Abstract
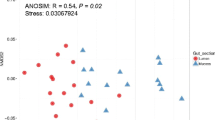
Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, is the principal fish bred in Egypt. A pilot study was designed to analyze the bacterial composition of the Nile tilapia fish guts from two saltwater lakes in Northern Egypt. Fish samples were obtained from two Delta lakes: Manzala (ML) and Borollus (BL). DNA was extracted, and the bacterial communities in the stomach content were classified (down to the species level) using the 16S rRNA-based analysis. From the two metagenomics libraries in this study, 1,426,740 reads of the amplicon sequence corresponding to 508 total taxonomic operational units were recorded. The most prevalent bacterial phyla were Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, and Synergistetes in all samples. Some of the strains identified belong to classes of pathogenic zoonotic bacteria. A notable difference was observed between gut bacteria of Nile tilapia fish obtained from BL and ML. There is a remarkable indication that Nile tilapia fish living in BL is heavily burdened with pathogenic microbes most remarkably those involved with methylation of mercury and its accumulation in fish organs. These pathogenic microbes could have clinical implications and correlated with many diseases. This result was also consistent with the metagenomic data’s functional prediction that indicated that Nile tilapia species harboring these two Egyptian northern lakes may be exposed to numerous anthropogenic pollutants. The findings show that the host environment has a significant impact on the composition of its microbiota. The first step towards exploring the better management of this profit-making fish is recognizing the structure of the microbiome.
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The nucleotide sequence dataset generated in this study was deposited in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) under the accession numbers: Bioproject: PRJNA626022, Biosample 1 (Manzala Lake): SRR11565277, Biosample 2 (Borollus Lake): SRR11565276.
References
Abriouel, H., Lerma, L. L., Casado Muñoz, M. del C., Montoro, B. P., Kabisch, J., Pichner, R., Benomar, N. (2015). The controversial nature of the Weissella genus: technological and functional aspects versus whole genome analysis-based pathogenic potential for their application in food and health. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.01197
Adeoye, A. A., Yomla, R., Jaramillo-Torres, A., Rodiles, A., Merrifield, D. L., & Davies, S. J. (2016). Combined effects of exogenous enzymes and probiotic on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) growth, intestinal morphology and microbiome. Aquaculture, 463, 61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.05.028
Al-Harbi, A. H., & Uddin, M. N. (2004). Seasonal variation in the intestinal bacterial flora of hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus x Oreochromis aureus) cultured in earthen ponds in Saudi Arabia. Aquaculture, 229(1–4), 37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(03)00388-0
Badiea, E. A., Sayed, A. A., Maged, M., Fouad, W. M., Said, M. M., & Esmat, A. Y. (2019). A novel thermostable and halophilic thioredoxin reductase from the Red Sea Atlantis II hot brine pool. PLoS ONE, 14(5), e0217565. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217565
Baroiller, J. F., D’Cotta, H., & Saillant, E. (2009). Environmental effects on fish sex determination and differentiation. Sexual Development, 3, 118–135. https://doi.org/10.1159/000223077
Baumgartner, A., Thurnheer, T., Lüthi-Schaller, H., Gmür, R., & Belibasakis, G. N. (2012). The phylum Synergistetes in gingivitis and necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis. Journal of Medical Microbiology, 61(11), 1600–1609. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.047456-0
Bentzon-Tilia, M., Sonnenschein, E. C., & Gram, L. (2016). Monitoring and managing microbes in aquaculture - Towards a sustainable industry. Microbial Biotechnology, 9(5), 576–584. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12392
Booman, M., Forster, I., Vederas, J. C., Groman, D. B., & Jones, S. R. M. (2018). Soybean meal-induced enteritis in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) but not in pink salmon (O. gorbuscha). Aquaculture, 483, 238–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.10.025
Boutin, S., Bernatchez, L., Audet, C., & Derôme, N. (2013). Network analysis highlights complex interactions between pathogen, host and commensal microbiota. PLoS ONE, 8(12). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0084772
Burtseva, O., Kublanovskaya, A., Fedorenko, T., Lobakova, E., & Chekanov, K. (2020). Gut microbiome of the White Sea fish revealed by 16S rRNA metabarcoding. Aquaculture, 533,.
