Abstract
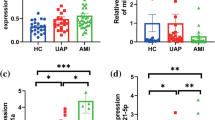
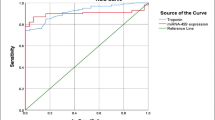
cTn and CK-MB are gold standard biomarkers for acute coronary syndrome (ACS) but are less sensitive in the first 3 h after onset of symptoms. A need thus exists for novel biomarkers for early detection of ACS. We evaluated circulating copeptin, miRNA-208, and miRNA-499 as possible biomarkers for early detection of unstable angina (UA) and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI). Sixty-five patients with probable ACS that presented within 4 h of the onset of chest pain (23 UA and 42 NSTEMI) and 25 apparently healthy individuals were studied. Two sets of blood samples collected in the first 3 h and at 6 h after onset were analyzed for copeptin levels via ELISA and miRNA-208 and miRNA-499 expression via real-time PCR. Copeptin, miRNA-208, and miRNA-499 expression levels were significantly increased in UA and NSTEMI patients compared with controls (p < 0.001) and in NSTEMT compared with UA patients (p < 0.001). Levels were also significantly elevated in UA and NSTEMI patients with negative cardiac troponin in the first 3 h (p < 0.001). ROC curves displayed AUC for prediction of ACS of 0.96 for copeptin, 0.97 for miRNA-208, and 0.97 for miRNA-499. Their combination improved AUC to 0.98. Copeptin and miRNA-208 and miRNA-499 expression are promising biomarkers for UA and NSTEMI that present in the first 3 h of pain onset. A combination of these markers with cTn may increase the accuracy of diagnosis by avoiding the gray zone of cTn as a biomarker.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Data and materials are available.
Change history
09 November 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03726-2
References
Hassanin, N., Gharib, S., El Ramly, M. Z., Meged, M. A., & Makram, A. (2015). Metabolic syndrome and coronary artery disease in young Egyptians presenting with acute coronary syndrome. Kasr Al Ainy Medical Journal, 21(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.4103/1687-4625.155666
Anderson, J. L., Adams, C. D., Antman, E. M., Bridges, C. R., Califf, R. M., Casey, D. E., Chavey, W. E., Fesmire, F. M., Hochman, J. S., Levin, T. N., Lincoff, A. M., Peterson, E. D., Theroux, P., Wenger, N. K., & Wright, R. S. (2013). Accf/Aha focused update incorporated into the Accf/Aha 2007 guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/non–St-elevation myocardial infarction: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 61(23), e179–e347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.01.014
Oerlemans, M. I., Koudstaal, S., Chamuleau, S. A., de Kleijn, D. P., Doevendans, P. A., & Sluijter, J. P. (2013). Targeting cell death in the reperfused heart: Pharmacological approaches for cardioprotection. International Journal of Cardiology, 165(3), 410–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.03.055
Apple, F. S., Jesse, R. L., Newby, L. K., Wu, A. H., Christenson, R. H., & National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry, & IFCC Committee for Standardization of Markers of Cardiac Damage. (2007). National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry and IFCC Committee for Standardization of Markers of Cardiac Damage Laboratory Medicine Practice Guidelines: Analytical issues for biochemical markers of acute coronary syndromes. Circulation, 115(13), e352–e355. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.182881
Morrow, D. A., Cannon, C. P., Jesse, R. L., Newby, L. K., Ravkilde, J., Storrow, A. B., Wu, A. H., Christenson, R. H., & National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry. (2007). National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry Laboratory Medicine Practice Guidelines: Clinical characteristics and utilization of biochemical markers in acute coronary syndromes. Circulation, 115(13), e356–e375. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.182882
Bauer, T., Hoffmann, R., Jünger, C., Koeth, O., Zahn, R., Gitt, A., Heer, T., Bestehorn, K., Senges, J., & Zeymer, U. (2009). Efficacy of a 24-H primary percutaneous coronary intervention service on outcome in patients with St elevation myocardial infarction in clinical practice. Clinical Research in Cardiology, 98(3), 171–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-008-0738-6
Keller, T., Post, F., Tzikas, S., Schneider, A., Arnolds, S., Scheiba, O., Blankenberg, S., Münzel, T., & Genth-Zotz, S. (2010). Improved outcome in acute coronary syndrome by establishing a chest pain unit. Clinical Research in Cardiology, 99(3), 149–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-009-0099-9
