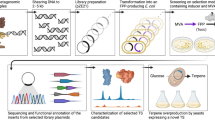
Abstract
As a green and powerful tool, biocatalysis has emerged as a perfect alternative to traditional chemistry. The bottleneck during process development is discovery of novel enzymes with desired properties and independent intellectual property. Herein, we have successfully bioprospected three novel bacterial α-l-rhamnosidases from human fecal metagenome using a combinatorial strategy by high-throughput de novo sequencing combined with in silico searching for catalytic key motifs. All three novel α-l-rhamnosidases shared low sequence identities with reported (< 35%) and putative ones (< 57%) from public database. All three novel α-l-rhamnosidases were over-expressed as soluble form in Escherichia coli with high-level production. Furthermore, all three novel α-l-rhamnosidases hydrolyzed the synthetic substrate p-nitrophenyl α-l-rhamnopyranoside and natural flavonoid glycosides rutin and naringin with some excellent properties, such as high activity in acidic pH, high activity at low or high temperature, and good tolerance for alcohols and DMSO. Our findings would provide a convenient route for target discovery of the promising biocatalysts from the metagenomes for biotransformation and biosynthesis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burton, S. G., Cowan, D. A., & Woodley, J. M. (2002). The search for the ideal biocatalyst. Nature Biotechnology, 20(1), 37–45.
Lorenz, P., Liebeton, K., Niehaus, F., & Eck, J. (2002). Screening for novel enzymes for biocatalytic processes: accessing the metagenome as a resource of novel functional sequence space. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 13(6), 572–577.
Lorenz, P., & Schleper, C. (2002). Metagenome-a challenging source of enzyme discovery. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 19, 13–19.
Lorenz, P., & Eck, J. (2005). Metagenomics and industrial applications. Nature Review Microbiology, 3(6), 510–516.
Madhavan, A., Sindhu, R., Parameswaran, B., Sukumaran, R. K., & Pandey, A. (2017). Metagenome analysis: a powerful tool for enzyme bioprospecting. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 183(2), 636–651.
Hess, M., Sczyrba, A., Egan, R., Kim, T. W., Chokhawala, H., Schroth, G., Luo, S., Clark, D. S., Chen, F., Zhang, T., Mackie, R. I., Pennacchio, L. A., Tringe, S. G., Visel, A., Woyke, T., Wang, Z., & Rubin, E. M. (2011). Metagenomic discovery of biomass-degrading genes and genomes from cow rumen. Science, 331(6016), 463–467.
Montella, S., Ventorino, V., Lombard, V., Henrissat, B., Pepe, O., & Faraco, V. (2017). Discovery of genes coding for carbohydrate-active enzyme by metagenomic analysis of lignocellulosic biomasses. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 42623.
Warnecke, F., Luginbuhl, P., Ivanova, N., Ghassemian, M., Richardson, T. H., Stege, J. T., Cayouette, M., McHardy, A. C., Djordjevic, G., Aboushadi, N., Sorek, R., Tringe, S. G., Podar, M., Martin, H. G., Kunin, V., Dalevi, D., Madejska, J., Kirton, E., Platt, D., Szeto, E., Salamov, A., Barry, K., Mikhailova, N., Kyrpides, N. C., Matson, E. G., Ottesen, E. A., Zhang, X., Hernandez, M., Murillo, C., Acosta, L. G., Rigoutsos, I., Tamayo, G., Green, B. D., Chang, C., Rubin, E. M., Mathur, E. J., Robertson, D. E., Hugenholtz, P., & Leadbetter, J. R. (2007). Metagenomic and functional analysis of hindgut microbiota of a wood-feeding higher termite. Nature, 450(7169), 560–565.
Yang, C., Xia, Y., Qu, H., Li, A. D., Liu, R., Wang, Y., & Zhang, T. (2016). Discovery of new cellulases from the metagenome by a metagenomics-guided strategy. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 9, 138.
Zhou, M., Guo, P., Wang, T., Gao, L., Yin, H., Cai, C., Gu, J., & Lu, X. (2017). Metagenomic mining pectinolytic microbes and enzymes from an apple pomace-adapted compost microbial community. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 10(1), 198.
