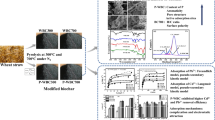
Abstract
The aim of this work is to develop partially delignified Ca2+-and-Mg2+-ion-exchanged product from lignocellulosic wheat straw for the removal of eight different heavy metals Pb2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, and Cu2+ and for detoxification of Cr(VI). Maximum fixation capacity, pH, and initial metal concentration dependence were determined to confirm strong affinity of Pb2+, Cd2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, and Hg2+ ions onto the product, whereas Co2+, Ni2+, and Mn2+ were the least fixed. Morphology of the product characterized by scanning electron microscope showed its physical integrity. Different experimental approaches were applied to determine the role of cations such as Ca2+, Mg2+, and Na+ and several functional groups present in the product in an ion exchange for the fixation of metal ions. Potentiometric titration and Scatchard and Dahlquist interpretation were employed for determination of binding site heterogeneity. Results showed strong and weak binding sites in the product. This product has advantages over other conventional processes by virtue of abundance, easy operational process, and cost reduction in waste disposal of its raw material.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, J., & Chen, C. (2014). Chitosan-based biosorbents: modification and application for biosorption of heavy metals and radionuclides. Bioresource Technology, 160, 129–141.
Rosales, E., Ferreira, L., Sanromán, Á. M., Tavares, T., & Pazos, M. (2015). Enhanced selective metal adsorption on optimised agroforestry waste mixtures. Bioresource Technology, 182, 41–49.
Volesky, B., & Holan, Z. R. (1995). Biosorption of heavy metals. Biotechnology Progress, 11, 235–250.
Kudo, A., & Miyahara, S. (1991). A case history; Minamata mercury pollution in Japan—from loss of human lives to decontamination. Water Science and Technology, 23, 283–290.
Schalcsha, E., & Ahumada, I. T. (1998). Heavy metals in rivers and soils of central Chile. Water Science and Technology, 37, 251–255.
Schrope, M. (2001). US to take the temperature of mercury threat. Nature, 409, 124.
Krishnani, K. K., Azad, I. S., Kailasam, M., Thirunavukkarasu, A. R., Gupta, B. P., Joseph, K. O., Muralidhar, M., & Abraham, M. (2003). Acute toxicity of some heavy metals to Lates calcarifer fry with a note on its histopathological manifestations. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, 38(4), 645–655.
Fu, F. L., & Wang, Q. (2011). Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. Journal of Environmental Management, 92, 407–418.
USEPA. (1996). USEPA Drinking water regulations and health advisories. EPA 822-B-96-002. Washington DC: USEPA.
WHO. (1997). Guidelines for drinking water quality. Health criteria and other supporting information (2nd ed., Vol. 1). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Tennessee Department of Environment and Conservation (Tennessee Water Quality Control Board), January 2004 (revised).
Bhatnagar, A., & Sillanpaa, M. (2010). Utilization of agro-industrial and municipal waste materials as potential adsorbents for water treatment—a review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 157, 277–296.
Lalwani, S. B., Wiltowski, T., Hubner, A., Weston, A., & Mandich, N. (1998). Removal of hexavalent chromium and metal cations by a selective and novel carbon adsorbent. Carbon, 36, 1219–1226.
Yang, G. C. C., & Lin, S. (1998). Removal of lead from a silt loam soil by electrokinetic remediation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 58, 285–299.
Abdolali, A., Guo, W. S., Ngo, H. H., Chen, S. S., Nguyen, N. C., & Tung, K. L. (2014). Typical lignocellulosic wastes and by-products for biosorption process in water and wastewater treatment: a critical review. Bioresource Technology, 160, 57–66.
Fomina, M., & Gadd, G. M. (2014). Biosorption: current perspectives on concept, definition and application. Bioresource Technology, 160, 3–14.
Pauli, G., & Gravitis, J. (1997). Environmental management of plantations: through zero emission approach-plantation management for the 21st century. Proceedings of the International Planters Conference on Plantation Management for the 21st Century, Kuala Lumper, Malaysia. The Incorporated Society of Planters, I, 193–207.