Butt, R. L., & Volkoff, H. (2019). Gut microbiota and energy homeostasis in fish. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 10https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00009
Caporaso, J. G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F. D., Costello, E. K., & Knight, R. (2010). QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods, 7(5), 335–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Clements, K. D., Pasch, I. B. Y., Moran, D., & Turner, S. J. (2007). Clostridia dominate 16S rRNA gene libraries prepared from the hindgut of temperate marine herbivorous fishes. Marine Biology, 150(6), 1431–1440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-006-0443-9
Clements, K. D., Raubenheimer, D., & Choat, J. H. (2009). Nutritional ecology of marine herbivorous fishes: Ten years on. Functional Ecology, 23, 79–92. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2435.2008.01524.x
Comeau, A. M., Harding, T., Galand, P. E., Vincent, W. F., & Lovejoy, C. (2012). Vertical distribution of microbial communities in a perennially stratified Arctic lake with saline, anoxic bottom waters. Scientific Reports, 2https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00604
Comeau, A. M., Li, W. K. W., Tremblay, J. -É., Carmack, E. C., & Lovejoy, C. (2011). Arctic Ocean Microbial Community Structure before and after the 2007 Record Sea Ice Minimum. PLoS ONE, 6(11), e27492. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027492
Copley, S. D. (2009). August). Evolution of efficient pathways for degradation of anthropogenic chemicals. Nature Chemical Biology, 5, 559–566. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.197
Dahle, H., & Birkeland, N. K. (2006). Thermovirga lienii gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel moderately thermophilic, anaerobic, amino-acid-degrading bacterium isolated from a North Sea oil well. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 56(7), 1539–1545. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63894-0
de Albuquerque, F. P., de Oliveira, J. L., Moschini-Carlos, V., & Fraceto, L. F. (2020). An overview of the potential impacts of atrazine in aquatic environments: Perspectives for tailored solutions based on nanotechnology. Science of the Total Environment, 700https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134868
DeSantis, T. Z., Hugenholtz, P., Larsen, N., Rojas, M., Brodie, E. L., Keller, K., … Andersen, G. L. (2006). Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72(7), 5069-5072https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03006-05
Dong, H. T., Techatanakitarnan, C., Jindakittikul, P., Thaiprayoon, A., Taengphu, S., Charoensapsri, W., & Senapin, S. (2017). Aeromonas jandaei and Aeromonas veronii caused disease and mortality in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Journal of Fish Diseases, 40(10), 1395–1403. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12617
Fadeev, E., Salter, I., Schourup-Kristensen, V., Nöthig, E. M., Metfies, K., Engel, A., Bienhold, C. (2018). Microbial communities in the east and west fram strait during sea ice melting season. Frontiers in Marine Science, 5(NOV). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00429
Fath El-Bab, A., Farag, M., Ramadan, A., & Hassan, A. (2011). Effect of temperature and female weight on reproductive performance of two Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) populations. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Biology and Fisheries, 15(2), 179–193. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejabf.2011.2087
Feio, M. J., Zinkevich, V., Beech, I. B., Llobet-Brossa, E., Eaton, P., Schmitt, J., & Guezennec, J. (2004). Desulfovibrio alaskensis sp. nov., a sulphate-reducing bacterium from a soured oil reservoir. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 54(5), 1747–1752. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63118-0
Fernández-Pinos, M.-C., Vila-Costa, M., Arrieta, J. M., Morales, L., González-Gaya, B., Piña, B., & Dachs, J. (2017). Dysregulation of photosynthetic genes in oceanic Prochlorococcus populations exposed to organic pollutants. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 8029. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08425-9
Foysal, M. J., Nguyen, T. T. T., Chaklader, M. R., Siddik, M. A. B., Tay, C.-Y., Fotedar, R., & Gupta, S. K. (2019). Marked variations in gut microbiota and some innate immune responses of fresh water crayfish, marron (Cherax cainii, Austin 2002) fed dietary supplementation of Clostridium butyricum. PeerJ, 7(8), e7553. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7553
Fusco, V., Quero, G. M., Cho, G. S., Kabisch, J., Meske, D., Neve, H., … Franz, C. M. A. P. (2015). The genus Weissella: Taxonomy, ecology and biotechnological potential. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6, 155https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00155