Seffernick, J. L., de Souza, M. L., Sadowsky, M. J., & Wackett, L. P. (2001). Melamine deaminase and atrazine chlorohydrolase: 98 percent identical but functionally different. Journal of Bacteriology, 183(8), 2405–2410.
Glasner, M. E., Fayazmanesh, N., Chiang, R. A., Sakai, A., Jacobson, M. P., Gerlt, J. A., & Babbitt, P. C. (2006). Evolution of structure and function in the o-succinylbenzoate synthase/N-acylamino acid racemase family of the enolase superfamily. Journal of Molecular Biology, 360(1), 228–250.
Gerlt, J. A., Allen, K. N., Almo, S. C., Armstrong, R. N., Babbitt, P. C., Cronan, J. E., Dunaway-Mariano, D., Imker, H. J., Jacobson, M. P., Minor, W., Poulter, C. D., Raushel, F. M., Sali, A., Shoichet, B. K., & Sweedler, J. V. (2011). The enzyme function initiative. Biochemistry, 50(46), 9950–9962.
Gerlt, J. A., Bouvier, J. T., Davidson, D. B., Imker, H. J., Sadkhin, B., Slater, D. R., & Whalen, K. L. (2015). Enzyme function initiative-enzyme similarity tool (EFI-EST): a web tool for generating protein sequence similarity networks. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1854(8), 1019–1037.
Levin, B. J., Huang, Y. Y., Peck, S. C., Wei, Y., Martinez-Del Campo, A., Marks, J. A., Franzosa, E. A., Huttenhower, C., & Balskus, E. P. (2017). A prominent glycyl radical enzyme in human gut microbiomes metabolizes trans-4-hydroxy-l-proline. Science, 355(6325), eaai8386.
Hohne, M., Schatzle, S., Jochens, H., Robins, K., & Bornscheuer, U. T. (2010). Rational assignment of key motifs for function guides in silico enzyme identification. Nature Chemical Biology, 6(11), 807–813.
Jiang, J., Chen, X., Zhang, D., Wu, Q., & Zhu, D. (2015). Characterization of (R)-selective amine transaminases identified by in silico motif sequence blast. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 99(6), 2613–2621.
Barriuso, J., Prieto, A., & Martinez, M. J. (2013). Fungal genomes mining to discover novel sterol esterases and lipases as catalysts. BMC Genomics, 14(1), 712.
Henke, E., Pleiss, J., & Bornscheuer, U. T. (2002). Activity of lipases and esterases towards tertiary alcohols: insights into structure-function relationships. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 41(17), 3211–3213.
Nguyen, G. S., Thompson, M. L., Grogan, G., Bornscheuer, U. T., & Kourist, R. (2011). Identification of novel esterases for the synthesis of sterically demanding chiral alcohols by sequence-structure guided genome mining. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 70(3-4), 88–94.
Fraaije, M. W., Wu, J., Heuts, D. P., van Hellemond, E. W., Spelberg, J. H., & Janssen, D. B. (2005). Discovery of a thermostable Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase by genome mining. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 66(4), 393–400.
Lombard, V., Golaconda Ramulu, H., Drula, E., Coutinho, P. M., & Henrissat, B. (2014). The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Research, 42(D1), D490–D495.
Cui, Z., Maruyama, Y., Mikami, B., Hashimoto, W., & Murata, K. (2007). Crystal structure of glycoside hydrolase family 78 α-L-rhamnosidase from Bacillus sp. GL1. Journal of Molecular Biology, 374(2), 384–398.
Fujimoto, Z., Jackson, A., Michikawa, M., Maehara, T., Momma, M., Henrissat, B., Gilbert, H. J., & Kaneko, S. (2013). The structure of a Streptomyces avermitilis α-L-rhamnosidase reveals a novel carbohydrate-binding module CBM67 within the six-domain arrangement. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288(17), 12376–12385.
O’Neill, E. C., Stevenson, C. E., Paterson, M. J., Rejzek, M., Chauvin, A. L., Lawson, D. M., & Field, R. A. (2015). Crystal structure of a novel two domain GH78 family α-rhamnosidase from Klebsiella oxytoca with rhamnose bound. Proteins, 83(9), 1742–1749.
Pachl, P., Škerlová, J., Šimčíková, D., Kotik, M., Křenková, A., Mader, P., Brynda, J., Kapešová, J., Křen, V., Otwinowski, Z., & Řezáčová, P. (2018). Crystal structure of native α-L-rhamnosidase from Aspergillus terreus. Acta Crystallographica Section D, 74(11), 1078–1084.
