Abstract
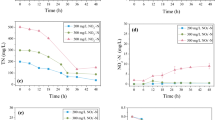
A novel aerobic denitrifier strain HNR, isolated from activated sludge, was identified as Enterobacter cloacae by16S rRNA sequencing analysis. Glucose was considered as the most favorable C-source for strain HNR. The logistic equation well described the bacterial growth, yielding a maximum growth rate (μmax) of 0.283 h−1 with an initial NO3 −-N concentration of 110 mg/L. Almost all NO3 −-N was removed aerobically within 30 h with an average removal rate of 4.58 mg N L−1 h−1. Nitrogen balance analysis revealed that proximately 70.8 % of NO3 −-N was removed as gas products and only 20.7 % was transformed into biomass. GC-MS result indicates that N2 was the end product of aerobic denitrification. The enzyme activities of nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase, which are related to the process of aerobic denitrification, were 0.0688 and 0.0054 U/mg protein, respectively. Thus, the aerobic denitrification of reducing NO3 − to N2 by strain HNR was demonstrated. The optimal conditions for nitrate removal were C/N ratio 13, pH value 8, shaking speed 127 rpm and temperature 30 °C. These findings show that E. cloacae strain HNR has a potential application on wastewater treatment to achieve nitrate removal under aerobic conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kesik, M., Blagodatsky, S., Papen, H., & Butterbach -Bahl, K. (2006). Effect of pH, temperature and substrate on N2O, NO and CO2 production by Alcaligenes faecalis sp. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 101, 655–667.
Baytshtok, V., Lu, H., Park, H., Kim, S., Yu, R., & Chandran, K. (2009). Impact of varying electron donors on the molecular microbial ecology and biokinetics of methylotrophic denitrifying bacteria. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 102, 1527–1536.
Islam, M., George, N., Zhu, J., & Chowdhury, N. (2009). Impact of carbon to nitrogen ratio on nutrient removal in a liquid–solid circulating fluidized bed bioreactor (LSCFB). Process Biochemistry, 44, 578–583.
Robertson, L. A., & Kuenen, J. G. (1984). Heterotrophic nitrification in Thisophaera pantotropha: oxygen uptake and enzyme studies. Journal of General Microbiology, 134, 857–863.
Wan, C., Yang, X., Lee, D. J., Du, M., Wan, F., & Chen, C. (2011). Aerobic denitrification by novel isolated strain using NO2 −-N as nitrogen source. Bioresource Technology, 102, 7244–7248.
Yang, X. P., Wang, S. M., Zhang, D. W., & Zhou, L. X. (2011). Isolation and nitrogen removal characteristics of an aerobic heterotrophic nitrifying-denitrifying bacterium, Bacillus subtilis A1. Bioresource Technology, 102, 854–862.
Chen, Q., & Ni, J. R. (2012). Ammonium removal by Agrobacterium sp. LAD9 capable of heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 113, 619–623.
Zheng, H. Y., Liu, Y., Gao, X. Y., Ai, G. M., Miao, L. L., & Liu, Z. P. (2012). Characterization of a marine origin aerobic nitrifying-denitrifying bacterium. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 114, 33–37.
Chen, P. Z., Li, J., Li, Q. X., Wang, Y. C., Li, S. P., Ren, T. Z., & Wang, L. G. (2012). Simultaneous heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by bacterium Rhodococcus sp.CPZ24. Bioresource Technology, 116, 266–270.
Tatusova, T. A., & Madden, T. L. (1999). BLAST 2 sequences, a new tool for comparing protein and nucleotide sequences. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 174, 247–250.
Kumar, S., Nei, M., Dudley, J., & Tamura, K. (2008). MEGA: a biologist centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequence. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 9, 299–306.
Yao, S., Ni, J. R., Ma, T., & Li, C. (2013). Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification at low temperature by a newly isolated bacterium, Acinetobacter sp. HA2. Bioresource Technology, 139, 80–86.
