Katz, A. J. (2001). Tissue engineering part A, 7, 211–228.
De Jong, O. G., Verhaar, M. C., Chen, Y., Vader, P., Gremmels, H., Posthuma, G., Schiffelers, R. M., Gucek, M., Van Balkom, Bas W. M. (2012). Journal of extracellular vesicles, 1(1), 18396.
Pablo, G., Matos, M., Gemma, G., Pazos, C., & María, C. B., (2018). Journal of extracellular vesicles, 7, 1422676.
LÖTvall, J., Hill, A. F., Hochberg, F., Buzás, E. I., Di Vizio, D., Gardiner. C., Gho, Y. S., Kurochkin, I. V., Mathivanan, S., Quesenberry, P., Sahoo, S., Tahara, H., Wauben, M. H., Witwer, K. W., & Thery, C. (2014). Journal of extracellular vesicles, 3, 26913.
Johnsen, K. B., Gudbergsson, J. M., Skov, M. N., Christiansen, G., Gurevich, L., & Moos, T. (2016). Cytotechnology, 68(5), 2125–2138.
Funding
This work is supported by the Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program (XLYC2007040).
Program for Liaoning Innovative Talents in University,XLYC2007040
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study conception and design were conducted by XZ. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by CH and DN. Revision was done by BD and CH. Manuscript review was performed by WZ and GH. Supervising and funding support were given by GH.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The procedure of isolation fats and cells from C57BL/6 mice has been approved by the Ethics Committee of Dalian University of Technology.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All the authors consent to publish.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Han, C., Du, B. et al. Isolation and Identification of Adipose Stem Cell Exosomes and the Study of Its Potential as Drug Delivery Carrier In Vitro. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194, 2594–2603 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03835-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03835-6