Pitson, S. M., Mutter, M., van den Broek, L. A., Voragen, A. G., & Beldman, G. (1998). Stereochemical course of hydrolysis catalysed by alpha-L-rhamnosyl and alpha-D-galacturonosyl hydrolases from Aspergillus aculeatus. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 242(3), 552–559.
Zverlov, V. V., Hertel, C., Bronnenmeier, K., Hroch, A., Kellermann, J., & Schwarz, W. H. (2000). The thermostable α-L-rhamnosidase RamA of Clostridium stercorarium: biochemical characterization and primary structure of a bacterial α-L-rhamnoside hydrolase, a new type of inverting glycoside hydrolase. Molecular Microbiology, 35(1), 173–179.
Li, B., Ji, Y., Li, Y., & Ding, G. (2018). Characterization of a glycoside hydrolase family 78 α-L-rhamnosidase from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482 and identification of functional residues. 3 Biotech, 8(2), 120.
Kaoutari, A. E., Armougom, F., Gordon, J. I., Raoult, D., & Henrissat, B. (2013). The abundance and variety of carbohydrate-active enzymes in the human gut microbiota. Nature Review Microbiology, 11(7), 497–504.
Robert, X., & Gouet, P. (2014). Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Research, 42(W1), W320–W324.
Liang, Y., Li, B., & Li, Y. (2017). Discovering novel α-L-rhamnosidases based on the metagenomic approach. Chinese Journal Biochemistry Molecular Biology, 33, 66–72.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., & Tamura, K. (2016). Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33(7), 1870–1874.
Grote, A., Hiller, K., Scheer, M., Munch, R., Nortemann, B., Hempel, D. C., & Jahn, D. (2005). JCat: a novel tool to adapt codon usage of a target gene to its potential expression host. Nucleic Acids Research, 33(Web Server), W526–W531.
Kennedy, J., O’Leary, N. D., Kiran, G. S., Morrissey, J. P., O’Gara, F., Selvin, J., & Dobson, A. D. (2011). Functional metagenomic strategies for the discovery of novel enzymes and biosurfactants with biotechnological applications from marine ecosystems. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 111(4), 787–799.
Tasse, L., Bercovici, J., Pizzut-Serin, S., Robe, P., Tap, J., Klopp, C., Cantarel, B. L., Coutinho, P. M., Henrissat, B., Leclerc, M., Dore, J., Monsan, P., Remaud-Simeon, M., & Potocki-Veronese, G. (2010). Functional metagenomics to mine the human gut microbiome for dietary fiber catabolic enzymes. Genome Research, 20(11), 1605–1612.
Thies, S., Rausch, S. C., Kovacic, F., Schmidt-Thaler, A., Wilhelm, S., Rosenau, F., Daniel, R., Streit, W., Pietruszka, J., & Jaeger, K. E. (2016). Metagenomic discovery of novel enzymes and biosurfactants in a slaughterhouse biofilm microbial community. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 27035.
Ichinose, H., Fujimoto, Z., & Kaneko, S. (2013). Characterization of an α-L-rhamnosidase from Streptomyces avermitilis. Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 77(1), 213–216.
Avila, M., Jaquet, M., Moine, D., Requena, T., Peláez, C., Arigoni, F., & Jankovic, I. (2009). Physiological and biochemical characterization of the two α-L-rhamnosidases of Lactobacillus plantarum NCC245. Microbiology, 155(8), 2739–2749.
Zhang, R., Zhang, B. L., Xie, T., Li, G. C., Tuo, Y., & Xiang, Y. T. (2015). Biotransformation of rutin to isoquercitrin using recombinant α-L-rhamnosidase from Bifidobacterium breve. Biotechnology Letters, 37(6), 1257–1264.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31400684) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi (No. 2014021030-3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Our study had been approved by the Committee on the Ethics of Human and Animal Experiments of Shanxi University
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1281 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, BC., Zhang, T., Li, YQ. et al. Target Discovery of Novel α-l-Rhamnosidases from Human Fecal Metagenome and Application for Biotransformation of Natural Flavonoid Glycosides. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 189, 1245–1261 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03063-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03063-5