Abstract
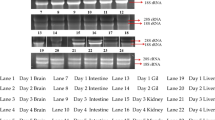
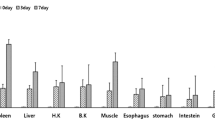
The aims of this study were to identify alternative myxovirus (Mx) stimulatory compounds in Cirrhinus mrigala and to characterize the kinetics and intensity of their stimulated responses by semi-quantitative RT-PCR. Mx transcripts were measured in C. mrigala injected with Aeromonas OmpC (outer membrane protein) at a dose 0.4 mg/fish. At day 1, day 2, day 3, day 5, day 10, day 20 and day 30, samples were collected from kidney, spleen, liver, heart brain, gill, intestine and muscle for the study of Mx transcript and housekeeping gene β-actin. Similarly, Mx gene expression was also studied in Aeromonas hydrophila-infected fish for a period of 10 days. Mx/β-actin ratio was constitutively expressed from all the organs of OmpC-vaccinated fish. The expression was significantly highest (P ≤ 0.05) in spleen, followed by liver, kidney, intestine, gill, heart, muscle and brain. The expression was highest in day 2 except spleen (on day 3) and subsequently reduced up to day 30. Control fish also showed Mx expression. Similarly, A. hydrophila-infected fish showed Mx/β-actin ratio upregulated significantly in the spleen and kidney on day 5, liver on day 2 and intestine on day 3. This study revealed that OmpC of A. hydrophila and its infection could stimulate the antiviral Mx gene of C. mrigala.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kontsek, P., Karayianni-Vasconcelos, G., & Kontsekova, E. (2003). The human interferon system: characterization and classification after discovery of novel members. Acta Virologica, 47(4), 201–15.
Vilcek, J., & Sen, G. C. (1996). Interferons and other cytokines. In B. N. Fields, D. M. Knipe, & P. M. Howley (Eds.), Fields Virology (pp. 375–99). Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven publishers.
Jensen, V., & Robertsen, B. (2000). Cloning of a Mx cDNA from Atlantic halibut [Hippoglossus hippoglossus] and characterization of Mx mRNA expression in response to double-stranded RNA and infectious pancreatic necrosis virus. Journal Interferon & Cytokine Research, 20, 701–10.
Eaton, W. D. (1990). Anti-viral activity of four species of salmonids following exposure to poly inosinic:cytidylic acid. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 9, 193–8.
Lockhart, K., Bowden, T. J., & Ellis, A. E. (2004). Poly I:C-induced Mx responses in Atlantic salmon parr, post-smolts and growers. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 17(3), 245–54.
Jorgensen, J. B., Johansen, L. H., Steiro, K., & Johansen, A. (2003). CpG DNA induces protective antiviral immune responses in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Journal of Virology, 77, 11471–9.
McLauchan, P. E., Collet, B., Ingerslev, E., Secombes, C. J., Lorenzen, N., & Ellis, A. E. (2003). DNA vaccination against viral haemorrhagic septicemia (VHS) in rainbow trout: size, dose, route of injection and duration of protection early protection correlates with Mx expression. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 15, 39–50.
Danino, D., & Hinshaw, J. E. (2001). Dynamin family of mechanoenzymes. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 13, 454–60.
Staeheli, P., Yu, Y.-X., Grob, R., & Haller, O. (1989). A double-stranded RNA-inducible fish gene homologous to the murine influenza virus resistance gene Mx. Molecular Cell. Biology, 9, 3117–21.
Trobridge, G. D., & Leong, J. O. N. N. C. (1995). Characterization of a rainbow trout Mx gene. Journal Interferon & Cytokine Research, 15, 691–702.
Robertsen, B., Trobridge, G., & Leongt, J. A. (1997). Molecular cloning of double-stranded RNA inducible Mx genes from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 21, 397–412.
Lee, J. Y., Hirono, I., & Aoki, T. (2000). Cloning and analysis of expression of Mx cDNA in Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 24, 407–415.
Yap, W. H., Tay, A., Brenner, S., & Venkatesh, B. (2003). Molecular cloning of the pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) Mx gene and functional characterization of its promoter. Immunogenetics, 54, 705–713.