Gerzova, L., Videnska, P., Faldynova, M., Sedlar, K., Provaznik, I., Cizek, A., & Rychlik, I. (2014). Characterization of microbiota composition and presence of selected antibiotic resistance genes in carriage water of ornamental fish. PLoS ONE, 9(8), e103865. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103865
Gilmour, C. C., Elias, D. A., Kucken, A. M., Brown, S. D., Palumbo, A. V., Schadt, C. W., & Wall, J. D. (2011). Sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfovibrio desulfuricans ND132 as a model for understanding bacterial mercury methylation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77(12), 3938–3951. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02993-10
Giovannoni, S. J. (2017). SAR11 bacteria: The most abundant plankton in the oceans. Annual Review of Marine Science, 9(1), 231–255. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-marine-010814-015934
Hagi, T., Tanaka, D., Iwamura, Y., & Hoshino, T. (2004). Diversity and seasonal changes in lactic acid bacteria in the intestinal tract of cultured freshwater fish. Aquaculture, 234(1–4), 335–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.01.018
Han, D., Gao, P., Li, R., Tan, P., Xie, J., Zhang, R., & Li, J. (2020). Multicenter assessment of microbial community profiling using 16S rRNA gene sequencing and shotgun metagenomic sequencing. Journal of Advanced Research, 26, 111–121.
Harman, M., Vig, D. K., Radolf, J. D., & Wolgemuth, C. W. (2013). Viscous dynamics of lyme disease and syphilis spirochetes reveal flagellar torque and drag. Biophysical Journal, 105(10), 2273–2280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2013.10.004
Hauser, L. J., Land, M. L., Brown, S. D., Larimer, F., Keller, K. L., Rapp-Giles, B. J., … Wall, J. D. (2011, August). Complete genome sequence and updated annotation of Desulfovibrio alaskensis G20. Journal of Bacteriology, 193, 4268-4269https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.05400-11
Huson, D. H., Albrecht, B., Bağci, C., Bessarab, I., Górska, A., Jolic, D., & Williams, R. B. H. (2018). MEGAN-LR: New algorithms allow accurate binning and easy interactive exploration of metagenomic long reads and contigs. Biology Direct, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13062-018-0208-7
Iwatsuki, T., Kanazawa, T., Ogasawara, T., Hosotani, K., Tsuchiya, K., Watanabe, S., ... & Dohra, H. (2021). 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing of Gut Microbiota in Three Species of Deep-Sea Fish in Suruga Bay, Japan. Microbiology Resource Announcements, 10(1)
Janßen, R., Zabel, J., von Lukas, U., & Labrenz, M. (2019). An artificial neural network and Random Forest identify glyphosate-impacted brackish communities based on 16S rRNA amplicon MiSeq read counts. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 149,.
Kannika, K., Pisuttharachai, D., Srisapoome, P., Wongtavatchai, J., Kondo, H., Hirono, I., & Areechon, N. (2017). Molecular serotyping, virulence gene profiling and pathogenicity of Streptococcus agalactiae isolated from tilapia farms in Thailand by multiplex PCR. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 122(6), 1497–1507. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13447
Kayed, A. S., Kandeil, A., Gomaa, M. R., El-Shesheny, R., Mahmoud, S., Hegazi, N., & Ali, M. A. (2019). Surveillance for avian influenza viruses in wild birds at live bird markets, Egypt, 2014–2016. Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses, 13(4), 407–414. https://doi.org/10.1111/irv.12634
Khalil, M. T. (1990). The physical and chemical environment of Lake Manzala. Egypt. Hydrobiologia, 196, 193–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00006132
Khalil M.T. (2018) Physical and chemical properties of Egypt’s coastal wetlands; Burullus Wetland as a Case Study. In: Negm A., Bek M., Abdel-Fattah S. (eds) Egyptian coastal lakes and wetlands: Part I. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry, vol 71. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/698_2017_205
Kim, M., Morrison, M., & Yu, Z. (2011). Evaluation of different partial 16S rRNA gene sequence regions for phylogenetic analysis of microbiomes. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 84(1), 81–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2010.10.020
Langille, M. G. I., Zaneveld, J., Caporaso, J. G., McDonald, D., Knights, D., Reyes, J. A., & Huttenhower, C. (2013). Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nature Biotechnology, 31(9), 814–821. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2676
Larsen, A. M., Mohammed, H. H., & Arias, C. R. (2014). Characterization of the gut microbiota of three commercially valuable warmwater fish species. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 116(6), 1396–1404. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12475