Barik, S. K., Mishra, S., & Ayyappan, S. (2002). Decomposition patterns of unprocessed and processed lignocellulosics in a freshwater fish pond. Aquatic Ecology, 34, 184–204.
Azim, M. E., Wahab, M. A., Verdegem, M. C. J., Van Dam, A. A., van Rooij, J. M., & Beveridge, C. M. (2002). The effects of artificial substrates on freshwater pond productivity and water quality and the implications for periphyton-based aquaculture. Aquatic Living Resources, 15, 231–241.
Keshawanath, P., Ramesh, T. J., Gangadhar, B., Beveridge, M. C. M., van DAM, A. A., & Sandifer, P. A. (2001). On-farm evaluation of Indian major carp production with sugarcane bagasse as substrate for periphyton. Asian Fisheries Science, 14(4), 367–376.
Krishanni, K. K., Meng, X., & Boddu, V. M. (2008). Fixation of heavy metals onto lignocellulosic sorbent prepared from paddy straw. Water Environment Research, 80(11), 2165–2174.
Krishnani, K. K., Meng, X., Christodoulatos, C., & Boddu, V. M. (2008). Biosorption mechanism of nine different heavy metals onto biomatrix from rice husk. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 153, 1222–1234.
Krishnani, K. K., Meng, X., & Dupont, L. (2009). Metal ions binding onto lignocellulosic biosorbent. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, A44, 1–12.
Miretzky, P., & Cirelli, A. F. (2010). Cr(VI) and Cr(III) removal from aqueous solution by raw and modified lignocellulosic materials: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 180, 1–19.
Yasin, M., Bhutto, A. W., Bazmi, A. A., & Karim, S. (2010). Efficient utilization of rice-wheat straw to produce value added composite products. International Journal of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 1(2), 136–143.
Dupont, L., Bouanda, J., Dumonceau, J., & Aplincourt, M. (2003). Metal ions binding onto a lignocellulosic substrate extracted from wheat bran: a NICA-Donnan approach. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 263L, 35–41.
American Public Health Association. (1989). American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (17th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Boehm, H. P. (1966). Chemical identification of surface groups. Advances in Catalysis, 16, 179–225.
Boddu, V. M., Abburi, K., Talbott, J. L., & Smith, E. D. (2003). Removal of hexavalent chromium from wastewater using a new composite chitosan biosorbent. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 4449–4456.
Montazer-Rahmati, M. M., Rabbani, P., Abdolali, A., & Keshtkar, A. (2011). Kinetics and equilibrium studies on biosorption of cadmium, lead, and nickel ions from aqueous solutions by intact and chemically modified brown algae. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 185, 401–407.
Witek-Krowiak, A. (2012). Analysis of temperature-dependent biosorption of Cu2+ ions on sunflower hulls: kinetics, equilibrium and mechanism of the process. Chemical Engineering Journal, 192, 13–20.
Muhamad, H., Doan, H., & Lohi, A. (2010). Batch and continuous fixed-bed column biosorption of Cd2+ and Cu2+. Chemical Engineering Journal, 158, 369–377.
Torab-Mostaedi, M., Asadollahzadeh, M., Hemmati, A., & Khosravi, A. (2013). Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies for biosorption of cadmium and nickel on grapefruit peel. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 44, 295–302.
Ofomaja, A. E. (2011). Kinetics and pseudo-isotherm studies of 4-nitrophenol adsorption onto mansonia wood sawdust. Industrial Crops and Products, 33, 418–428.
Ahmady-Asbchin, S., Andres, Y., Gerente, C., & Cloirec, P. L. (2008). Biosorption of Cu(II) from aqueous solution by Fucus serratus: surface characterization and sorption mechanisms. Bioresource Technology, 99(14), 6150–6155.
Chen, J. P., & Yang, L. (2005). Chemical modification of Sargassum sp. for prevention of organic leaching and enhancement of uptake during metal biosorption. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 44(26), 9931–9942.
Acknowledgments
Author is greatly beholden to Dr G. Gopikrishna, Head, Biotechnology and Nutrition Division, CIBA, Chennai, for reviewing this manuscript extensively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnani, K.K. Lignocellulosic Wheat Straw-Derived Ion-Exchange Adsorbent for Heavy Metals Removal. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 178, 670–686 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1901-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1901-y