Zhao, B., He, Y. L., Hughes, J., & Zhang, X. F. (2010). Heterotrophic nitrogen removal by a newly isolated Acinetobacter calcoaceticus HNR. Bioresource Technology, 101, 5194–5200.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1951). Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
Ren, Y. X., Yang, L., & Liang, X. (2014). The characteristics of a novel heterotrophic nitrifying and aerobic denitrifying bacterium, Acinetobacter junii YB. Bioresource Technology, 171, 1–9.
APHA. (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (19th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Frear, D. S., & Burrell, R. C. (1955). Spectrophotometric methods for determining hydroxylamine reductase activity in higher plants. Analytical Chemistry, 27, 1664–1665.
Her, J. J., & Huang, J. S. (1995). Influences of carbon source and C/N ratio on nitrate/nitrate denitrification and carbon breakthrough. Bioresource Technology, 54, 45–51.
Elefsiniotis, P., Wareham, D. G., & Smith, M. O. (2004). Use of volatile fatty acids from an acid-phase digester for denitrification. Journal of Biotechnology, 114, 289–297.
Shrimali, M., & Singh, K. P. (2001). New methods of nitrate removal from water. Environmental Pollution, 112, 351–359.
Takaya, N., Catalan-Sakairi, M. A. B., Sakaguchi, Y., Kato, I., Zhou, Z. M., & Shoun, H. (2003). Aerobic denitrifying bacteria that produce low levels of nitrous oxide. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69, 3152–3157.
Patureau, D., Bernet, N., Delgenes, J. P., & Moletta, R. (2000). Effect of dissolved oxygen and carbon–nitrogen loads on denitrification by an aerobic consortium. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 54, 535–542.
Richardson, D. J., & Watmough, N. J. (1999). Inorganic nitrogen metabolism in bacteria. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 3, 207–219.
Padhi, S. K., Tripathy, S., & Sen, R. (2013). Characterisation of heterotrophic nitrifying and aerobic denitrifying Klebsiella pneumoniae CF-S9 strain for bioremediation of wastewater. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 78, 67–73.
Shi, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhou, J. T., Chen, M. X., & Wang, X. J. (2013). Biological removal of nitrate and ammonium under aerobic atmosphere by Paracoccus versutus LYM. Bioresource Technology, 148, 144–148.
Robertson, L. A., & Kuenen, J. G. (1990). Combined heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification in Thiosphaera pantotropha and other bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 57, 139–152.
Kim, M., Jeong, S. Y., Yoon, S. J., Cho, S. J., Kim, Y. H., Kim, M. J., Ryu, E. Y., & Lee, S. J. (2008). Aerobic denitrification of Pseudomonas putida AD-21 at different C/N ratio. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 106, 498–502.
Huang, H. K., & Tseng, S. K. (2001). Nitrate reduction by Citrobacter diversus under aerobic environment. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 55, 90–94.
Lloyd, D., Boddy, L., & Davies, K. J. P. (1987). Persistence of bacterial denitrification capacity under aerobic condition: the rule rather than the exception. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 45, 185–190.
Joo, H. S., Hirai, M., & Shoda, M. (2005). Characteristics of ammonium removal by heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification by Alcaligenes faecalis no.4. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 100, 184–191.
Guo, Y., Zhou, X., Li, Y., Li, K., Wang, C., Liu, J., & Xing, J. (2013). Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by a novel Halomonas campisalis. Biotechnology Letters, 35, 2045–2049.
Zhang, J., Wu, P., Hao, B., & Yu, Z. (2011). Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by the bacterium Pseudomonas stutzeri YZN-001. Bioresource Technology, 102, 9866–9869.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51208534/51209240) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 106112013 CDJZR 210003). We would also like to thank 111 Project (No. B13041) for providing their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, LJ., Zhao, B., An, Q. et al. Characteristics of a Novel Aerobic Denitrifying Bacterium, Enterobacter cloacae Strain HNR. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 178, 947–959 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1920-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1920-8