Libonatti, C., Agüeria, D., García, C., & Basualdo, M. (2019). Weissella paramesenteroides encapsulation and its application in the use of fish waste. Revista Argentina de Microbiologia, 51(1), 81–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ram.2018.03.001
Liu, C., Chang, O. Q., Zhang, D. F., Li, K. B., Wang, F., Lin, M. H., & Bergmann, S. M. (2018). Aeromonas shuberti as a cause of multi-organ necrosis in internal organs of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Journal of Fish Diseases, 41(10), 1529–1538. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12848
Maged, M., El Hosseiny, A., Saadeldin, M. K., Aziz, R. K., & Ramadan, E. (2018). Thermal stability of a mercuric reductase from the Red Sea Atlantis II hot brine environment as analyzed by site-directed mutagenesis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 85(3), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02387-18
Matsuyama, T., Yasuike, M., Fujiwara, A., Nakamura, Y., Takano, T., Takeuchi, T., Nakayasu, C. (2017). A Spirochaete is suggested as the causative agent of Akoya oyster disease by metagenomic analysis. PLoS ONE, 12(8). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0182280
Meenatchi, R., Thinesh, T., Brindangnanam, P., Hassan, S., Kiran, G. S., & Selvin, J. (2020). Revealing the impact of global mass bleaching on coral microbiome through 16S rRNA gene-based metagenomic analysis. Microbiological Research, 233,.
Morris, R. M., Rappé, M. S., Connon, S. A., Vergin, K. L., Siebold, W. A., Carlson, C. A., & Giovannoni, S. J. (2002). SAR11 clade dominates ocean surface bacterioplankton communities. Nature, 420(6917), 806–810. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01240
Ortiz-Estrada, Á. M., Gollas-Galván, T., Martínez-Córdova, L. R., & Martínez-Porchas, M. (2019). Predictive functional profiles using metagenomic 16S rRNA data: a novel approach to understanding the microbial ecology of aquaculture systems. Reviews in Aquaculture, 11(1), 234–245.
Ramadan, E., Maged, M., Hosseiny, A. El, Chambergo, F. S., Setubal, J. C., & Dorry, H. El. (2019). Molecular adaptations of bacterial mercuric reductase to the hypersaline Kebrit Deep in the Red Sea. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 85(4). https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01431-18
Ringø, E., Hoseinifar, S. H., Ghosh, K., Doan, H. Van., Beck, B. R., & Song, S. K. (2018). Lactic acid bacteria in finfish-An update. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 1818. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01818
Romarheim, O. H., Øverland, M., Mydland, L. T., Skrede, A., & Landsverk, T. (2011). Bacteria grown on natural gas prevent soybean meal-induced enteritis in Atlantic Salmon. The Journal of Nutrition, 141(1), 124–130. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.110.128900
Sabry, M., El-Moein, K. A., Hamza, E., & Kader, F. A. (2016). Occurrence of Clostridium perfringens types A, E, and C in fresh fish and its public health significance. Journal of Food Protection, 79(6), 994–1000. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-15-569
Salgado-Flores Id, A., Tveit, A. T., Wright, A.-D., Pope, P. B., & Sundset, M. A. (2019). Characterization of the cecum microbiome from wild and captive rock ptarmigans indigenous to Arctic Norway.https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213503
Schmalenberger, A., Schwieger, F., & Tebbe, C. C. (2001). Effect of primers hybridizing to different evolutionarily conserved regions of the small-subunit rRNA gene in PCR-based microbial community analyses and genetic profiling. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67(8), 3557–3563. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.8.3557-3563.2001
Si, Y., Skidmore, A. K., Wang, T., De Boer, W. F., Debba, P., Toxopeus, A. G., & Prins, H. H. T. (2009). Spatio-temporal dynamics of global H5N1 outbreaks match bird migration patterns. Geospatial Health, 4(1), 65–78. https://doi.org/10.4081/gh.2009.211
de Silva, F. C. P., Nicoli, J. R., Zambonino-Infante, J. L., Kaushik, S., & Gatesoupe, F. J. (2011). Influence of the diet on the microbial diversity of faecal and gastrointestinal contents in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) and intestinal contents in goldfish (Carassius auratus). FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 78(2), 285–296. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01155.x
Soares, J. M., Gomes, J. M., Reis, G. C. L., Hoyos, D. C. M., Custódio, F. B., & Gloria, M. B. A. (2021). Biogenic amines in amazonian fish and their health effects are affected by species and season of capture. Food Control, 107773,. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107773.