Gu, Y. L., Voors, A. A., Zijlstra, F., Hillege, H. L., Struck, J., Masson, S., Vago, T., Anker, S. D., Van Den Heuvel, A. F., Van Veldhuisen, D. J., & de Smet, B. J. (2011). Comparison of the temporal release pattern of copeptin with conventional biomarkers in acute myocardial infarction. Clinical Research in Cardiology, 100(12), 1069–1076. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-011-0343-y
Morgenthaler, N. G. (2010). Copeptin: A biomarker of cardiovascular and renal function. Congestive Heart Failure, 16(Suppl. 1), S37–S44. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-7133.2010.00177.x
Vargas, K. G., Kassem, M., Mueller, C., Wojta, J., & Huber, K. (2016). Copeptin for the early rule-out of non-St-elevation myocardial infarction. International Journal of Cardiology, 223, 797–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.08.304
Pheasant, M., & Mattick, J. S. (2007). Raising the estimate of functional human sequences. Genome Research, 17(9), 1245–1253. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.6406307
Cortez, M. A., Bueso-Ramos, C., Ferdin, J., Lopez-Berestein, G., Sood, A. K., & Calin, G. A. (2011). MicroRNAs in body fluids—The mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nature Reviews. Clinical Oncology, 8(8), 467–477. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.76
Shen, E., Diao, X., Wei, C., Wu, Z., Zhang, L., & Hu, B. (2010). MicroRNAs target gene and signaling pathway by bioinformatics analysis in the cardiac hypertrophy. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 397(3), 380–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.05.116
Wilson, K. D., Shen, P., Fung, E., Karakikes, I., Zhang, A., InanlooRahatloo, K., Odegaard, J., Sallam, K., Davis, R. W., Lui, G. K., Ashley, E. A., Scharfe, C., & Wu, J. C. (2015). A rapid, high-quality, cost-effective, comprehensive and expandable targeted next-generation sequencing assay for inherited heart diseases. Circulation Research, 117(7), 603–611. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306723
Pagiatakis, C., Gordon, J. W., Ehyai, S., & McDermott, J. C. (2012). A novel Rhoa/Rock-Cpi-17-Mef2c signaling pathway regulates vascular smooth muscle cell gene expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287(11), 8361–8370. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.286203
Dimmeler, S., & Zeiher, A. M. (2010). Circulating microRNAs: Novel biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases? European Heart Journal, 31(22), 2705–2707. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehq221 Oxford University Press.
Xu, J., Zhao, J., Evan, G., Xiao, C., Cheng, Y., & Xiao, J. (2012). Circulating microRNAs: Novel biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 90(8), 865–875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0840-5
Liu, X., Fan, Z., Zhao, T., Cao, W., Zhang, L., Li, H., Xie, Q., Tian, Y., & Wang, B. (2015). Plasma Mir-1, Mir-208, Mir-499 as potential predictive biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction: An independent study of Han population. Experimental Gerontology, 72, 230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2015.10.011
Thygesen, K., Alpert, J. S., Jaffe, A. S., Chaitman, B. R., Bax, J. J., Morrow, D. A., White, H. D., Thygesen, K., Alpert, J. S., Jaffe, A. S., Chaitman, B. R., Bax, J. J., Morrow, D. A., White, H. D., Mickley, H., Crea, F., Van de Werf, F., Bucciarelli-Ducci, C., Katus, H. A., & Corbett, S. (2019). Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). European Heart Journal, 40(3), 237–269. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy462
El shafey, W. E. D. H., & Ahmedy, I. A. (2016). Diagnostic values of copeptin as a novel cardiac marker in relation to traditional markers in acute myocardial infarction. Clinical Trials and Regulatory Science in Cardiology, 19, 13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrsc.2016.05.003
Twerenbold, R., Jaffe, A., Reichlin, T., Reiter, M., & Mueller, C. (2012). High-sensitive troponin T measurements: What do we gain and what are the challenges? European Heart Journal, 33(5), 579–586. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehr492
Reinstadler, S. J., Klug, G., Feistritzer, H. J., Metzler, B., & Mair, J. (2015). Copeptin testing in acute myocardial infarction: Ready for routine use? Disease Markers, 2015, 614145. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/614145
Jafar, T. H., Qadri, Z., & Chaturvedi, N. (2008). Coronary artery disease epidemic in Pakistan: More electrocardiographic evidence of ischaemia in women than in men. Heart, 94(4), 408–413. https://doi.org/10.1136/hrt.2007.120774
Reda, A. A., Mina, M. B., & Hussein, A. N. T. (2018). Pattern of risk factors and management strategies in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Menoufia Medical Journal, 31(2), 378.