Plant, K. P., & Thune, R. L. (2004). Cloning and characterisation of a channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Mx gene. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 16, 391–405.
Chen, Y. M., Su, Y. L., Lin, J. H. Y., Yang, H. L., & Chen, T. Y. (2006). Cloning of an orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) Mx cDNA and characterisation of its expression in response to nodavirus. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 20, 58–71.
Su, J., Yang, C., Zhu, Z., Wang, Y., Jang, S., & Liao, L. (2009). Enhanced resistance to grass carp reovirus infection in Mx-transgenic rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 26, 828–835.
Tafalla, C., Aranguren, R., Secombes, C. J., Figueras, A., & Novoa, B. (2004). Cloning and analysis of expression of a gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) Mx cDNA. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 16, 11–24.
Singh, M., & O’Hagan, D. T. (2003). Recent advances in veterinary vaccine adjuvants. International Journal of Parasitology, 33, 469–78.
Strandskog, G., Villoing, S., Iliev, D. B., Thim, H. L., Christie, K. E., & Jorgensen, J. B. (2011). Formulations combining CpG containing oliogonucleotides and poly I:C enhance the magnitude of immune responses and protection against pancreas disease in Atlantic salmon. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 35, 1116–27.
Vollmer, J., & Krieg, A. M. (2009). Immunotherapeutic applications of CpG oligodeoxynucleotide TLR9 agonists. Advances Drug Delivery Reviews, 61, 195–204.
Salinas, I., Lockhart, K., Bowden, T. J., Collet, B., Secombes, C. J., & Ellis, A. E. (2004). An assessment of immunostimulants as Mx inducers in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) parr and the effect of temperature on the kinetics of Mx responses. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 17, 159–70.
Mulder, I. E., Wadsworth, S., & Secombes, C. J. (2007). Cytokine expression in the intestine of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during infection with Aeromonas salmonicida. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 23(4), 747–59.
Livak, K. J., & Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C (T). Methods, 25, 402–408.
Duncan, D. B. (1955). Multiple range and multiple ‘F’ tests. Biometrics, 11, 1–42.
Lallemand, C., Lebon, P., Rizza, P., Blanchard, B., & Tovey, M. G. (1996). Constitutive expression of specific interferon isotypes in peripheral blood leukocytes from normal individuals and in promonocytic U937 cells. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 60, 137–6.
Ronni, T., Sareneva, T., Pirhonen, J., & Julkunen, I. (1995). Activation of IFN-alpha, IFN-gamma, MxA, and IFN regulatory factor 1 genes in influenza A virus-infected human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Journal of Immunology, 154, 2764–74.
Staeheli, P., Pitossi, F., & Pavlovic, J. (1993). Mx proteins: GTPases with antiviral activity. Trends in Cell Biology, 3(8), 268–72.
Taylor, G. A., Feng, C. G., & Sher, A. (2004). p47 GTPases: regulators of immunity to intracellular pathogens. Nature Reviews Immunology, 4(2), 100–9.
Martens, S., & Howard, J. (2006). The interferon-inducible GTPases. Annual Reviews Cell and Devlopmental Biology, 22, 559–89.
Galdiero, S., Falanga, A., Cantisani, M., Tarallo, R., Pepa, M. E. D., D’Oriano, V., & Galdiero, M. (2012). Microbe-host interactions: structure and role of Gram-negative bacterial porins. Current Protein and Peptide Science, 13, 843–854.
Monroe, K. M., McWhirter, S. M., & Vance, R. (2010). Induction of type I interferons by bacteria. Cellular. Microbiology, 12, 881–890.
Jinhui, S.Q.W., Zhiyi, Q., Dongqing, B., Jingfeng, S., Xiuting, Q.(2011). Effect of lipopolysaccharide [LPS] and outer membrane protein [OMP] vaccines on protection of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) against Aeromonas hydrophila. The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture - Bamidgeh, IIC.63, 655–63.
Youngner, J. S., & Stinebring, W. R. (1965). Interferon appearance stimulated by endotoxin, bacteria or viruses in mice pre-treated with Escherichia coli endotoxin or infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nature, 208, 456–8.
