Abstract
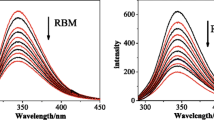
Cancer is the consequence of abnormal cell proliferation, which leads to the formation of abnormal mass. In this study, we aimed to determine the anticancer properties of Cu(II)-Schiff base complex and low-frequency electromagnetic field, and the interaction between BSA and Cu(II) complex. Firstly, Schiff base of the Cu(II) complex in the N,N′-dipyridoxyl(1,2 diaminobenzene) was originally synthesized. Following, the breast cancer was transplanted with the TUBO cells in vivo. Then, treatment of the cancerous mice was done by low-frequency electromagnetic field and the Cu(II)-Schiff base complex. In this project, antiproliferative activity on breast cancer cells was tested by TUBO cells using MTT assay and apoptosis properties were studied by flow cytometry. The interaction between the Cu(II)-Schiff base complex and bovine serum albumin (BSA) was checked by fluorescence and UV-vis absorbance spectroscopy. Tumor tissue investigation demonstrated that the low-frequency electromagnetic field and Cu(II)-Schiff base complex induce apoptosis and inhibit tumor growth. MTT results unveiled a cytotoxic impact on breast cancer cells. Flow cytometry analysis demonstrates that the anticancer effect of Cu(II)-Schiff base complex on breast cancer cells (MCF7) was associated with the cell cycle arrest. The results of fluorescence spectra and UV-vis absorption spectra showed that the conformation of bovine serum albumin has been changed in the presence of Cu(II)-Schiff base complex. Cu(II)-Schiff base complex and low-frequency electromagnetic field have anticancer properties. The spectroscopy method indicates the binding between Cu(II)-Schiff base complex and BSA.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeVita, V. T., Jr., Lawrence, T. S., Rosenberg, S. A., & Cancer, P. P. O. (2015). 10e primer. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Wong, R. S. (2011). Apoptosis in cancer: from pathogenesis to treatment. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 30(1), 87.
Bargou, R. C., Daniel, P. T., Mapara, M. Y., Bommert, K., Wagener, C., Kallinich, B., Royer, H. D., & Dörken, B. (1995). Expression of the bcl-2 gene family in normal and malignant breast tissue: low bax-α expression in tumor cells correlates with resistance towards apoptosis. International Journal of Cancer, 60(6), 854–859.
Kerr, J. F., Winterford, C. M., & Harmon, B. V. (1994). Apoptosis. Its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer, 73(8), 2013–2026.
Strasser, A., O'Connor, L., & Dixit, V. M. (2000). Apoptosis signaling. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 69(1), 217–245.
Carter, D. C., & Ho, J. X. (1994). Structure of serum albumin. Advances in Protein Chemistry, 45: Elsevier, 153–203.
Guo, X.-J., Sun, X.-D., & Xu, S.-K. (2009). Spectroscopic investigation of the interaction between riboflavin and bovine serum albumin. Journal of Molecular Structure, 931(1-3), 55–59.
He, X. M., & Carter, D. C. (1992). Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature, 358(6383), 209–215.
Tian, J., Liu, J., Hu, Z., & Chen, X. (2005). Interaction of wogonin with bovine serum albumin. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 13(12), 4124–4129.
Tian, J., Liu, J., Zhang, J., Hu, Z., & Chen, X. (2003). Fluorescence studies on the interactions of barbaloin with bovine serum albumin. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 51(5), 579–582.
Wang, Y.-P., Wei, Y.-L., & Dong, C. (2006). Study on the interaction of 3, 3-bis (4-hydroxy-1-naphthyl)-phthalide with bovine serum albumin by fluorescence spectroscopy. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology, A: Chemistry, 177(1), 6–11.
Bi, S., Song, D., Tian, Y., Zhou, X., Liu, Z., & Zhang, H. (2005). Molecular spectroscopic study on the interaction of tetracyclines with serum albumins. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy., 61(4), 629–636.
Hu, Y.-J., Liu, Y., Zhang, L.-X., Zhao, R.-M., & Qu, S.-S. (2005). Studies of interaction between colchicine and bovine serum albumin by fluorescence quenching method. Journal of Molecular Structure, 750(1-3), 174–178.
Shaikh, S., Seetharamappa, J., Ashoka, S., & Kandagal, P. (2007). A study of the interaction between bromopyrogallol red and bovine serum albumin by spectroscopic methods. Dyes and Pigments, 73(2), 211–216.