Ay, M. O., Erenler, A. K., Dogan, T., & Yetim, M. (2017). Diagnostic value of copeptin in acute myocardial infarction. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 21(7), 1576–1582.
Katan, M., Morgenthaler, N., Widmer, I., Puder, J. J., König, C., Müller, B., & Christ-Crain, M. (2008). Copeptin, a stable peptide derived from the vasopressin precursor, correlates with the individual stress level. Neuro Endocrinology Letters, 29(3), 341–346.
Reichlin, T., Hochholzer, W., Stelzig, C., Laule, K., Freidank, H., Morgenthaler, N. G., Bergmann, A., Potocki, M., Noveanu, M., Breidthardt, T., Christ, A., Boldanova, T., Merki, R., Schaub, N., Bingisser, R., Christ, M., & Mueller, C. (2009). Incremental value of copeptin for rapid rule out of acute myocardial infarction. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 54(1), 60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2009.01.076
Anderson, J. L., Adams, C. D., Antman, E. M., Bridges, C. R., Califf, R. M., Casey, D. E., Chavey, W. E., Fesmire, F. M., Hochman, J. S., Levin, T. N., Acc, & Aha. (2007). Guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/non–St-elevation myocardial infarction. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 50(7), 652–726.
El Baky, A., Mahmoud, M., Shaaban, M. A. A., & Ali Ramzy, A. (2018). Clinical role of serum copeptin in acute coronary syndrome. Egyptian Heart Journal, 70(3), 155–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ehj.2018.04.008
Martinez, M. C., Tual-Chalot, S., Leonetti, D., & Andriantsitohaina, R. (2011). Microparticles: Targets and tools in cardiovascular disease. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 32(11), 659–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2011.06.005
Olivieri, F., Antonicelli, R., Lorenzi, M., D’Alessandra, Y., Lazzarini, R., Santini, G., Spazzafumo, L., Lisa, R., La Sala, L., Galeazzi, R., Recchioni, R., Testa, R., Pompilio, G., Capogrossi, M. C., & Procopio, A. D. (2013). Diagnostic potential of circulating Mir-499-5p in elderly patients with acute non St-elevation myocardial infarction. International Journal of Cardiology, 167(2), 531–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.01.075
Agiannitopoulos, K., Pavlopoulou, P., Tsamis, K., Bampali, K., Samara, P., Nasioulas, G., Mertzanos, G., Babalis, D., & Lamnissou, K. (2018). Expression of Mir-208b and Mir-499 in Greek patients with acute myocardial infarction. In Vivo, 32(2), 313–318. https://doi.org/10.21873/invivo.11239
Boštjančič, E., Zidar, N., Štajer, D., & Glavač, D. (2010). MicroRNAs Mir-1, Mir-133a, Mir-133b and Mir-208 are dysregulated in human myocardial infarction. Cardiology, 115(3), 163–169. https://doi.org/10.1159/000268088
Wang, G. K., Zhu, J. Q., Zhang, J. T., Li, Q., Li, Y., He, J., Qin, Y. W., & Jing, Q. (2010). Circulating microRNA: A novel potential biomarker for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in humans. European Heart Journal, 31(6), 659–666. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehq013
Devaux, Y., Vausort, M., Goretti, E., Nazarov, P. V., Azuaje, F., Gilson, G., Corsten, M. F., Schroen, B., Lair, M. L., Heymans, S., & Wagner, D. R. (2012). Use of circulating microRNAs to diagnose acute myocardial infarction. Clinical Chemistry, 58(3), 559–567. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2011.173823
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the entire participants in this study, particularly the patients, nurses, and medical biochemistry lab workers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Marwa A Gaber and Omnia HM Omar conceptualized and designed the study protocol development, assessment, and writing of the manuscript. Ayman KM Hassan and Marwan S Mahmoud performed clinical assessments and selection of all cases and revised the manuscript. Marwa A Gaber and Omnia HM Omar performed all lab investigations. Sahar EM El-Deek and Abdel-Raheim MA Meki revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agreed to be responsible for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The study protocol was approved by the institutional ethics committee (IRB local approval number 17101364) and explained to all participants, and only those who gave informed written consent were included in the study.
Guarantor: Marwa A Gaber.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaber, M.A., Omar, O.H.M., El-Deek, S.E.M. et al. Copeptin, miRNA-208, and miRNA-499 as New Biomarkers for Early Detection of Acute Coronary Syndrome. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194, 1193–1205 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03695-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03695-6