Srionnual, S., Yanagida, F., Lin, L. H., Hsiao, K. N., & Chen, Y. S. (2007). Weissellicin 110, a newly discovered bacteriocin from Weissella cibaria 110, isolated from plaa-som, a fermented fish product from Thailand. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73(7), 2247–2250. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02484-06
Tepaamorndech, S., Nookaew, I., Higdon, S. M., Santiyanont, P., Phromson, M., Chantarasakha, K., ... & Visessanguan, W. (2020). Metagenomics in bioflocs and their effects on gut microbiome and immune responses in Pacific white shrimp. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 106, 733–741
Vieira, F. do N., Jatobá, A., Mouriño, J. L. P., Vieira, E. A., Soares, M., Silva, B. C. da, Vinatea, L. A. (2013). In vitro selection of bacteria with potential for use as probiotics in marine shrimp culture. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 48(8), 998https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2013000800027
Whiteley, A. S., Jenkins, S., Waite, I., Kresoje, N., Payne, H., Mullan, B., … O’Donnell, A. (2012). Microbial 16S rRNA Ion Tag and community metagenome sequencing using the Ion Torrent (PGM) Platform. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 91(1), 80–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2012.07.008
Yin, X., Mu, L., Wu, H., Han, K., Guo, Z., & Ye, J. (2020). Expression and functional analysis of Nile tilapia transferrin receptors (TfRs) in host resistance to pathogenic bacteria and iron ion metabolism. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 100, 407–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2020.03.027.
Yu, Z., & Morrison, M. (2004). Comparisons of different hypervariable regions of rrs genes for use in fingerprinting of microbial communities by PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70(8), 4800–4806. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.8.4800-4806.2004
Yukgehnaish, K., Kumar, P., Sivachandran, P., Marimuthu, K., Arshad, A., Paray, B. A., & Arockiaraj, J. (2020). Gut microbiota metagenomics in aquaculture: factors influencing gut microbiome and its physiological role in fish. Reviews in Aquaculture. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12416.
Zhou, T., Yuan, Z., Tan, S., Jin, Y., Yang, Y., Shi, H., Liu, Z. (2018). A review of molecular responses of catfish to bacterial diseases and abiotic stresses. Frontiers in Physiology, 9(AUG). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01113
Zhou, A., Xie, S., Junaid, M., Sun, D., Tang, H., Chuan, J., ... & Zou, J. (2021). First insight into the environmental microbial communities associated with potentially pathogenic strains in pond cultured tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) at various growth stages based on 16S, 18S, and ITS2 rRNA gene amplicons sequencing. Aquaculture, 532, 736007
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the scientific research fund at the Benha University for funding this work through the research support program, Project No. (M5/3/2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. S., M. A., M. E., and M. M. collected and analyzed the samples. A. S., M. A., M. E., M. M., M. M., and M. R. carried out the experimental analyses. M. F. R. and M. R. reviewed and edited the article. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Research Highlights
• Manzala and Borollus lakes in the north of Egypt are subject to anthropogenic pollutants and man-made contaminants.
• This pilot study compared the gut microbiome of the Nile tilapia fish from both lakes.
• The presence of pathogenic bacteria in Nile tilapia fish guts from both lakes is alarming.
• The abundance of mercury accumulating bacteria in Lake Borollus may have negative consequences to the fish members and to humans consuming this fish.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serag, A., Abdel-Sabour, M., El-Hadidi, M. et al. Comparative 16S Metabarcoding of Nile Tilapia Gut Microbiota from the Northern Lakes of Egypt. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194, 2168–2182 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03750-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03750-2