Cozzi, P. G. (2004). Metal–Salen Schiff base complexes in catalysis: practical aspects. Chemical Society Reviews, 33(7), 410–421.
Chohan, Z. H., & Sherazi, S. K. (1999). Synthesis and characterisation of some Co (II), Cu (II) and Ni (II) complexes with nicotinoylhydrazine derivatives and the biological role of metals and anions (SO4 2-, NO3−, CzO4 2-and CH3CO− 2) on the antibacterial properties. Synthesis and Reactivity in Inorganic and Metal-Organic Chemistry, 29(1), 105–118.
Dharmaraj, N., Viswanathamurthi, P., & Natarajan, K. (2001). Ruthenium (II) complexes containing bidentate Schiff bases and their antifungal activity. Transition Metal Chemistry, 26(1-2), 105–109.
Jayabalakrishnan, C., & Natarajan, K. (2001). Synthesis, characterization, and biological activities of ruthenium (II) carbonyl complexes containing bifunctional tridentate Schiff bases. Synthesis and Reactivity in Inorganic and Metal-Organic Chemistry, 31(6), 983–995.
Mashaly, M. M. (2004). Heterobinuclear and heterotrinuclear complexes of oxorhenium (V) with Cu (II), Ni (II), Fe (III), UO2 (VI) and Th (IV) in the solid state. Journal of Coordination Chemistry, 57(3), 199–215.
Solomon, E. I., & Lowery, M. D. (1993). Electronic structure contributions to function in bioinorganic chemistry. Science, 259(5101), 1575–1582.
Gerdemann, C., Eicken, C., & Krebs, B. (2002). The crystal structure of catechol oxidase: new insight into the function of type-3 copper proteins. Accounts of Chemical Research, 35(3), 183–191.
Tümer, M., Köksal, H., Sener, M. K., & Serin, S. (1999). Antimicrobial activity studies of the binuclear metal complexes derived from tridentate Schiff base ligands. Transition Metal Chemistry, 24(4), 414–420.
Chakraborty, A., Kumar, P., Ghosh, K., & Roy, P. (2010). Evaluation of a Schiff base copper complex compound as potent anticancer molecule with multiple targets of action. European Journal of Pharmacology, 647(1-3), 1–12.
Repacholi, M. H., & Greenebaum, B. (1999). Interaction of static and extremely low frequency electric and magnetic fields with living systems: health effects and research needs. Bioelectromagnetics., 20(3), 133–160.
Evan, G. I., & Vousden, K. H. (2001). Proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature., 411(6835), 342–348.
Hanahan, D., & Weinberg, R. A. (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. cell., 100(1), 57–70.
LaCasse, E. C., Baird, S., Korneluk, R. G., & MacKenzie, A. E. (1998). The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) and their emerging role in cancer. Oncogene, 17(25), 3247–3259.
Toozandejani, T., Beyramabadi, S. A., Chegini, H., Khashi, M., Morsali, A., & Pordel, M. (2017). Synthesis, experimental and theoretical characterization of a Mn (II) complex of N, N′-dipyridoxyl (1, 2-diaminobenzene). Journal of Molecular Structure, 1127, 15–22.
Ma, Z.-Y., Qiao, X., Xie, C.-Z., Shao, J., Xu, J.-Y., Qiang, Z.-Y., & Lou, J. S. (2012). Activities of a novel Schiff base copper (II) complex on growth inhibition and apoptosis induction toward MCF-7 human breast cancer cells via mitochondrial pathway. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 117, 1–9.
Easmon, J., Pürstinger, G., Heinisch, G., Roth, T., Fiebig, H. H., Holzer, W., Jäger, W., Jenny, M., & Hofmann, J. (2001). Synthesis, cytotoxicity, and antitumor activity of copper (II) and iron (II) complexes of 4 N-azabicyclo [3.2. 2] nonane thiosemicarbazones derived from acyl diazines. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 44(13), 2164–2171.
Liang, F., Wu, C., Lin, H., Li, T., Gao, D., Li, Z., Wei, J., Zheng, C., & Sun, M. (2003). Copper complex of hydroxyl-substituted triazamacrocyclic ligand and its antitumor activity. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 13(15), 2469–2472.