Danneving, B. H., Lauve, A., Press, C., & Landsverk, T. (1994). Receptor-mediated endocytosis and phagocytosis by rainbow trout head kidney sinusoidal cells. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 4, 3–18.
Brattgjerd, S., & Evensen, O. (1996). A sequential light microscopic and ultrastructural study on the uptake and handling of Vibrio salmonicida in the head kidney phagocytes of experimentally infected Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. Veterinary Pathology, 33, 55–65.
Fierro-Castro, C., Barrioluengo, L., López-Fierro, P., Razquin, B. E., Carracedo, B., & Villena, A. J. (2012). Fish cell cultures as in vitro models of pro-inflammatory responses elicited by immunostimulants. Fish & Shellfish Immunol, 33, 389–400.
Carracedo, B. (2003). Caracterización de cultivos celulares angiogénicos obtenidos de órganos linfóides de trucha arco iris, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Thesis Doctoral. Spain: University of León.
Robertsen, B., Trobridge, G. D., & Leong, J. C. (1997). Molecular cloning of double-stranded RNA inducible Mx gene from Atlantic salmon [Salmo salar L.]. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 21, 397–412.
Bravo, J., Real, F., Padilla, D., Olveira, J. G., Grasso, V., Román, L., & Acosta, F. (2013). Effect of lipopolysaccharides from Vibrio alginolyticus on the Mx gene expression and virus recovery from gilthead sea bream [Sparus aurata L.] experimentally infected with Nodavirus. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 34, 383–6.
Doggett, A., & Harris, J. E. (1987). The ontogeny of the gut-associated lymphoid tissue in Oreochromis mossambicus. Journal of Fish Biology, 31, 23–7.
Fernández-Trujillo, M. A., Novel, P., Manchado, M., Sepulcre, M. P., Mulero, V., & Borrego, J. J. (2011). Three Mx genes with differential response to VNNV infection have been identified in Gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Molecular Immunology, 48, 1216–23.
Bravo, J., Acosta, F., Padilla, D., Grasso, V., & Real, F. (2011). Mx expression in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata, L.) in response to poly I:C, bacterial LPS and chromosomal DNA: preliminary study. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 31, 170–2.
Solem, S. T., Jorgensen, J. B., & Robertsen, B. (1995). Stimulation of respiratory burst and phagocytic activity in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar, L.) macrophages by lipopolysaccharide. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 5, 475–91.
Decker, T., Muller, M., & Stockinger, S. (2005). The yin and yang of type I interferon activity in bacterial infection. Nature Reviews Immunology, 5, 675–687.
Bei, H., Wen, S. H., & Nie, P. (2013). Characterization of four Mx isoforms in the European eel, Anguilla anguilla. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 35, 1048–1054.
Koichiro, K., Shigeyuki, T., Kazuyoshi, H., Kyosuke, A., Yasutoshi, Y., Atsushi, Y., Osamu, N., & Tasuku, W. (2009). Expression profiles of cytokines released in intestinal epithelial cells of the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, in response to bacterial infection. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 33, 499–506.
Khan, R. A. (2012). Host-parasite interactions in some fish species. Journal of Parasitic Research, 1–8.
Bina, J. E., Provenzano, D., Wang, C., Bina, X. R., & Mekalanos, J. J. (2006). Characterization of the Vibrio cholerae vex AB and vex CD efflux systems. Archieves of Microbiology, 186, 171–81.
Cordwell, S. J. (2006). Technologies for bacterial surface proteomics. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 93, 20–29.
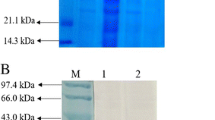
Roy, P., Sahu, I., Rana, N., Behera, B, Pal, A., Das, B.K. (2015) Evaluation of outer membrane protein, OmpC of Aeromonas hydrophila as potential vaccine candidate for Labeo rohita communicated
Acknowledgment
The authors are thankful to the Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India, New Delhi for financial support and Director ICAR-CIFA for providing facilities to carry out the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, P., Panda, S.P., Pal, A. et al. Expression of Mx Gene in Cirrhinus mrigala (Hamilton, 1822) to OmpC Protein of Aeromonas hydrophila and Bacterial Infection. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 178, 640–653 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1899-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1899-1