Filomeni, G., Cerchiaro, G., Ferreira, A. M. D. C., De Martino, A., Pedersen, J. Z., Rotilio, G., et al. (2007). Pro-apoptotic activity of novel Isatin-Schiff base copper (II) complexes depends on oxidative stress induction and organelle-selective damage. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282(16), 12010–12021.
Hanahan, D., & Weinberg, R. A. (2011). Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. cell., 144(5), 646–674.
Hajrezaie, M., Golbabapour, S., Hassandarvish, P., Gwaram, N. S., Hadi, A. H. A., Ali, H. M., et al. (2012). Acute toxicity and gastroprotection studies of a new schiff base derived copper (II) complex against ethanol-induced acute gastric lesions in rats. PLoS One, 7(12), e51537.
Jayashree, B., Kaur, M., & Pai, A. (2012). Synthesis, characterisation, antioxidant and anticancer evaluation of novel Schiff’s bases of 2-quinolones. Elixir Online Journal, 52, 11317.
Zhang, X., Bi, C., Fan, Y., Cui, Q., Chen, D., Xiao, Y., et al. (2008). Induction of tumor cell apoptosis by taurine Schiff base copper complex is associated with the inhibition of proteasomal activity. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 22(5), 677–682.
Liang, C., Xia, J., Lei, D., Li, X., Yao, Q., & Gao, J. (2014). Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity of symmetrical bis-Schiff base derivatives of isatin. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 74, 742–750.
Duff, B., Thangella, V. R., Creaven, B. S., Walsh, M., & Egan, D. A. (2012). Anti-cancer activity and mutagenic potential of novel copper (II) quinolinone Schiff base complexes in hepatocarcinoma cells. European Journal of Pharmacology, 689(1-3), 45–55.
Ruiz, G. M., Pastor, V. J., De La Pena, L., Gil, C. L., & Martínez, M. M. (1999). Growth modification of human colon adenocarcinoma cells exposed to a low-frequency electromagnetic field. Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry, 55(2), 79–83.
Tofani, S., Barone, D., Cintorino, M., de Santi, M. M., Ferrara, A., Orlassino, R., Ossola, P., Peroglio, F., Rolfo, K., & Ronchetto, F. (2001). Static and ELF magnetic fields induce tumor growth inhibition and apoptosis. Bioelectromagnetics., 22(6), 419–428.
Williams CD, Markov MS, Hardman WE, Cameron IL. Therapeutic electromagnetic field effects on angiogenesis and tumor growth. 2001.
Barbault, A., Costa, F. P., Bottger, B., Munden, R. F., Bomholt, F., Kuster, N., & Pasche, B. (2009). Amplitude-modulated electromagnetic fields for the treatment of cancer: discovery of tumor-specific frequencies and assessment of a novel therapeutic approach. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 28(1), 51.
Filipovic, N., Djukic, T., Radovic, M., Cvetkovic, D., Curcic, M., Markovic, S., et al. (2014). Electromagnetic field investigation on different cancer cell lines. Cancer Cell International, 14(1), 84.
Sunil, D., Isloor, A. M., Shetty, P., Nayak, P. G., & Pai, K. (2013). In vivo anticancer and histopathology studies of Schiff bases on Ehrlich ascitic carcinoma cells: 1st cancer update. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 6(1), 25–33.
Fleisig, H., & Wong, J. (2012). Measuring cell cycle progression kinetics with metabolic labeling and flow cytometry. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (63), e4045.
Roccio, M., Schmitter, D., Knobloch, M., Okawa, Y., Sage, D., & Lutolf, M. P. (2013). Predicting stem cell fate changes by differential cell cycle progression patterns. Development, 140(2), 459–470.
Volotskova, O., Hawley, T. S., Stepp, M. A., & Keidar, M. (2012). Targeting the cancer cell cycle by cold atmospheric plasma. Scientific Reports, 2(1), 636.
Yazdanparast, R., & Sadeghi, H. (2004). Nucleic acid synthesis in cancerous cells under the effect of gnidilatimonoein from Daphne mucronata. Life Sciences, 74(15), 1869–1876.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Islamic Azad University, Mashhad, Iran, and therefore is appreciated by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadamani, S., Neamati, A., Homayouni-Tabrizi, M. et al. Anticancer Activities of Cu(II) Complex-Schiff Base and Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields and the Interaction Between Cu(II) Complex-Schiff Base with Bovine Serum Albumin by Spectroscopy. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 190, 997–1009 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03118-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03118-7